printer-friendly sample test questions
advertisement

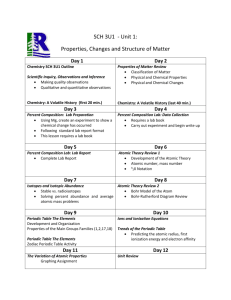
Content Benchmark P.12.A.2 Students know elements in the periodic table are arranged into groups and periods by repeating patterns and relationships. E/S Sample Test Questions 1st Item Specification: Explain why elements in the main groups (metals, nonmetals, alkali metals, alkaline earths, halogens, and noble [inert] gases) on the periodic table have similar properties. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 1. What is common among a family of elements? A. Number of valence electrons. B. Number of energy levels. C. Shielding effect of electrons. D. Amount of protons in the nucleus. 2. Why do elements in the same families (groups) on the periodic table have the same properties? A. They have the same atomic number and mass number. B. They have the same number of electrons. C. They have the same number of valance electrons. D. They have very similar mass and atomic numbers. 3. The alkali metals have similar properties due to the number of valence electrons and therefore they A. are all in the same period on the periodic table. B. are all in the same group on the periodic table. C. all have the same number of electrons. D. all have the same atomic number. Depth of Knowledge Level 2 4. Elements in the same group on the periodic table have similar A. mass numbers and atomic masses. B. physical properties and mass numbers. C. chemical properties and atomic masses. D. chemical and physical properties. 5. Use the following periodic table to answer the question below. (From http://gpc.edu/~pgore/PhysicalScience/periodic-table.gif) Which of the following pairs share similar properties? A. Bromine (Br) and Iodine (I) B. Oxygen (O) and Iodine (I) C. Fluorine (F) and Neon (Ne) D. Helium (He) and Hydrogen (H) 6. Use the following periodic table to answer the question below. (From http://gpc.edu/~pgore/PhysicalScience/periodic-table.gif) Which of the following elements will react similarly to selenium (Se)? A. Germanium (Ge) B. Xenon (Xe) C. Sulfur (S) D. Titanium (Ti) 7. Which group of elements would be expected to have very similar properties? A. Oxygen, sulfur, selenium. B. Nitrogen, oxygen, fluorine. C. Sodium, magnesium, potassium. D. Neon, sodium, potassium. 8. When comparing the noble gas family and halogen family on the periodic table, which of the following statements is true about their chemical properties? A. They are similar to each other because they are side by side on the periodic table. B. They are different from each other because they are side by side on the periodic table. C. They are similar to each other because they have the same number of valance electrons. D. They are different from each other because the have a different number of valance electrons. 2nd Item Specification: Identify the positions of metals and non-metals on the periodic table. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 9. Use the following periodic table to answer the question below. (From http://gpc.edu/~pgore/PhysicalScience/periodic-table.gif) Where are the metals located on the periodic table? A. On the far right of the periodic table. B. On the far left of the periodic table. C. To the right of the metalloids. D. To the left of the metalloids. 10. Use the following periodic table to answer the question below. (From http://gpc.edu/~pgore/PhysicalScience/periodic-table.gif) Where are the non-metals located on the periodic table? A. On the far right of the periodic table. B. On the far left of the periodic table. C. In the middle of the periodic table. D. Along the bottom of the periodic table. Depth of Knowledge Level 2 11. The location of the metals and non-metals on the periodic table are because of their A. valence electrons. B. energy levels. C. atomic mass. D. atomic numbers. 12. Which of the statements below correctly describe where fluorine is located on the periodic table and why? A. It is to the right of the metalloids because it is a metal. B. It is to the left of the metalloids because it is a metal. C. It is to the right of the metalloids because it is a non-metal. D. It is to the left of the metalloids because it is a non-metal. 3rd Item Specification: Classify elements as metals and non-metals. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 13. Which of the following are properties of metals? A. Malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity. B. Malleable, dull, and good conductors of heat and electricity. C. Ductile, shiny, and poor conductors of heat and electricity. D. Ductile, malleable, and poor conductors of heat and electricity. 14. Which of the following are properties of non-metals? A. Dull luster, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity. B. Dull luster and poor conductors of heat and electricity. C. Malleable, ductile, and good conductors of heat and electricity. D. Malleable and poor conductors of heat and electricity. Depth of Knowledge Level 2 15. Is Cobalt (Co) a metal or a non-metal and why? A. It is a metal because it is dull and is a poor conductor of electricity. B. It is a metal because it is ductile and is a good conductor of heat. C. It is a non-metal because it is shiny and is a good conductor of electricity. D. It is a non-metal because it is malleable and is a poor conductor of heat. 16. Is Chlorine (Cl) a metal or a non-metal and why? A. It is a metal because it is in period four, is ductile and shiny. B. It is a metal because it is on the right side of the periodic table and it is dull. C. It is a non-metal because it is in period four and is ductile and a gas. D. It is a non-metal because it is on the right side of the periodic table and is a gas. 4th Item Specification: Predict periodic trends in atomic mass and atomic number. