Chapter 6 Student study guide
advertisement

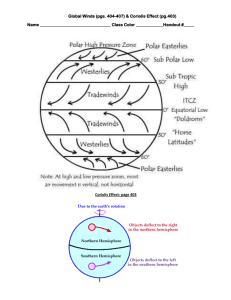
Study Guide Chapter 6 We will be going over the answers tomorrow have it filled out completely 1) Energy transferred as electromagnetic waves is called what? 2) Energy transferred as heat through a material is called what? 3) Thermal energy transferred by circulation of a liquid or gas is called what? 4) The process by which gases in the atmosphere absorb thermal energy and radiate it back to earth is called what? 5) When the amount of energy received from the sun and the amount of energy returned to space are about equal, it is called what? 6) One reason for global warming may be what? 7) What causes wind? 8) What causes differences in air pressure around the Earth? 9) In the Northern Hemisphere, winds traveling north appear to curve to the east because of what? 10) Global winds that blow from west to east are called what? 11) Narrow belts of winds that can reach 400 km/h are called what? 12) Local winds are produced by what? 13) What is the major source of human-caused air pollution? 14) What happens to most solar energy that reaches Earth’s atmosphere? 15) Radiation is the transfer of energy as what? 16) Thermal conduction is the transfer of energy as what? 17) Convection is the transfer of energy by what? 18) Global warming may be caused by what? 19) Wind occurs because of differences in what? 20) Why does warm air rise and cold air sink? Study Guide Chapter 6 We will be going over the answers tomorrow have it filled out completely 1) Energy transferred as electromagnetic waves is called what? 2) Energy transferred as heat through a material is called what? 3) Thermal energy transferred by circulation of a liquid or gas is called what? 4) The process by which gases in the atmosphere absorb thermal energy and radiate it back to earth is called what? 5) When the amount of energy received from the sun and the amount of energy returned to space are about equal, it is called what? 6) One reason for global warming may be what? 7) What causes wind? 8) What causes differences in air pressure around the Earth? 9) In the Northern Hemisphere, winds traveling north appear to curve to the east because of what? 10) Global winds that blow from west to east are called what? 11) Narrow belts of winds that can reach 400 km/h are called what? 12) Local winds are produced by what? 13) What is the major source of human-caused air pollution? 14) What happens to most solar energy that reaches Earth’s atmosphere? 15) Radiation is the transfer of energy as what? 16) Thermal conduction is the transfer of energy as what? 17) Convection is the transfer of energy by what? 18) Global warming may be caused by what? 19) Wind occurs because of differences in what? 20) Why does warm air rise and cold air sink? Study Guide Chapter 6 We will be going over the answers tomorrow have it filled out completely 1) Energy transferred as electromagnetic waves is called what? 2) Energy transferred as heat through a material is called what? 3) Thermal energy transferred by circulation of a liquid or gas is called what? 4) The process by which gases in the atmosphere absorb thermal energy and radiate it back to earth is called what? 5) When the amount of energy received from the sun and the amount of energy returned to space are about equal, it is called what? 6) One reason for global warming may be what? 7) What causes wind? 8) What causes differences in air pressure around the Earth? 9) In the Northern Hemisphere, winds traveling north appear to curve to the east because of what? 10) Global winds that blow from west to east are called what? 11) Narrow belts of winds that can reach 400 km/h are called what? 12) Local winds are produced by what? 13) What is the major source of human-caused air pollution? 14) What happens to most solar energy that reaches Earth’s atmosphere? 15) Radiation is the transfer of energy as what? 16) Thermal conduction is the transfer of energy as what? 17) Convection is the transfer of energy by what? 18) Global warming may be caused by what? 19) Wind occurs because of differences in what? 20) Why does warm air rise and cold air sink? Study Guide Chapter 6 We will be going over the answers tomorrow have it filled out completely 1) Energy transferred as electromagnetic waves is called what? 2) Energy transferred as heat through a material is called what? 3) Thermal energy transferred by circulation of a liquid or gas is called what? 4) The process by which gases in the atmosphere absorb thermal energy and radiate it back to earth is called what? 5) When the amount of energy received from the sun and the amount of energy returned to space are about equal, it is called what? 6) One reason for global warming may be what? 7) What causes wind? 8) What causes differences in air pressure around the Earth? 9) In the Northern Hemisphere, winds traveling north appear to curve to the east because of what? 10) Global winds that blow from west to east are called what? 11) Narrow belts of winds that can reach 400 km/h are called what? 12) Local winds are produced by what? 13) What is the major source of human-caused air pollution? 14) What happens to most solar energy that reaches Earth’s atmosphere? 15) Radiation is the transfer of energy as what? 16) Thermal conduction is the transfer of energy as what? 17) Convection is the transfer of energy by what? 18) Global warming may be caused by what? 19) Wind occurs because of differences in what? 20) Why does warm air rise and cold air sink?