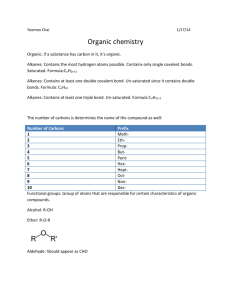
Assignment 4 Task 1a

Scenario: You are working as a CSI in a forensic biochemistry laboratory. You have been assigned to a new case and are working as part of a team to solve the case. Working in the laboratory you will need to have a good understanding of the conventions adopted to ensure that all chemical compounds have unambiguous names. You also need to understand how a combination of elements with carbon at the centre can have a number of different structures and how these structures influence their properties. This will allow you to be able to identify compounds and use this to continue with further analysis.
You should also have an understanding of some organic processes, such as esterification, to enable you to develop solutions to chemical problems and to be able to relate your knowledge to biological situations.
Assignment 4 Task 1a:
Naming organic compounds
1.
Match the correct name to the correct formula.
Chemical name
Structural formula
A. 1,2-difluropropene 1
B. 2-methylpropene 2
CH
2
BrCH ═ CHBr
C. cyclohexene 3
CH
3
CHBrCH
2
I
D. 2-iodo-3-methylbutane 4
CH
3
H
E. 2-bromo-1-iodopropane 5
C ═ C
F F
CH
3
C ═ CH
2
F. benzene 6
CH
3
G. 1,3-dibromopropene 7
2. Complete the table by filling in the spaces.
Family Group Suffix
Examples
(name Full structural IUPAC
ending) formula name
Alkene but-1-ene
-ene
Halogeno- -Cl
alkanes -Br
-I
C-OH propan-2-ol
Carboxylic oxalic acid
Acids
CH
3
CH
2
Aldehydes
C=O
H
-one propanone
Amine -amine diethylamine
3.Name these alcohols:
(a) CH
3
CH
2
CH
2
CH
2
OH n-butanol
(b) CH
3
CH(OH)CH
3 isopropil alcohol
4.
Write down the full structural formula for the following alcohols:
(a) butan-2-ol CH3CH(OH)CH2CH3
(b) 2-methylpropan-1-ol C4H10O1
(c) 4-methylhexan-1-ol C7 H16 O
5.
Draw cis and trans isomers for 3-methyl-2-pentene.
H3C
CH3
CH3
6.
Draw cis and trans isomers for butane.
7.
Draw the optical isomers for (+)-butan-2-ol and (-)-butan-2-ol.
8.
Draw the optical isomers for 2-amino propanoic acid.
H
CH3 C COOH
NH2
Properties of organic compounds
Task 1b
[P7 criteria]
The ability of carbon to form extensive molecules made up of chains and branches and including
unique functional groups gives rise to an almost infinite number of organic compounds that have properties and structures that lend themselves to biological processes. Some of these processes involve the functional groups and others rely upon the physical shape of the molecule. An additional part of your work in the biochemistry laboratory involves knowledge of how organic molecules will behave in certain situations.
Task 1b details:
Design a poster (one slide on Powerpoint or draw by hand.
-At least 6 classes of organic compounds (alkenes, alcohols, aldehydes, ketones, carboxylic acids and amines). Draw and name an example of each.
-The physical properties of the organic compounds chosen
-Write down the names of main reactions that these compounds take part in.
- Also write down the chemical equations for the reactions you have selected.
Display your information clearly and neatly.
Use your knowledge and understanding of task 1a, along with the information sheet for this task
(task 1b) to complete this task.
Simple Organic Reactions
Task 2
[M4 criteria]
Carbon has an ability to form a virtually unlimited range of compounds, which has led to a wide range of living organisms made out of molecules containing carbon. Knowledge of organic chemistry enables chemists to develop and manufacture medicines, agricultural chemicals, anesthetic’s and other chemicals whose effects on life processes are important to humans. So there is little doubt of the importance of organic chemistry in industry, particularly in forensic analysis.
Task 2 details:
Complete worksheet 2 – ‘Predicting the products of organic reactions.’
You will need to correctly
-identify and name the products of the organic reactions shown.
-draw out the correct chemical structures.
-Also write the reaction condition and the reagents.
Use your knowledge and understanding of tasks 1a and 1b to complete this task.
Task 2 – Predicting the products of organic reactions
Write down the name of the reactions shown below and draw the structures of and name the products that are formed.
(1) Amine reaction
C
3
H
7
NH
2
+ HCl →
Reaction name ………………………………… ..
Product(s) formed …………………………………
(2) Alcohol reaction
CH
3
CH
2
OH + K
2
Cr
2
O
7
→ CH3COOH
Reaction name … ……………………………… ..
Product(s) formed … Acetic acid ………………………………
(3) Alkene reaction
H
2
C=CH
2
+ HBr →
CH3 CH2 Br
Reaction name ……… halogen acid ………………………… ..
Product(s) formed …………………………………
(4) Alcohol reaction
CH
3
CH
3
CHOH + K
2
Cr
2
O
7
→
Reaction name ………………………………… ..
Product(s) formed …………………………………
(5)Aldehyde reaction
O
CH
3
C-H + K
2
Cr
2
O
7
→
Reaction name ………………………………… ..
Product(s) formed…………………………………
(6) Aldehyde reaction
O
C
2
H
5
CH + NaBH
4
→
Reaction name ………………………………… ..
Product(s) formed…………………………………
(7) Ketone reaction
O
CH
3
CCH
3
+ NaBH
4
→
Reaction name ………………………………… ..
Product(s) formed…………………………………
(8) Carboxylic acid reaction
O
CH
3
COH + NaOH →
Reaction name ………………………………… ..
Product(s) formed…………………………………
(9) Alcohol and carboxylic acid reaction
O reflux
CH
3
COH + C
2
H
5
OH →
Reaction name ………………………………… ..
Product(s) formed…………………………………