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 17. The periodic table is arranged in order of A. protons lost. B. electrons lost. C. protons added. D. electrons added. 18. Atomic mass on the periodic table progressively changes left to right and top to bottom because A. a proton is being lost. B. an electron is being lost. C. a proton is being added. D. an electron is being added. Depth of Knowledge Level 2 19. Use the following periodic table to answer the question below. (From http://gpc.edu/~pgore/PhysicalScience/periodic-table.gif) Since the element Cobalt(Co) is located to the right of Iron(Fe), which of the following can be predicted about its atomic mass and atomic number? A. Cobalt has a lower atomic mass and atomic number than Iron. B. Cobalt has a higher atomic mass and atomic number than Iron. C. Cobalt has a lower atomic mass and higher atomic number than Iron D. Cobalt has a higher atomic mass and lower atomic number than Iron. 20. Use the following periodic table to answer the question below. (From http://gpc.edu/~pgore/PhysicalScience/periodic-table.gif) An element found in the upper right corner of the periodic table should A. have a higher atomic number than Barium (Ba), but a lower atomic mass. B. have a higher atomic number and atomic mass than Barium (Ba). C. have a lower atomic number than Barium (Ba), but a higher atomic mass. D. have a lower atomic number and lower atomic mass than Barium (Ba). 5th Item Specification: Recognize the difference between the atomic number and the atomic mass of an element. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 21. The atomic mass of an element represents the A. average mass of all its known isotopes. B. total mass of all its known isotopes. C. the average mass of the protons and neutrons. D. the total mass of the protons and neutrons. 22. The atomic number of an element represents the number of A. protons. B. neutrons. C. nulceons. D. valence electrons. Depth of Knowledge Level 2 23. Which of the following explains the difference between atomic number and atomic mass? A. The atomic number is the number of protons and the atomic mass is the average mass of the element’s known isotopes. B. The atomic number is the number of protons and the atomic mass is the total mass of the protons and electrons. C. The atomic number is the total number of protons and neutrons and the atomic mass is the average mass of the isotopes. D. The atomic number is the total number of protons and neutrons and the atomic mass is the total mass of the protons and electrons. 24. Only two isotopes of copper exist in nature: copper-63 and copper-65. Which of the following is true? A. The atomic mass for copper is the average of the two isotopes or 64 a.m.u. B. The atomic mass for copper is the total mass of both isotopes or 128 a.m.u. C. The atomic mass is the average of the abundances of the isotopes of 63.45 a.m.u. D. The atomic mass is based on the heaviest element and is 65.21 a.m.u. 6th Item Specification: Calculate the number of electrons, protons, and neutrons given the atomic number and atomic mass for a given isotope of any element in the periodic table. Depth of Knowledge Level 1 25. How many protons are in an element with the atomic number of 25? A. 5 B. 12 C. 13 D. 25 26. How many electrons are in a neutral atom with an atomic number of 12? A. 4 B. 6 C. 12 D. 24 Depth of Knowledge Level 2 27. Use the table below to answer the following question. 25 26 27 Manganese Element #26 Cobalt Mn El Co 54.94 ? 58.69 Which of the following could be the atomic mass of Element #26? A. 52.64 B. 54.0 C. 56.21 D. 63.98 28. Use the table below to answer the following question. 48 ? 50 Cadmuim Element X Tin Cd X Sn 112.41 ? 118.71 Predict the properties for Element X? A. It is a metal, atomic number 49, approximate average atomic mass of 114. B. It is a semi-metal, approximate average atomic mass of 113, atomic number 49. C. It is a non-metal, approximate average atomic mass of 118, atomic number 49. D. It is a gas, approximate average atomic mass of 117, atomic number 49. Content Benchmark P.12.A.2 Students know elements in the periodic table are arranged into groups and periods by repeating patterns and relationships. E/S Answers to Sample Test Questions 1. A, DOK Level 1 2. C, DOK Level 1 3. B, DOK Level 1 4. D, DOK Level 2 5. A, DOK Level 2 6. C, DOK Level 2 7. A, DOK Level 2 8. C, DOK Level 2 9. D, DOK Level 1 10. A, DOK Level 1 11. A, DOK Level 2 12. C, DOK Level 2 13. A, DOK Level 1 14. B, DOK Level 1 15. B, DOK Level 2 16. D, DOK Level 2 17. C, DOK Level 1 18. C, DOK Level 1 19. B, DOK Level 2 20. D, DOK Level 2 21. A, DOK Level 1 22. A, DOK Level 1 23. A, DOK Level 2 24. C, DOK Level 2 25. D, DOK Level 1 26. C, DOK Level 1 27. C, DOK Level 2 28. A, DOK Level 2