Name: Date: Reactions and Solubility Key terms/concepts: Reaction
advertisement

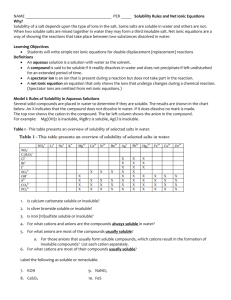
Name: Date: Reactions and Solubility Key terms/concepts: Reaction types: - - Synthesis: two or more substances react to form a larger compound. Decomposition: One substance reacts to form smaller compounds. 1. (Know specific examples of decomposition reactions.) Single Displacement: An element exchanges places with an ion of a compound to form a different compound and element. 1. (Know activity series.) Double Displacement: The ions from two compounds exchange places in aqueous solutions to form two different compounds. Combustion: A compound reacts with oxygen, releasing large amounts of energy int the form of heat and light. Steps to producing reaction types: 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) 5.) Identify type (Synthesis? Decomposition? Etc…) Predict products (dependent upon reaction type) Write formulas (write products and make sure they’re balanced) Balance equation Phases of matter (solubility rules) Things to know: 1.) 2.) 3.) 4.) Polyatomic ions Naming compounds Activity series Solubility rules Reaction Practice Problems Identify type, predict products, balance equation, indicate phases of matter. Also write word equation. Na( + ) Cl2( ) Reaction type: Word Equation: Fe( ) + ) CuSO4( Reaction Type: Word Equation: CH4( ) + O2( ) Cl2( ) Reaction Type: Word Equation: P( ) + Reaction Type: Word Equation: Cl2( ) + NaBr( Reaction Type: Word Equation: KClO3( ) Reaction Type: Word Equation: ) CH4( )+ CaO ( ) + O2( ) Reaction Type: Word Equation: NaCl( + ) AgNO3( ) Reaction Type: Word Equation: ) HgO( Reaction Type: Word Equation: HCl( ) + FeS( ) Reaction Type: Word Equation: Practice Problems State whether the following compounds are soluble or insoluble 1. KCl 2. PbCl2 3. CaSO4 4. NaOH 5. BaSO4 6. HNO3 7. Pb(OH)2 8. LiBr Answer Key: 2 Na(s ) + 1 Cl2( g ) 2NaCl(s) Reaction type: Synthesis Word Equation: Sodium + Chlorine Sodium Chloride 1 Fe(s)+ 1 CuSO4(aq) FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s) Reaction Type: Single Displacement Word Equation: Iron + Copper(II)Sulfate Iron(III)Sulfate + Copper 1 CH4(g)+ 1 O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(liq) Reaction Type: Combustion Word Equation: Methane + Oxygen Carbon dioxide + water 2 K(s) + 1 Cl2(g) 2KCl(aq) Reaction Type: Synthesis Word Equation: Potassium + Chlorine Potassium Chloride 1 Cl2(g) + 2 NaBr(aq) 2NaCl(aq) + Br2(liq) Reaction Type: Single Replacement Word Equation: Chlorine + Sodium Bromide Sodium Chloride + Bromine 2 KClO3(s) 2KCl(s) + 3O2(g) Reaction Type: Decomposition Word Equation: Potassium Chlorate Potassium Chloride + Oxygen 1 CH4(g) + 2 CaO (s) + 1 O2(g) CO2(g) + 2H2O(liq) + 2Ca(s) Reaction Type: Combustion Word Equation: Methane + Calcium oxide + oxygen carbon dioxide + water + calcium 1 NaCl(s) + 1 AgNO3(aq) NaNO3(aq) + AgCl(s) Reaction Type: Double Displacement Word Equation: Sodium Chloride + Silver nitrate Sodium Nitrate + silver chloride HgO(s) 2Hg(liq) + O2(g) 2 Reaction Type: Decomposition Word Equation: Mercury oxide Mercury and Oxygen 1 HCl(aq) + 1 FeS(s) FeCl2(aq) + H2S(g) Reaction Type: Double Displacement Word Equation: Hydrochloric acid + Iron Sulfide Hydrogen sulfide + Iron Chloride Solubility Questions: 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. Soluble Insoluble Insoluble Soluble Insoluble Soluble insoluble soluble