Bond Energy Homework: Materials Science & Engineering
advertisement
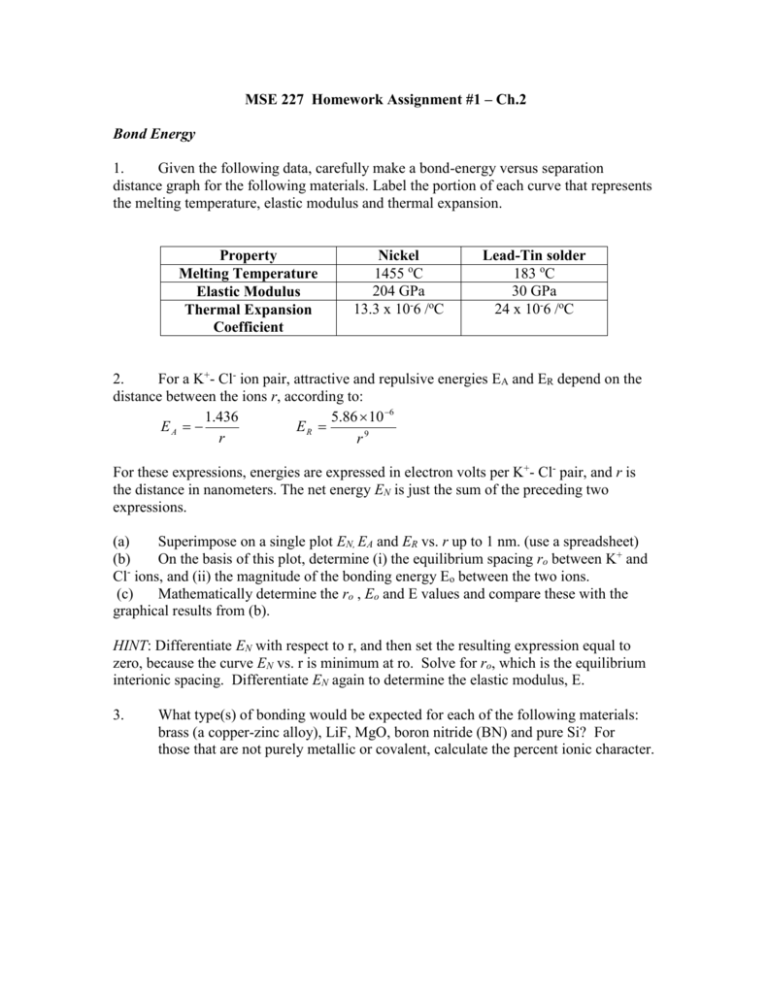
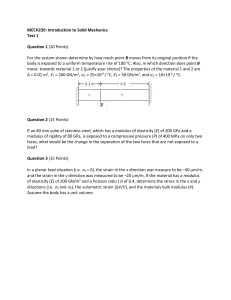
MSE 227 Homework Assignment #1 – Ch.2 Bond Energy 1. Given the following data, carefully make a bond-energy versus separation distance graph for the following materials. Label the portion of each curve that represents the melting temperature, elastic modulus and thermal expansion. Property Melting Temperature Elastic Modulus Thermal Expansion Coefficient Nickel 1455 oC 204 GPa 13.3 x 10-6 /oC Lead-Tin solder 183 oC 30 GPa 24 x 10-6 /oC 2. For a K+- Cl- ion pair, attractive and repulsive energies EA and ER depend on the distance between the ions r, according to: 1.436 5.86 10 6 EA ER r r9 For these expressions, energies are expressed in electron volts per K+- Cl- pair, and r is the distance in nanometers. The net energy EN is just the sum of the preceding two expressions. (a) Superimpose on a single plot EN, EA and ER vs. r up to 1 nm. (use a spreadsheet) (b) On the basis of this plot, determine (i) the equilibrium spacing ro between K+ and Cl ions, and (ii) the magnitude of the bonding energy Eo between the two ions. (c) Mathematically determine the ro , Eo and E values and compare these with the graphical results from (b). HINT: Differentiate EN with respect to r, and then set the resulting expression equal to zero, because the curve EN vs. r is minimum at ro. Solve for ro, which is the equilibrium interionic spacing. Differentiate EN again to determine the elastic modulus, E. 3. What type(s) of bonding would be expected for each of the following materials: brass (a copper-zinc alloy), LiF, MgO, boron nitride (BN) and pure Si? For those that are not purely metallic or covalent, calculate the percent ionic character.