Factors Affecting Solubility of Ionic Substances - OISE-IS
advertisement

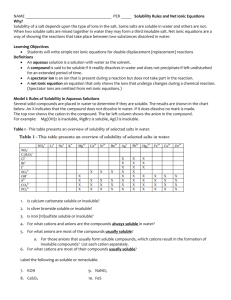
Factors Affecting Solubility of Ionic Substances Ion charge – smaller ion charge = more soluble e.g. NaCl (sodium +1) is more soluble than MgCl2 (magnesium +2) Ion size – larger ions = more soluble - metallic ions are smaller than their atoms (lose valence electrons) - non-metallic ions are larger than their atoms (gain valence electrons) - small ions bond more closely together than large ions – thus, the bond between small ions is stronger than the bond between large ions with the same charge – so small ions tend to be less soluble than large ions e.g. fluoride compounds are less soluble than chloride, or bromide General Solubility Rules – Higher guideline (on handout) takes precedence - predicting solubility is neither straightforward nor simple – handout provides a useful summary of ionic-compound interactions with water - e.g barium (Ba+2) is listed as insoluble (guideline #4), but chloride (Cl-1) is listed as soluble (guideline #3) – #3 takes precedence, so BaCl2 is predicted as soluble - chart below is useful to identify salts that are soluble and insoluble in aqueous solutions – WARNING – water is a powerful solvent, so even an “insoluble” salt may dissolve enough to present a serious hazard if it is highly poisonous General Solubility Guidelines Table 9.1 – Page 334 Guideline 1 2 3 4 5 Cations Anions Result Li+1, Na+1, NO3-, +1 +1 K , Rb , CH3COO-, soluble +1 +1 Cs , H , ClO3+1 NH4 Exceptions Ca(ClO3)2 is insoluble BaO and CO3-2, Ba(OH)2 are +1 +2 Ag , Pb , -3 -2 PO4 , O , insoluble soluble; group Hg+1 S-2, OH-1 2 sulfides tend to decompose Cl-1, Br-1, soluble I-1 Ba+2, Ca+2, insoluble Sr+2 Mg+2, Cu+2, Zn+2, SO4-2 soluble +2 +3 Fe , Fe , Al+3, Ni+2 Sample Problems 1. Decide whether each of the following salts is soluble or insoluble in distilled water. Give reasons for your answer. a) lead chloride, PbCl2 b) zinc oxide, ZnO c) silver acetate, AgCH3COO 2. Which of the following compounds are soluble in water? Explain your reasoning for each compound. a) potassium nitrate, KNO3 b) lithium carbonate, Li2CO3 c) lead (II) oxide, PbO 3. Which of the following compounds are insoluble in water? a) calcium carbonate, CaCO3 b) magnesium sulfate, MgSO4 c) aluminum phosphate, AlPO4 Homework – Page 336 # 1 – 6 1. a) The size of the ion and the charge on the ion are the two factors that affect its solubility in water. b) Ions with large charges tend to be insoluble because increasing the charge increases the force that holds the ions together. Thus, the compound will prefer to remain bonded and not dissolve in water. Small ions bond more closely together than large ions, forming stronger ionic bonds that cannot be broken by water during the dissolving process. Compounds with small ions tend to be less soluble than compounds with large ions. 2. Sodium fluoride would be less soluble because its ions are smaller and would form a stronger ionic bond, whereas the iodide bond would be soluble because it is larger and would not form as strong an ionic bond with sodium. 3. a) calcium sulfie – insoluble in water b) iron (II) sulfate – soluble in water c) magnesium chloride – soluble in water 4. a) barium sulfate – insoluble in water – used in making x-rays of the intestines as it is opaque and can be seen as a dark area in the x-ray b) aluminum hydroxide – insoluble in water – used in antacids so that it will neutralize the acids of the stomach more effectively c) zinc carbonate – insoluble in water – used in suntan lotions and will not be dissolved when people sweat or go for a swim 5. Add a solution of sodium chloride to each of these solutions – calcium will not react with sodium chloride since calcium chloride is soluble; whereas the silver forms the insoluble silver chloride precipitate. 6. Bottle 1 contains the silver ion. Bottle 2 contains the sulfate ion. Bottle 3 contains the barium ion and bottle 4 contains the chloride ion. Thus, when 1 and 4 are mixed the white precipitate silver chloride is formed. When 1 and 2 are mixed, the white precipitate silver sulfate is formed. When 2 and 3 are mixed, barium sulfate (another white precipitate) is formed.