Objective
advertisement

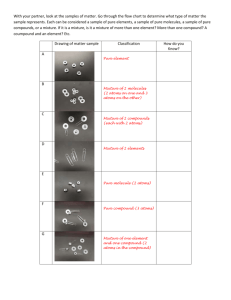
Objective 1. Students will define element and give examples and identify their symbols. 2. Students will define pure substance. 3. Students will define mixture, solution, solute, and solvent. 4. Students will define molecule, diatomic molecule, and compound. II. Elements, Mixtures and Compounds A. An element is a pure substance that can not be broken down by physical or chemical means into a simpler substance. It is composed of atoms that maintain the properties of that element. Some elements are gold (Au), aluminum (Al), hydrogen (H), helium (He), and carbon (C). B. A pure substance is made of only one kind of matter and has definite properties. A pure substance can be elements or compounds. C. A mixture is two or more substances together that are not chemically combined. A mixture can be separated or broken down into the substances that made it. A solution is a mixture that is integrated so well that it is difficult to distinguish the substances that made it. A solution can be separated or broken down into the substances that made it. A solute is the part of a solution that gets dissolved while the solvent is the part of the solution that does the dissolving. 1. Water is called the universal solvent because it can dissolve almost anything. D. A molecule is the smallest part of a substance that still maintains the properties of that substance. A molecule is a particle made of two or more atoms bonded together. A molecule can be broken into simpler substances by chemical means. A diatomic molecule is a molecule made of two of the same atoms such as O2. A compound is a substance that is composed of two or more elements chemically combined in a specific ratio. A compound is a pure substance that contains only one kind of molecule and can only be broken down into its simpler substances by a chemical reaction.