File - Global Studies `10
advertisement

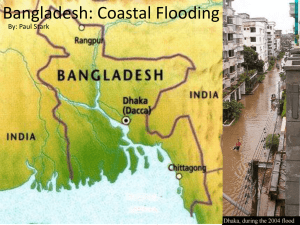
Flooding/Geography: Monsoons cause flooding (Almost 1/3 of country floods in rainy season) Due to the extremely fertile land, there are 3 rich harvests a year o But often, people, livestock and crops are swept away by natural disasters Cyclone Sidr (2007), 1970 Erosion is a big problem (silt, strong rivers) Flooding + below sea-level= land disappears and appears uncontrollably Population: Over 1000 people per square kilometer (over 1 person per square meter) Poverty: Most kids start working before age 10 due to meager family conditions Poverty: “deep and widespread; almost half of the population live on less that one dollar a day” Human Rights: Assaults on women and “allegations that police use torture against those in custody” Unemployment: Agriculture employs majority of population (not enough jobs to meet demand) Bangladeshis must seek work abroad (illegally at times) Crisis Prevention and Recovery “Tropical cyclones, tidal surges, tornados, floods, droughts and large-scale riverbank erosion all wreak havoc on the lives and livelihoods of the population.” “damage and losses to the country amount to about 96 percent of the global total.” “collecting and sharing indigenous knowledge about how to live safely with natural calamities, and expanding disaster preparedness strategies to cover risks emerging from rapid urbanization.” As sea levels rise, disaster and devastation will increase- MUST ACT NOW 1970: cyclone killed over 300,000 people and caused over $2.5 billion in property damage 1988 & 1998: immense suffering due to floods 1998: two-thirds of country was underwater, hugely disrupting economy and agriculture Malaria Control Project epidemiology: incidence, distribution and possible control of diseases entomology: study of insects life expectancy now is 67/69 years and through this project we expect it to greatly increase since less people are dying, starving or getting sick national health facilities are “providing a range of services relating to health, education and development.” 80% of malaria cases sick children miss school, tourism suffers, etc. Rural poor are the most affected. Can’t afford a way to avoid getting it or a way to be treated once they have it Considered both a cause and consequence of poverty Evans 1 Negative affect on economic productivity o Farmers choose subsistence crops because the labour is affected during harvest season o Markets receive less business because people don’t want to travel to them o Tourists don’t want to go to countries with malaria o Malaria infected families harvest under half of healthy families When educated, “people know how to prevent malaria, when to seek medical treatment and how to access effective treatment. The result: less sickness, fewer deaths and stronger communities.” Evans 2 Works Cited: Malaria: http://malarianomore.org.uk/malaria#preventing-malaria http://gharoni.org/ongoing.htm Crisis: http://www.undp.org/cpr/disred/english/regions/asia/bangladesh.htm Title: http://travel.nationalgeographic.com/travel/countries/bangladesh-guide/ Population of Bangladesh: http://www.bestcountryreports.com/Population_Map_Bangladesh.html man with child: http://shahidul.wordpress.com/2007/11/17/ cyclone sidr video: http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=zaiuaAt1b2k physical map: http://www.ezilon.com/maps/images/asia/Bangladesh-physical-map.gif two toned map: http://www.livingwiththejamuna.com/photos/Bangladesh_10m_LECZ_and_population_ density.jpg umbrellas: http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/in_pictures/6742541.stm sheep: http://www.global-changes.com/oxfam-to-aid-climate-change-victims/ crisis prevention: http://www.undp.org/cpr/disred/english/regions/asia/bangladesh.htm Evans 3