FRANCISCAN UNIVERSITY ENGLISH III TEACHER GABRIELA

FRANCISCAN UNIVERSITY
ENGLISH III
TEACHER GABRIELA
ENGLISH PAST TENSE PRONUNCIATION
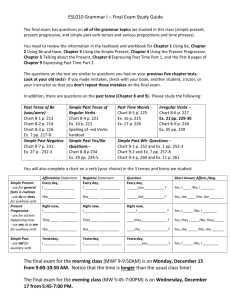
Grammar: Simple Past Statements – Regular Verbs
I) FORM
The simple past verb form does not change for different subjects. The negative in the simple past is formed with the auxiliary did + not (which is usually contracted to didn’t) and the base form of the verb.
Affirmative statements
Subject + (verb) ed
I rented a video.
He played video games.
Negative statements
Subject + didn’t + base form of the verb
She didn’t study French.
They didn’t e-mail their friends.
II) USE
The simple past is used for single or habitual actions completed at a definite time in the past. It can also be used to talk about states and feelings in the past (e.g., I didn’t want to go out last night. I didn’t like the movie.). It is often used with a past time expression (e.g., yesterday, last week).
III) SPELLING RULES: – ED ENDINGS
Spelling rules for adding –ed to verbs to form the simple past: a) For most verbs: add –ed to the base form of the verb (play – played, watch
– watched). b) When the verb ends in e: add –d (like – liked). c) When the verb ends in a consonant and y: change the y to I and add –ed
(study – studied). d) When the verb ends in a vowel and a consonant: double the consonant and add –ed (chat – chatted).
Exception: When the verb is not stressed on the final syllable, do not double the final consonant: visit – visited.
IV) SPEAKING NATURALLY: -ED ENDINGS
For English past tense pronunciation of regular verbs, the "-ed" ending has the following three distinct pronunciations: /id/, /t/, /d/
a) Teaching English Past Tense Pronunciation— /id/ Endings
Deciding when to use the /id/ pronunciation is pretty simple. This Past Tense ending is only used for verbs ending with a /t/ or /d/ sound. This is the only ending that is pronounced with an additional syllable.
Examples of /id/ Endings for Past Tense Verbs
"want" becomes "wanted" and is pronounced "want/id/" (two syllables)
"need" becomes "needed" and is pronounced "need/id/" (two syllables)
"decide" becomes "decided" and is pronounced "decide/id/" (three syllables)
"dedicate" becomes "dedicated" and is pronounced "dedicate/id/" (four syllables)
b) Teaching English Past Tense Pronunciation— /t/ and /d/ Endings
The "-ed" ending of unvoiced sounds takes on a /t/.
Voiceless or unvoiced sounds: / p / - / f / - / θ / - / k / - / s / - / / - / ʧ /
Examples of /t/ Endings for Past Tense Verbs
"laugh" becomes "laughed" and is pronounced "laugh/t/" (one syllable)
"walk" becomes "walked" and is pronounced "walk/t/" (one syllable)
"kiss" becomes "kissed" and is pronounced "kiss/t/" (one syllable)
"finish" becomes "finished" and is pronounced "finish/t/" (two syllables)
The "-ed" ending of voiced sounds take on a /d/.
Voiced sounds: / b /-/ v /-/ ð / - / g / - / z / - / ʒ /- / ʤ /- / m / - / n / - / ð /-
/ l / - / r / - / /
Examples of /d/ Endings for Past Tense Verbs
"clean" becomes "cleaned" and is pronounced "clean/d/" (one syllable)
"dream" becomes "dreamed" and is pronounced "dream/d/" (one syllable
"save" becomes "saved" and is pronounced "save/d/" (one syllable)
"enjoy" becomes "enjoyed" and is pronounced "enjoy/d/" (two syllables)
"marry" becomes "married" and is pronounced "marry/d/" (two syllables)