Grammar Study Guide for Latin I Stages 1-24/5
advertisement

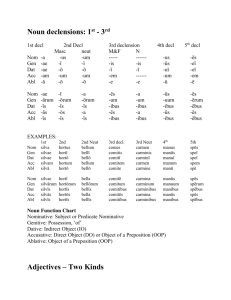
Grammar Study Guide for Latin II Nouns: describe a person, place or thing. Declensions: Latin nouns belong to “families” called declensions. Each declension has its on set of endings for the various cases. 1st : All nouns end in –a in the nominative case and all are feminine expect when the noun indicates a male (e.g. poeta and agricola) 2nd : Almost all nouns end in –us in the nominative and all are masculine. However, there are a few neuters. 3rd : The largest group of nouns and all genders are present (masc., fem., and neuter)\ 4th : Dominated by the letter u. 5th: Dominated by the letter e. Cases: In Latin, nouns change their endings according to their function in a sentence. These different forms of the same noun are called cases. Nominative: the subject of the verb Caesar died. Genitive: belonging to someone/something The home of my friend. Dative: the indirect object of the verb I gave the book to my son. Accusative: the direct object of the verb The cat ate the mouse. Ablative: says by, with or from whom/what This was agreed by the Senate. Vocative: addressing someone or something Welcome, Alexander. Noun Charts: 1st Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Voc. 4th Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Voc. sing -a -ae -ae -am -a -a pl 2nd sing -ae -arum -is -as -is -ae sing Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Voc. -us -i -o -um -o -e -us -us -ui -um -u -us pl -us -uum -ibus -us -ibus -us pl -i -orum -is -os -is -i 5th Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Voc. 3rd Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Voc. sing --------is -i -em -e -------sing -es -ei -ei -em -e -es pl -es -um -ibus -es -ibus -es pl -es -erum -ebus -es -ebus -es Verbs: indicate an action. Conjugations: There are four patterns of regular Latin verbs called conjugations. Each can be identified by the ending of the present infinitve. 1st : verbs end in –are (e.g. amare—to love) 2nd : verbs end in –ere (e.g. habere—to have) 3rd : verbs end in –ere (e.g. mittere—to send) 4th : verbs end in –ire (e.g. audire---to hear) over--> Tenses: These forms of the verb show when an action takes place in the present, in the past or in the future. Present: describes an action that is occurring right now. Imperfect: describes an action that happened in the past but was going on for some time. Perfect: describes an action that happened in the past, but it is a completed action that happened once. PluPerfect: describes an action that happened in the past, it is the farthest in the past you can go. Verb Charts Present 1 2 3 Active Voice Sing -o/-m -s -t Translated: PluPerf 1 2 3 Indicative Mood Plural -mus -tis -nt Imperfect 1 2 3 Sing -bam -bas -bat Plural -bamus -batis -bant Translated: Sing -eram -eras -erat Perfect 1 2 3 Sing -i -isti -it Plural -imus -istis -erunt Translated: Plural -eramus -eratis -erant Translated: **Irregular Verbs** Refer to p206-207 in the blue book to study these irregular verbs. The most prominent is: sum, esse ----to be Present: sum---I am sumus---we are Imperfect: eram---I was eramus—we were es—you are estis---you(pl) are eras—you were eratis—you (pl) were est—He/she/it is sunt---- they are erat--- he/she/it was errant—they were Infinitives: are basically verbal nouns, they have tense and voice but no person or number. They are the 2nd principle part of all verbs. Eg. amare- to love ducere-to lead Adjectives: add quality or describe a noun. In Latin they must agree with the noun they modify in case, number, and gender. E.g. longus, longior, longissimus Positive: the adjective in its simplest form. Easy Comparative: the adjective used when things are being compared easier Superlative: the adjective used when things are the most of something easiest Pronouns: take the place of nouns. Relative Pronouns: placed at the beginning of a relative clause and translated “who”, “which”, and “whom.” The noun described by the relative clause is known as the antecedent of the relative pronoun. Singular Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Masc. Fem. Neuter Plural Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Masc. Fem. Neuter Demonstrative Pronouns: demonstrate or show and are translated “this” and “these” and “that” and “those.” This Singular Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. That Singular Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Masc. Masc. Fem. Fem. Neuter Neuter These Plural Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Those Plural Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Masc. Fem. Neuter Masc. Fem. Neuter Participles: are verbal adjectives, meaning they are part verb but describe a noun like an adjective. e.g. The running man was hit by the car. Present Active: are translated –ing are taken from the infinitive (2nd part of the verb) – (-re) + the appropriate endings. Singular Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl. Plural Nom. Gen. Dat. Acc. Abl.