Vector control ppt T..
advertisement

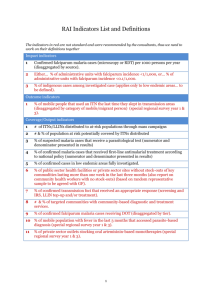
VECTOR CONTROL BY Dr. Ladslaus L. Mnyone Mating .. . . . ........ ..... .. . . . Sugar feeding Host seeking Partial surface application Full surface application Rest 2-3 days Oviposition Bed net application Point-source application Vector control methods Indoor residual spraying (IRS) Use of personal protection measures e.g. ITNs, repellents etc Larviciding Biological control Environmental management Education Integrated mosquito management Scale up Vector Control measures Combination of personal and community protective measures e.g. ITNs and LLITNs e.g. ITNs for everyone at risk of malaria, especially children and pregnant women. Framework of ITNs = “Catch up” coverage and “Keep up” coverage strategy Roles of RBM 1o goal is to provide a coordinated global approach to fighting malaria Lead in advocacy campaigns to raise awareness of malaria at the global, regional, national and community levels Mobilize resources for malaria control and research into new and more effective tools Ensure that vulnerable individuals are key participants in rolling back of malaria Formulate task forces to carry out RBM tasks