CHAPTER 10 – ORGANIC CHEMISTRY
advertisement

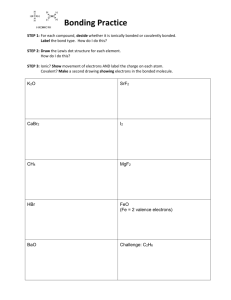
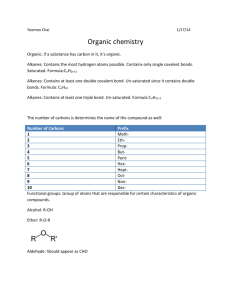
CHAPTER 10 – ORGANIC CHEMISTRY In 18th century classified compounds as organic & inorganic. (organic – produced by living organisms, could not synthesize from inorganic compounds; inorganic – rocks, minerals) Wohler (1828): synthesized an organic compound from 2 inorganic compounds: NH4Cl + AgNCO NH2CONH2 + Urea (found in urine) AgCl Organic Chemistry - study of compounds containing carbon. What are 4 most abundant elements necessary for life? Organic compounds occur naturally or are prepared synthetically Inorganic Chemistry - study of compounds not containing carbon. More than 10,000,000 known organic compounds, only about 1,700,000 inorganic compounds known. Structures of Organic Compounds Molecular Formula: Shows how many of each atom is present, i.e. C2H6O Structural Formula: Shows number of atoms plus the bonds between atoms (how the atoms are attached to each other). H H H–C–C–O–H H H H H H–C–O–C–H H Ethanol Dimethyl ether H Properties of a compound depend on its structure and not molecular formula. To Draw Organic Structures: Carbon combines primarily w/ H, O, N, S, and halogens. Each atom forms a specific number of covalent bonds. SYMBOL H C N O S F, Cl, Br, I # OF BONDS 1 4 3 2 2 1 ELEMENT NAME Hydrogen Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Sulfur Fluorine, Chlorine, Bromine, Iodine HONC Draw the structural formula for: CH4 C2H6 C2H5Cl CH4O Why atoms form a specific # of bonds? Review: Lewis Dot Structures Octet Rule – 8 electrons in outer shell, except H H O C2H5Cl CH5N N C Double and Triple Bonds C= C C= N– C= O –C=C– –C=N C= S Draw the structural formula for: C2H4 C2H2 HCN H2CO Functional Groups – an atom or group of atoms within a molecule that cause the molecule to function in a specific manner. Funct. Groups are used to classify and name organic compounds. 1) Alcohols functional group: –OH (hydroxyl group) bonded to a carbon having 4 single bonds H H H–C – C– O – H H Ethanol H Molecular Formula: _____ C2H6O _______________ Condensed Structural Formula: shows structure/function of compound, without drawing all the bonds CH3CH2CH- carbon bonded to 3 hydrogens carbon bonded to 2 hydrogens carbon bonded to 1 hydrogen i.e. Ethanol: CH3CH2OH Write the condensed structural formula for: ____________ H H H H H H H H H–C – C– C – C – C – C – C– C–H H H H H H H H H Three classes of Alcohols: Primary (1o) Alcohol Carbon bonded to -OH group is bonded to only one other C i.e. H H H–C–C–O–H H H Secondary (2o) Alcohol Carbon bonded to -OH group is bonded to 2 other carbons i.e. H H H–C–C–O–H Condensed Struct Form: __________ H CH3 Tertiary (3o) Alcohol Carbon bonded to -OH group is bonded to 3 other carbons i.e. H CH3 H–C–C–O–H H CH3 Is this a primary, secondary or tertiary alcohol? H H O H H–C–C–C–H H 2) H H Amines functional group: –NH2 (amino group) bonded to one, two or three carbons Three classes of Amines: Primary (1o) Amine Nitrogen bonded to 1 carbon & 2 hydrogens i.e. H H–C–N–H H H Secondary (2o) Amine Nitrogen bonded to 2 carbons & 1 hydrogen i.e. H H–C–N–H H CH3 Tertiary (3o) Amine Nitrogen bonded to 3 carbons i.e. CH3 CH3 – N CH3 Is this a primary, secondary or tertiary amine? CH3 CH3 – C – N – H H H Carbonyl group: C=O 3) Aldehyde: carbon of the carbonyl bonded to a hydrogen i.e. O H – C – CH3 4) Ketone: carbon of carbonyl group bonded to 2 other carbons i.e. O H3C – C – CH3 5) Carboxylic Acids (-COOH carboxyl group): carbon of carbonyl group bonded to a hydroxyl (OH) group i.e. O CH3 – C – O - H 6) Carboxylic Esters: carbon of carbonyl group bonded to an oxygen which is bonded to another C i.e. CH3 – C – O – CH3 O Identify functional groups in these compounds: O O CH3 – C – CH2 – CH2 – C – OH O CH3 – CH – C – OH NH2 H O O CH3 – CH – CH2 – CH2 – C – O - C H3