reebop meiosis: exploring meiosis by raising reebops in the classroom
advertisement

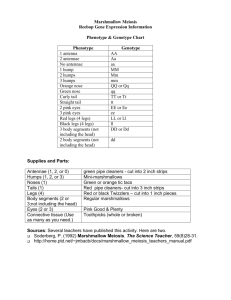
REEBOP MEIOSIS: EXPLORING MEIOSIS BY RAISING REEBOPS IN THE CLASSROOM BIO H DR WEINER Purpose: To show how variations in offspring are the result of random separation of homologous chromosomes during meiosis Materials: 5 pairs of homologous chromosomes, colored pushpins, pipe cleaners, small pins, Reebop bodies Procedure: 1. Using a piece of construction paper DIFFERENT IN COLOR from your partner’s, cut out 10 strips of the following dimensions: 2 strips that are 1 in x 8 in (label 1 A and the other a) 2 strips that are 1 in x 6 in (label 1 N and the other n) 2 strips that are 1 in x 4 in (label 1 T and the other t) 2 strips that are 1 in x 2 in (label 1 E and the other e) 2 strips that are 1 in x 1 in (label 1 L and the other l) 2. Each parent is responsible for one color chromosomes. Each parent should pair up his chromosomes by size, with the letters facing down. Each group of colored chromosomes represents one parent’s set of homologous pairs of chromosomes. Each parent has 5 pairs of homologous chromosomes. 3. Each parent should take one chromosome from each of their 5 pairs and place them in a “baby” pile. These are the baby’s chromosomes: one from the mother and one from the father. Put the remaining chromosomes back in the envelope to avoid confusion. 4. Turn over the baby’s chromosomes and decode what the baby Reebop will look like according to the key. In the table III, write down the baby’s genotype and phenotype. Genotype: what chromosomes the baby has Phenotype: how the chromosomes express themselves in the baby 5. Construct the baby Reebop. 6. Repeat steps 3 and 4, 5 more times. Note the phenotypes and record them in Table IV for Reebops 2-6. TABLES III AND IV ARE NEEDED IN YOUR LAB REPORT Questions: 1. Summarize the differences and similarities between the baby Reebops with each other and with the parents. 2. What do each set of paired chromosomes represent? Explain your answer. 3. Why does each pair of chromosomes differ from the others? Explain your answer. 4. What do the different colored chromosomes in the baby Reebop represent? 5. How come all of the baby Reebops were not identical even though all parent Reebops were? EXPLAIN YOUR ANSWER!! 6. How come identical twins are the same? Explain your answer. TABLE I: CHROMOSOME KEY GENOTYPE AA Aa aa NN Nn nn TT Tt tt EE Ee ee LL Ll ll PHENOTYPE 1 antenna (pins) 2 antennas 3 antennas Red nose (push pins) Green nose Blue nose Curly tail (pipe cleaners) Straight tail No tail Red eyes (push pins) Green eyes Blue eyes Red legs (push pins) Green legs Blue legs TABLE II: PARENT REEBOPS GENOTYPE AND PHENOTYPE GENOTYPE PHENOTYPE Aa 2 antennas Nn Green nose Tt Straight tail Ee Green eyes Ll Green legs TABLE III: BABY REEBOP’S GENOTYPE AND PHENOTYPE GENOTYPE PHENOTYPE TABLE IV: PHENOTYPES OF OTHER BABY REEBOPS PHENOTYPE REEBOP 2 REEBOP 3 REEBOP 4 REEBOP 5 NUMBER OF ANTENNAE COLOR OF NOSE TYPE OF TAIL COLOR OF EYES COLOR OF LEGS REEBOP 6