PAKISTAN - University of Nairobi
advertisement
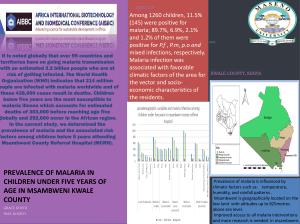
NATURAL PRODUCTS FROM PLANT BIODIVERSITY AND MALARIA Dr. Joseph M Nguta, UNIVERSITY OF NAIROBI MALARIA Malaria is the most difficult problem afflicting people in the tropics In Africa, more than 100 million people are infected annually, with a mortality of 1-1.5m a year Currently the drug of choice is artemesinin and its derivatives High rate of resistance development to drugs by the parasite makes the necessity for research in new antimalarial drugs One possible solution is to carry out research on to the traditionally used herbal remedies STUDY AREA Msambweni district Conducting an interview Herbal Clinic Objectives of the study • To establish an inventory of plants and formulations used to manage Malaria in Msambweni community • To determine the efficacy and toxicity of the priority plants and formulation to the community. • To isolate and characterize the bioactive compounds in the efficacious plants extracts • Develop appropriate formulations based on identified bioactive compounds and indigenous knowledge • To explore feasibility for commercialization The study • • • • • • • • How do they identify malaria? Which plants do they use to manage malaria? Which is the most preferred plant? Which part of plant do they use? How is it formulated Which is the route of administration? Are the plants readily available? Are the plants used safe? How the Study was done Semistructured questionnaires and interviews Focused group discussion Botanical identification of the collected plants by a taxonomist Information gathered included • • • • • • plant species parts used plant habit method of preparation dosage vernacular names Ethnodiagnosis • The most frequently mentioned symptoms • fever • joint pains • vomiting • tiredness • Loss of appetite • headache Commonly used plants 27 species in 24 genera distributed in 20 families were documented. 13 species were reported for the first time The most commonly used species were Azadirachta indica (L) Burm. (95%) Zanthoxylum chalybeum (Eng) Engl. (25%) Aloe deserti Berger. (25%) Harrisonia abyssinica Oliv. (15%) Ricinus communis L.(10%) Habit of the species used in treatment of malaria Shrub 4% 22% 41% 33% Herb Tree Liana Part of the species used in treatment of malaria. 60% 50% 40% 30% 20% 10% 0% Column2 Column1 Percentage frequency Percentage frequency Discussion and conclusion The commonly used plants were Azadirachta indica (L) Burm, Zanthoxylum chalybeum (Eng) Engl and Aloe deserti Berger. 13 plant species are documented for the first time for the treatment of malaria Some species documented in this study have been widely used as antimalarials in other continents e.g Ricinus communis, Lantana camara The leaves were the most commonly used part Roots were the second most commonly used plant partand this calls for conservation and good harvesting practices Way forward • Evaluate safety and efficacy of these plants • Carry out phytochemical tests • Report back to the community on the findings Acknowledgements The Carnegie Corporation of New York for financially supporting this work through Regional Initiative in Science and Education (RISE-AFNNET) The community of Msambweni district, for sharing their knowledge The RISE-AFNNET Nairobi node for their positive criticism and constant encouragement THANK YOU