FEBS_6492_sm_DocS1_TablesS1-S4_FigsS1-S2
advertisement
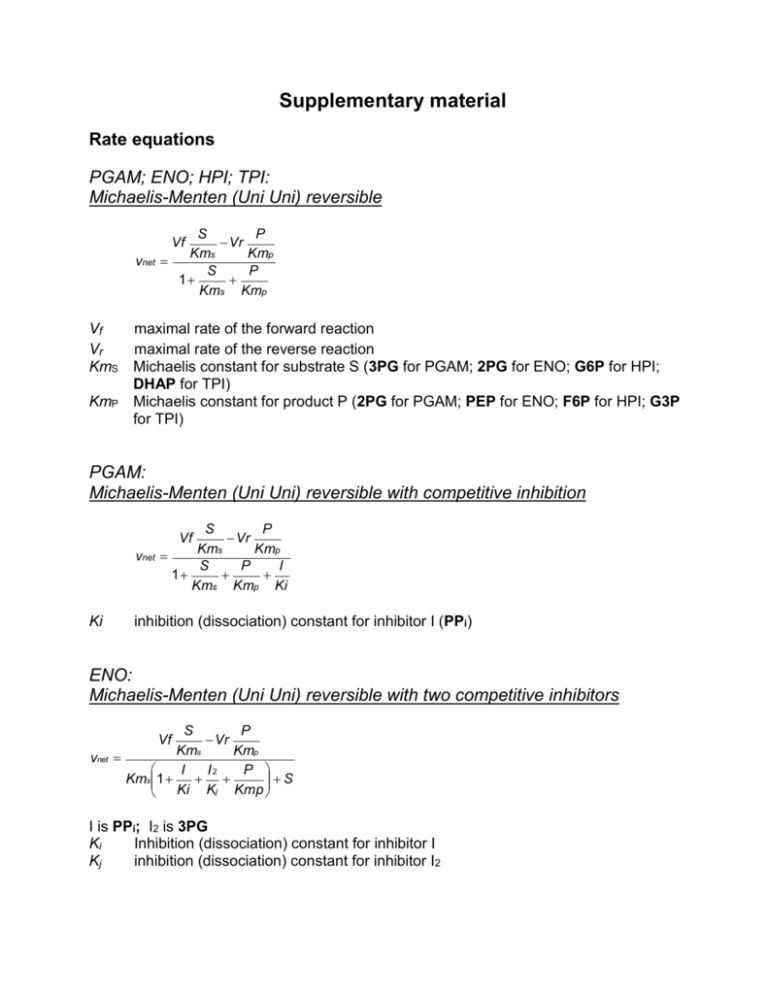
Supplementary material Rate equations PGAM; ENO; HPI; TPI: Michaelis-Menten (Uni Uni) reversible S P Vr Kms Kmp S P 1 Kms Kmp Vf vnet Vf Vr KmS KmP maximal rate of the forward reaction maximal rate of the reverse reaction Michaelis constant for substrate S (3PG for PGAM; 2PG for ENO; G6P for HPI; DHAP for TPI) Michaelis constant for product P (2PG for PGAM; PEP for ENO; F6P for HPI; G3P for TPI) PGAM: Michaelis-Menten (Uni Uni) reversible with competitive inhibition S P Vr Kms Kmp S P I 1 Kms Kmp Ki Vf vnet Ki inhibition (dissociation) constant for inhibitor I (PPi) ENO: Michaelis-Menten (Uni Uni) reversible with two competitive inhibitors S P Vr Kms Kmp I I2 P S Kms1 Ki Kj Kmp Vf vnet I is PPi; I2 is 3PG Ki Inhibition (dissociation) constant for inhibitor I Kj inhibition (dissociation) constant for inhibitor I2 PPDK: Bi Bi Ping Pong reversible vnet PQ Vf AB Keq Q Vf A AB KmBA KmAB1 KmQP 1 QKmp P KiQ Vr Keq KiA where Keq equilibrium constant KiA product inhibition constant of A acting on the reverse reaction KiQ product inhibition constant of Q acting on the forward reaction A is PEP B is PPi or Ter-reactant reversible vnet PQR Vf ABC Keq Vf KmQ P Vf KmP Q Vf KmQ R Vf KmR Q Vf PQR KmAB KmBA KmCB KmBC ABC Vr Keq Vr Keq Vr Keq Vr Keq Vr Keq KmA KmP KmB KmQ KmC KmR Michaelis constant for the first bound substrate A (PEP) Michaelis constant for the first released product P (Pyr) Michaelis constant for the second bound substrate B (AMP) Michaelis constant for the second released product Q (ATP) Michaelis constant for the third bound substrate C (PPi) Michaelis constant for the third released product R (Pi) PYK: Bi Bi Ordered reversible vnet PQ Vf AB Keq P Vf A KmAB B AB1 KmQP 1 KmB A KiA KmAB QKmP 1 PQ1 Vr Keq Kip KiA KiAKmB KiB HK: Bi Bi Random reversible with both mixed-type inhibition and activation Vmf AB Act PQ AB KaKb Kact Keq vnet A B AB I AI BI ABI Act A Act B Act AB Act P Q PQ 1 Ka Kb KaKb Ki KaKi KbKi KaKbKi Kact KaKact KbKact KaKbKact Kp Kq KpKq Kact activation constant for activator Act (PPi). PPi-PFK: Bi Bi Random reversible vnet VfAB VrPQ KaKb KpKq A B AB P Q PQ 1 Ka Kb KaKb Kp Kq KpKq ALDO: Uni Bi Random reversible Vf S Vr PQ Ks KpKq vnet S P Q PQ 1 Ks Kp Kq KpKq The equation with simple competitive inhibition by PPi includes an additional I/Ki term in the denominator. For each rate-equation where inhibition or activation parameters are