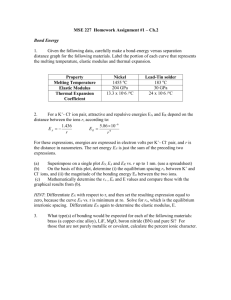
Chapter 8 problems solving
advertisement

Chapter 9 – Chemical bondingsI: Basic Concepts
Dr. Pahlavan
1. Write electron configuration, Lewis dot symbols for carbon and phosphorous and
determine total valence electrons.
2. Determine the total valence electrons for atoms with the following identities.
a) electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3
b) core configuration of [Ar]4s2
c) group IV and period 3
3. Draw the Lewis symbols (electron dot symbols) for each of the following atoms or ions:
Cl
Al3+
O2Ar
N34. Write the chemical formula for the ionic compound formed between following pairs of
elements:
a) Ca and F
b) Mg and N
c) Lithium and O
) Barium and Iodine
e) Cr3+ and O2-
5. Write the electron configuration for each of the following ions, and determine which one
possess noble-gas configurations(obey octet or duet rule , having a complete outershell).
a) Cl-
b) Co3+
c) Co2+
d) Cr3+
e) Ti3+
f) Li+
6. Determine the one with larger lattic energy (circle one) in each of the following pairs.
(please give a reason)
a) CaO, MgO
b) NaF, MgO
c) MgO, MgS
d) Fe2O3 , FeO
7. Using the given set of ions and atoms, arrange them in order of increasing sizes;
a) Fe2+ , Fe, Fe3+
b) S2-, Ar, Se2-
c) Al,Cl-, S2-, K+
d) S2-, Cl-, K+, Ca2+
8. Select the ions or atoms from the following sets that are isoelectronic with each
other;write Y=yes or N=no)
a) S2- , Se2-, Ar
b) Cl-, Cl, Ar
c) Ca2+, Cl-, S2-, K+
1
d) H-, Li+, He
9. Using only periodic table, select the most electronegative atom in each of the following
sets: a) As, Si, Ge, Ga
b) Li, Be, B, Al
c) Cl, F, I, Br
10. Using electronegativity table classify the following as ionic, polar covalent, or non-polar
covalent bonds;
a) H-Br
b) K-H
c) Na-I
d) Br-Br
e) N-H
11. Which of the following bonds are polar? (circle the more polar or more electronegative
one)
a) B-Cl
b) P-F
c) Br-Cl
d) O-Br
e) Hg-Sb
f) N-H, C-H, O-H
g) I-F, Br-Cl, I-Br
12. Draw Lewis dot structures for the followings, and identify those that do not obey octet
rule. (Please draw all resonance structures if any)
a) CH3b) CH3+
c) SO3
d) SO32
13. Determine the formal charge of each atom in each of the followings;
a) :N - C= S:
b) :C Ξ N:
c) S = Si
Cl
H
14. Using the bond enthalpies table (bond dissociation energies in KJ/mol), estimate
enthalpy change for each of the following gas-phase reactions:
a)
H H
H - C - C - O - H (g)
H H
b)
H
H
H-C-NΞC H-C-CΞN
H
H
H H
H - C – O- C - H (g)
H H
c) C2H4 (g) + 3 O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)
2
Chapter 9 – Chemical bondingsI: Basic Concepts
(Answers)
Dr. Pahlavan
1. Write electron configuration, Lewis dot symbols for carbon and phosphorous and determine
total valence electrons.
C [He]2s22p2
•Ċ: 4 valence electrons
P [Ne]3s23p3
: Ρ. : 5 valence electrons
2. Determine the total valence electrons for atoms with the following identities.
a) electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3 5 valence electrons
b) core configuration of [Ar]4s2 2 valence electrons
c) group IV and period 3 4 valence electrons
3. Draw the Lewis symbols (electron dot symbols) for each of the following atoms or ions:
Cl
Al3+
O2Ar
N3:Ċ:
[Al]3+
[: Ő :]2:Är:
[:N:]*
4. Write the chemical formula for the ionic compound formed between following pairs of
elements:
a) Ca and F
b)Mg & N
c)Li & O d)Barium and Iodine e) Cr3+ and O2CaF2
Mg3N2
Li2O
BaI2
Cr2O3
5. Write the electron configuration for each of the following ions, and determine which one
ossess noble-gas configurations(obey octet or duet rule , having a complete outershell).
a) Clb) Co3+
c) Co2+
d) Cr3+
e) Ti3+
f) Li+
[Ar]
[Ar]3d6
[Ar]3d7
[Ar]3d3
[Ar]3d1
[He]
6. Determine the one with larger lattic energy (circle one) in each of the following pairs. (please
give a reason)
a) CaO, MgO smaller internuclear distance
b) NaF, MgO
larger ion charge value
c) MgO, MgS smaller internuclear distance
d) Fe2O3 , FeO larger ion charge value
7. Using the given set of ions and atoms, arrange them in order of increasing sizes;
a) Fe2+ , Fe, Fe3+ ( Fe3+, Fe2+ , Fe)
b) S2-, Ar, Se2(Ar, S2- , Se2-)
c) Al,Cl-, S2-, K+ (K+, Al, Cl-, S2- )
d) S2-, Cl-, K+, Ca2+ (Ca2+ , K+ , Cl- , S2- )
8. Select the ions or atoms from the following sets that are isoelectronic with each other;write
Y=yes or N=no)
a) S2- , Se2-, Ar No
b) Cl-, Cl, Ar No c) Ca2+, Cl-, S2-, K+ Yes
d) H-, Li+, He Yes
9. Using only periodic table, select the most electronegative atom in each of the following
sets: a) As, Si, Ge, Ga
b) Li, Be, B, Al
c) Cl, F, I, Br
3
10. Using electronegativity table classify the following as ionic, polar covalent, or non-polar
covalent bonds;
a) H-Br PC
b) K-H PC
c) Na-I PC
d) Br-Br NP
e) N-H PC
11. Which of the following bonds are polar? (circle the more polar or more electronegativeone)
a) B-Cl
b) P-F
c) Br-Cl
d) O-Br
e) Hg-Sb
f) N-H, C-H, O-H
g) I-F, Br-Cl, I-Br
12. Draw Lewis dot structures for the followings, and identify those that do not obey octet rule.
(Please draw all resonance structures if any)
a) CH3-
b) CH3+
c) SO3
d) SO32
13. Determine the formal charge of each atom in each of the followings;
Cl
a) :N - C= S:
b) :C = N:
c) S = Si
H
14. Using the bond enthalpies table (bond dissociation energies in KJ/mol), estimate
enthalpy change for each of the following gas-phase reactions:
H H
H H
a) H - C - C - O - H (g) H - C - C - O - H (g)
H H
H H
5D(C-H) + D(C-C) + D(C-O) + D(O-H) –{4D(C-H) + 2D(O-H) + 2D(C-O)}
(3234) – (3294) = -60 kJ
H
H
b) H - C - N C H - C - C N
H
H
3D(C-H) + D(C-N) + D(C N) – {3D(C-H) + D(C-C) + D(C N)}
(293) – (348) = -55 kJ
c) C2H4 (g) + 3 O2 (g) 2 CO2 (g) + 2 H2O (g)
{2D(C-H) + D(C C) + 3D(O=O)} – {4D(C=O) + 4D(O-H)}
{3150} – {5048) = 1898 kJ
4