1. Draw the positions of the Sun and the Earth on the summer
advertisement

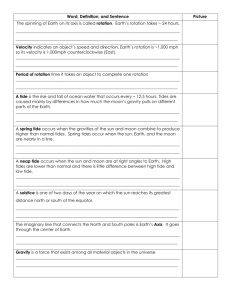
1. Draw the positions of the Sun and the Earth on the summer solstice and the winter solstice. Identify the dates of the summer solstice and winter solstice. 2. Define umbra and penumbra. How are they related to solar/lunar eclipses? 3. Describe the positions of the Earth, Moon and Sun during a total lunar eclipse and during a total solar eclipse. At what phase does a lunar eclipse occur? At what phase does a solar eclipse occur? 4. Why don’t eclipses happen every month? 5. Why do we always see the same side of the Moon? 6. What caused the craters and maria on the surface of the Moon? What are regolith and rays? 7. What causes the tides on the Earth? During which phases of the Moon is the tidal range the greatest? Explain why. Would this be a spring or neap tide? 8. What is the difference between rotation and revolution? Give an effect of each on Earth. 9. Identify the dates of the equinoxes. What is the position of the Sun relative to the Earth on an equinox day? How many hours of daytime and nighttime are there anywhere on Earth? 10. Draw positions of the Sun, Moon and Earth during a spring tide and a neap tide. 11. Why do we have seasons? 12. Draw and label the sun-Earth-Moon at each of the Moon’s 8 phases. Which side is illuminated for a waxing moon? Waning moon? 13. Draw a picture to help describe the giant impact theory. 14. What were the goals achievements of the Apollo, Mercury and Gemeni missions? Put the missions in order from earliest to most recent. 15. What percentage of the moon is always lit by the sun? What percentage of the Earth is always lit by the Sun? Explain why this is true. 1. Draw the positions of the Sun and the Earth on the summer solstice and the winter solstice. Identify the dates of the summer solstice and winter solstice. 2. Define umbra and penumbra. How are they related to solar/lunar eclipses? Umbra- inner/darker/smaller part of shadow Penumbra- outer/lighter/larger part of shadow Need to be in the umbra to see a total eclipse. Can see a partial eclipse in the penumbra. 3. Describe the positions of the Earth, Moon and Sun during a total lunar eclipse and during a total solar eclipse. At what phase does a lunar eclipse occur? At what phase does a solar eclipse occur? Lunar: occurs at full Solar: Occurs at New 4. Why don’t eclipses happen every month? The moon’s orbit is tilted 5 degrees to the plane in which Earth revolves around the Sun. They have to be perfectly aligned in order for eclipses to occur. 5. Why do we always see the same side of the Moon? Synchronous rotation- moon rotates at the same rate that it revolves (27.3 days) 6. What caused the craters and maria on the surface of the Moon? What are regolith and rays? Craters- caused by meteor impacts Maria- formed from cooled lava flows Regolith- rock dust that covers the surface of the moon Rays- material that is ejected from impact craters. 7. What causes the tides on the Earth? During which phases of the Moon is the tidal range the greatest? Explain why. Would this be a spring or neap tide? The gravitational pull of the moon on the ocean directly below it and the opposite side of the Earth causes high tides. The other 2 sides of Earth have low tides. During New and Full moon the tidal range (difference between high and low tide) is the greatest. This is because the Earth and Sun are in a line and are working together to make the high tides higher and low tides lower. These are known as spring tides. 8. What is the difference between rotation and revolution? Give an effect of each on Earth. Rotation- spinning of a body on its axis (day and night) Revolution- orbit of a body around another body (year, seasons) 9. Identify the dates of the equinoxes. What is the position of the Sun relative to the Earth on an equinox day? How many hours of daytime and nighttime are there anywhere on Earth? Equinoxes are on March 21 and September 23. The Sun will be directly overhead at the Equator on an equinox day. Almost all locations on Earth will have 12 hours of daylight and darkness. 10. Draw positions of the Sun, Moon and Earth during a spring tide and a neap tide. 11. Why do we have seasons? The Earth orbits the Sun while tilted on its axis. Sometimes our hemisphere is tilted towards the sun and other times it is pointed away. Due to the tilt, the length of days and the angle of the Sun’s rays will vary during the year. During summer we have long days and direct angle of the rays. In the winter we have short days and the angle of the Sun’s rays is indirect. 12. Draw and label the sun-Earth-Moon at each of the Moon’s 8 phases. Which side is illuminated for a waxing moon? Waning moon? Waxing- is lit on the right side; waning moon- lit on the left side 13. Draw a picture to help describe the giant impact theory. 14. Apollo- land a man safely on the moon; Gemnii- see the effects that space has on the human body; Mercury- get a man into space and in orbit around the Earth. The order is Mercury, Gemini, Apollo *remember that they go in reverse alphabetical order* 15. 50% of both the moon and the Earth are always illuminated by the Sun. This is because half of the moon and Earth are always facing the Sun as they rotate on their axis.