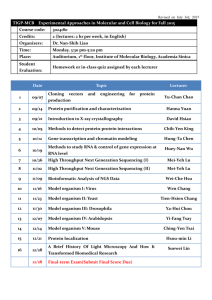
Overlaps: Oomycete, fungal, bacteria pathogens
advertisement

Trudy’s set of terms PROTECTION AGAINST HOST COMPOUNDS Manipulation of biochemical and physiological processes in host Suppression of host defense responses Inhibition of host proteases by another organism Inhibition of extracellular host proteases by another organism Inhibition of serine proteases by another organism Inhibition of subtilin-like serine proteases Inhibition of glucanase proteases by another organism Inhibition of extracellular host proteases by another organism Inhibition of cysteine protease by another organism Inhibition of papain-like cysteine protease by another organism Inhibition of extracellular host proteases by another organism Inhibition of aspartic proteases by another organism Synonyms Serpins for serine protease inhibitors Definitions Inhibition of host proteases: Ability of enzyme to prevent/antagonize or reduce the catalysis of hydrolysis of peptide bonds Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of proteases, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of nonterminal peptide linkages in oligopeptides or polypeptides Inhibition of extracellular host proteases by another organism Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of extracellular proteases, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of nonterminal peptide linkages in oligopeptides or polypeptides Inhibition of serine host proteases by another organism Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of serine proteases, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of nonterminal peptide linkages in oligopeptides or polypeptides; a serine residue (and a histidine residue) are at the active center of the enzyme. Inhibition of subtilin-like serine proteases Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of subtilinlike serine proteases, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of nonterminal peptide linkages in oligopeptides or polypeptides; a serine residue (and a histidine residue) are at the active center of the enzyme. Inhibition of glucanase proteases by another organism Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of glucanaes, enzymes that catalyze the hydrolysis of nonterminal peptide linkages in oligopeptides or polypeptides. Inhibition of host aspartic proteases by another organism: Stops, prevents or reduces the activity of aspartic-type proteases, enzymes that might suppress the endoglucanase-catalyzed release of glucan elicitors PMID: PMID: PMID: PMID: PMID: PMID: 15060002 16117831 15980196 15096512 16448329 12084830 Puente et al Tian et al Tian et al Tian et al Kamoun S Rose et al Comments: Protease inhibitor activity (GO:0030414) currently resides under molecular function. Definition should be modified to infer the interaction nature (as described above) and placed under the OBO node with Suppresion of host defense response as the direct parent. If we have to tackle the plant side of things (protease inhibitors of pathogens, insect etc) we could make use of similar termnology Recognition of symbionts Recognition of PAMPs from symbionts or Recognition of symbionts via PAMPs Definition: The process where a symbiont is detected via Pathogen Associated Molecular Patterns (PAMPs). The symbiont is the smaller of the organisms Synonym for PAMPs: General elicitors (of host defense) Note: Molecular patterns in PAMPs correspond to motifs or domains with conserved structural traits found in widely occurring compounds of microbes but not present in the host and essential for microbial fitness Innate immunity constitutes the first line of defense against attempted microbial invasion PAMPs have conserved molecular motifs or signatures the are recognized by the host immune system Killing of cells of another organism Programmed Cell Death Induction of HR in another organism Specific elicitor induced HR in host Specific elicitor induced HR in nonhost PAMP induced HR in host associated with defense PAMP induced HR in nonhost associated with defense Comment The above four in black should all be siblings under Induction of HR in another organism. I feel the above proposed terms are needed to differentiate HR induced by specific elicitors (AVR) and HR induced by general elicitors PAMPs in both host and nonhost Definition Specific elicitor induced HR in host : The rapid death of host cells in response to invasion by a symbiont/another organism Specific elicitor induced HR in nonhost: The rapid death of nonhost cells in response to invasion by a symbiont/another organism Killing of cells of another organism PAMP induced cell death in host resulting in susceptibility PAMP induced cell death in nonhost resulting in susceptibility Definition: PAMP induced cell death in host resulting in susceptibility: PAMP induced cell death in nonhost resulting in susceptibility: References PMID: 15199967 Nurenberger T Innate immunity in plants and animals PMID: 7753777 Nurenberger Review Ologopetide PMID: 10377992 Felix G et al bacterial flagellin PMID: 12471032 Felix G et al RNA binding protein RNP-1 PMID: 16430931 Gijzen and Nurenberger Nep1-like …. INDUCTION OF HOST DEFENSE RESPONSE PAMP INDUCED SIGNALLING CASCADES Various steps before those below if data is available(Still looking into this) Activation/ Induction of reactive oxygen species Activation of calcium fluxes Induction of nitric oxide Definitions Activation/ Induction of reactive oxygen species The chemical reactions and pathways involving dioxygen (O2), or any of the reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions (O2-), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals (-OH) where the pathway is activated by PAMPs from another organism Activation/ Induction of reactive oxygen species The chemical reactions and pathways involving dioxygen (O2), or any of the reactive oxygen species, e.g. superoxide anions (O2-), hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), and hydroxyl radicals (-OH) where the pathway is activated by specific elicitors from another organism Activation of calcium fluxes Comments: I propose that with all the responses downstream of the initial recognition, we should differentiate between those resulting from specific elicitors or PAMP triggers. Did not figure out how to incorporate that in the terms but the definitions specify for each trigger Note: PAMP INDUCED SIGNALLING CASCADES; resembles those known to induce mediate activation of innate immune responses in animals