12 Cons Bio 2009
advertisement

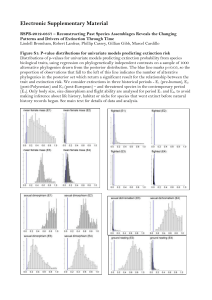
Lecture 11 CH 26 Extinction and Conservation of Single Species MAJOR CONCEPTS 1. Biological diversity has many components (ecological, genetic, geographic). 2. Extinction is natural but its present rate is not. 3. Five types of human activities have accelerated the rate of extinction. 4. Rarity has multiple components (Geographic range, habitat specificity, local abundance). 5. Small and large organisms differ in why they are vulnerable to human extinction and differ in how to conserve them. 6. Small populations are at great risk of extinction due to chance (stochastic events) and low genetic variation to confront environmental change. 7. A minimum population size is required that can withstand environmental variation and lower inbreeding. 8. Population viability analysis can predict the probability of extinction. Biodiversity Amount varies among taxa Components 547-8 Ecological: various adaptations to various niches Genetic: allelic variation within and between populations Geographic: regions with >>> #, but also endemic species 26.11 Values of conserving biodiversity 549-553 Extinction is natural and forever! Types: 554 Background (natural) 1 sp/yr Mass (up to 95% of species) Anthropogenic (1/ sp / day!) Deterministic causes of extinctions: the ‘evil quintet’ 555-562 Habitat destruction and fragmentation (67% of all cases) 26.9, 26.10 Problems associated with fragmentation Overexploitation Often changes species composition 26.11 Chains of linked extinctions 26.13 Introduction of exotic species Eliminate native species and alter ecosystem function 26.14 Islands, aquatic systems especially vulnerable Emerging diseases Conservation Planning: Approach for Single Species Focus on rare, endangered species. Components of rarity 547-8 Geographic range Habitat specificity Local abundance Classic rare = narrow range, endemic in restricted habitat, small pop. Vulnerability to anthropogenic extinction and conservation plans 562 Small species due to small range size and human population densities must protect threatened habitat Large species due to instrinsic qualities long development period, low reproductive rate, low population densities must concentrate on increasing survival and reproductive success. Populations that migrate hard to conserve: multiple habitats involved. 26.16 Small populations > risk of extinction via chance events 556-7; 260-262 Demographic stochasticity Genetic stochasticity Environmental stochasticity and natural catastrophes Stochastic processes produce a probability distribution of population size 12.16 Probability of stochastic extinction increases with time, especially as pop size decreases 12.17 Criteria for long-term survival Minimum Viable Population (MVP): 562-3 Smallest sustainable pop in face of environmental variation Wide distribution so local catastrophe doesn’t wipe out Some population subdivision so disease can’t spread How small is small? 50 short term – keeps inbreeding low 500 long-term – allows evolution to occur ‘Effective’ population size = 11% of actual size How big a preserve necessary to have MVP? Larger populations persist for longer time; but all eventually go extinct Population Viability Analysis (PVA) 566 Demographic information put into simulation model with: demographic, genetic, and environmental stochasticity added Predict probability of extinction within 100-1000 years Cumulative prob. of extinction rises more slowly in large than small pops. Small populations > risk of extinction via bottlenecks > genetic stochasticity Reduced genetic variation lost by genetic drift 277-8 Restored by mutation but > mutation in larger population 13.12, 13.13 Inbreeding loss of specific rare alleles or 13.15 > homozygous recessives impaired reproduction and increased mortality Reduced capacity to respond to environmental change Extinction vortex of small populations due to positive feedback loops Rescue critically endangered species: 566-7 Immigration (natural) 275 or by captive breeding and re-introductions (with added genetic variation too) Summary 5-16.