File
advertisement

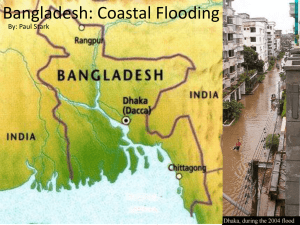
UNSADP – Bangladesh Facts about Bangladesh: History: Formerly East Pakistan, Bangladesh came into being only in 1971 Bangladesh spent 15 years under military rule and democracy was restored in 1990 Political tensions have spilled over into violence; hundreds of people have been killed in recent years. Bangladesh has been criticised for its human rights record, with particular concern about assaults on women and allegations that police use torture against those in custody. In 1970 a cyclone killed more than 300,000 people along the coast, and in 2007 Cyclone Sidr caused thousands of deaths along with significant damage to the country's infrastructure. Geography: Gas reserves both on and offshore keeps the hope for a good future. The low-lying country is vulnerable to flooding and cyclones and it stands to be badly affected by predicted rises in sea levels. Dhaka is the capital city It's also home to many spectacular river-swimming Bengal tigers. Threatened the largest river delta in the world, Inhabitant information: 164.4 million people live in Bangladesh within an area of 143,998 sq km. Life expectancy is 67 years (men), 69 years (women) Main language is Bengali; major religions are Islam and Hinduism. Main exports are Garments, fish, jute goods, leather products Literacy is 43 percent almost half of all Bangladeshis live on less than $1 a day Current situation: Unable to meet the demand for jobs because it’s over populated. People seek work abroad, sometimes illegally. The country is trying to diversify its economy, with industrial development a priority. Overseas investors have pumped money into manufacturing There has been a debate about whether the reserves should be kept for domestic use or exported. Some international energy companies are involved in the gas sector. Bangladesh is one of the most crowded places on the planet. Needs: Improved infrastructure Protection against floods and cyclones. education medicine PROGRAMS FOR IMPROVEMENT 1. Investment in medicine for treatments for diseases such as Trachoma, which exists in south Asia. Promoting the SAFE-strategy, which is also used in Ethiopia. 2. Infrastructures that are resistant against flooding, cyclones and earthquakes during the monsoon. 3. Investing in new education techniques, new materials. 43% literacy. 4. Invest in industry, provide jobs, and using raw materials for export and trading, leading to a more stable economy.