Acids and bases
advertisement

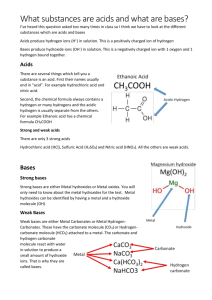
Chemistry Acids, bases and salts Acids have a pH of less than 7 and bases have a pH of more than 7. When bases are dissolved in water they are known as alkalis. Salts are made when an acid reacts with a base, carbonate or metal. The name of the salt formed depends on the metal in the base and the acid used. For example salts made using hydrochloric acid are called chlorides. 1. 2. 3. 4. Acids and bases Reactions of acids Acids, alkalis and neutralisation (Higher Tier) Salt preparation Acids and bases You'll already have learnt quite a bit about acids and bases in Key Stage 3 Science. If you feel a bit rusty on this topic, have a quick look at KS3 Bitesize Chemistry Acids and Alkalis. Here are the bare bones you need to know: Acids turn blue litmus paper red. Alkalis turn red litmus paper blue. Acids Substances with a pH of less than 7 are acids. The stronger the acid, the lower the pH number. Acids turn blue litmus paper red. They turn universal indicator red if they are strong, and orange or yellow if they are weak. Bases Substances that can react with acids and neutralise them to make a salt and water are called bases. They are usually metal oxides or metal hydroxides. For example, copper oxide and sodium hydroxide are bases. copper oxide Alkalis Bases that dissolve in water are called alkalis. Copper oxide is not an alkali because it does not dissolve in water, but sodium hydroxide is an alkali because it does dissolve in water. Alkaline solutions have a pH of more than 7. The stronger the alkali, the higher the pH number. Alkalis turn red litmus paper blue. They turn universal indicator dark blue or purple if they are strong, and blue-green if they are weak. Neutral solutions Neutral solutions have a pH of 7. They do not change the colour of litmus paper, but they turn universal indicator green. Water is neutral. Reactions of acids You need to be able to describe the reactions of acids with bases, carbonates and metals. You should be able to work out the particular salt formed in the reaction. Acids and bases When acids react with bases, a salt and water are made. This reaction is called neutralisation. In general, acid + metal oxide salt + water acid + metal hydroxide salt + water Remember that most bases do not dissolve in water. But if a base can dissolve in water it is also called an alkali. Carbonates When acids react with carbonates, such as calcium carbonate (found in chalk, limestone and marble), a salt, water and carbon dioxide are made. In general, acid + metal carbonate salt + water + carbon dioxide Notice that compared to the reaction with metal oxides and metal hydroxides, an extra product, carbon dioxide, is made. It causes bubbling during the reaction and can be detected using limewater. You usually meet this reaction when you study the effects of acid rain on rocks and building materials. Reactive metals Acids will react with reactive metals, such as magnesium and zinc, to make a salt and hydrogen. In general, acid + metal salt + hydrogen The hydrogen causes bubbling during the reaction and can be detected using a lighted splint. You usually meet this reaction when you study the reactivity series of metals. Acids, alkalis and neutralisation (Higher Tier) When atoms or groups of atoms lose or gain electrons, charged particles called ions are formed. Ions can be either positively or negatively charged. For the Higher Tier you need to know which ions are produced by acids and which are produced by alkalis. You'll also need to know the ionic equation for neutralisation. Acids When acids dissolve in water they produce hydrogen ions, H+. For example, looking at hydrochloric acid: HCl(aq) H+(aq) + Cl-(aq) Alkalis When alkalis dissolve in water they produce hydroxide ions, OH-. For example, looking at sodium hydroxide: NaOH(aq) Na+(aq) + OH-(aq) Ammonia is slightly different. This is the equation for ammonia in solution: NH3(aq) + H2O(l) (aq) + OH-(aq) Be careful to write OH- and not Oh-. Neutralisation reaction When the H+ ions from an acid react with the OH- ions from an alkali, a neutralisation reaction happens to form water. This is the equation for the reaction: H+(aq) + OH-(aq) H2O(l) If you look at the equations above for sodium hydroxide and hydrochloric acid you will see that there are Na+ ions and Cl- ions left over. These form sodium chloride, NaCl. Salt preparation You need to be able to work out which particular salt is made in a reaction. You may be asked to describe how to make a salt. Naming salts The name of a salt is in two parts. The first part of the name comes from the metal in the base or carbonate, or the metal itself if a reactive metal like magnesium or zinc is used. The second part of the name comes from the acid used to make it. The names of salts made from hydrochloric acid end in -chloride, while the names of salts made from sulphuric acid end in -sulphate. metal acid salt sodium hydroxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to make sodium chloride copper oxide reacts with hydrochloric acid to make copper chloride sodium hydroxide reacts with sulphuric acid to make sodium sulphate zinc oxide to make zinc sulphate reacts with sulphuric acid Ammonia forms ammonium salts when it reacts with acids. Thus ammonia reacts with hydrochloric acid to make ammonium chloride Making salts If the base dissolves in water, you need to add just enough acid to make a neutral solution (check a small sample with universal indicator paper), then evaporate the water. You get larger crystals if you evaporate the water slowly. Copper oxide and other transition metal oxides or hydroxides do not dissolve in water. If the base does not dissolve in water, you need an extra step. You add the base to the acid until no more will dissolve and you have some base left over (called an excess). You filter the mixture to remove the excess base then evaporate the water in the filtrate to leave the salt behind. Acids, bases and salts Test: 1. A solution has a pH of 4 - what does this mean? a) It is acidic. b) It is neutral. c) It is alkaline. 2. Which of the statements below is correct? a) Bases are acids that dissolve in water. b) Bases are alkalis that dissolve in water. c) Alkalis are bases that dissolve in water. 3. A liquid has a pH of 7. What does this tell you about the liquid? a) It is water. b) It is sodium chloride solution. c) It is neutral. 4. Which salt is made when calcium carbonate reacts with hydrochloric acid? a) sodium chloride b) calcium chloride c) calcium sulphate 5. Which pair of substances will react together to make copper sulphate? a) copper and sulphuric acid b) copper oxide and sulphuric acid c) copper oxide and hydrochloric acid 6. Which is the correct order of methods for making a salt from an acid and an insoluble base? a) filtration ==> evaporation ==> neutralisation b) neutralisation ==> evaporation ==> filtration c) neutralisation ==> filtration ==> evaporation