included, it was chosen the type of equation (competitive, non-competitive or mixed-type inhibition; competitive, non-competitive or mixed-type activation) that best fitted the experimental points. Table S1. Kinetic parameters of the enzymes in the final E. histolytica glycolytic segment pH 6.0 Enzyme Vf Vr PGAM 50* 44.8* ENO KmA 44.4* KmC 830** (3PG) 473 212 219* KmB KmQ KmR Others 106** (2PG) KiPPi 173# 102** (PEP) KiPPi 137# (6)# 60** (2PG) 86.4 33 KmP (5) # Kj3PG 610# PPDK 131* 8.2* 30** (PEP) 2**(AMP) 91** (PPi) 305** (Pyr) 284** (ATP) (Pi) Keq 0.73*** 221# 597 (2) # 1342 (2) # KiA 1000 † KiQ 1000 † mass action irreversible k= 2000 † LDH PYK 13.1* 0.8* 22.6§ 210§ 1000 † 1000 † Ordered bi bi Keq 100 † Kia 1000 † Kib 1000 † Kip 1000 † Table S1 continuation pH 7.0 PGAM 50* 21.3* ENO 292* 47* 500** 55** 66* KiPPi 660# 63* KiPPi 280# 95 60 (5) # Kj3PG 460# PPDK 148* 2* 24** (PEP) 20** (AMP) 470** (PPi) 68**(Pyr) (ATP) (Pi) Keq 0.73*** 85# 940# 340# Kia 1000 † Kiq 1000 † mass action irreversible k= 10000 † LDH PYK 14.8* 0.9* 22.6§ 210§ 1000 † 1000 † Ordered bi bi Keq 100 † Kia 1000 † Kib 1000 † Kip 1000 † Vf and Vr in mU; Km in M. *Data on enzyme proportion and Vr were calculated from Saavedra et al 2007 [10]. ** Kinetic data taken from Saavedra et al 2005 [16]. *** Keq PPDK at pH 6.3 and 37C [17]. # Data determined in the present paper. Data from Saavedra et al, 2004 [12]. † Data taken arbitrarily. § Table S2. Control analysis in the modeled final segment of Entamoeba histolytica glycolysis The enzyme activity proportions were PGAM 1 (50 mU), ENO 4.75, PPDK 2.64 at pH 6.0; PGAM 1 (50 mU), ENO 6.4, PPDK 2.8 at pH 7.0. The rate equation used for both PGAM and ENO in the modeling was Michaelis-Menten reversible, whereas that for PPDK was BiBi Ping-Pong with KmPi of 2 mM and KiPEP and Kipyr of 1 mM. pH 6.0 pH 7.0 Flux rate, nmol min-1 34.4 20.5 [2PG], M 47 312 [PEP], M 142 1420 J CPGAM 0.76 0.46 J CENO 0.10 0.13 J CPPDK 0.14 0.41 Table S3. Kinetic parameters of the enzymes in the first E. histolytica glycolytic segment pH 7.0 Enzyme Vf Vr KmA KmB KmP KmQ Others Keq 656 ** 1.38 # HK 50* 40** (Gluc) 77* (ATP) 89 11 (4)# 1000† (G6P) 120** (ADP) 1.59 # 2.5 # KactPPi 67.5 # KiAMP 24** 5.5 (2) # HPI PPi-PFK ALDO (+ Co2+) TPI GPDH 130** (F6P) 122.2* 112.7* 73.3 § 67.6 § 120* 153* 90 § 114.8 § 148* 201* 4** (FBP) 88.8 § 120.6 § 27 9 (3) # 1809* 5445* 740** (G3P) 170 # 660** (G6P) 455** (F6P) 50**(PPi) 76 32 (3) # 1.2† 124** (FBP) 1440** (Pi) 0.5 † Ki PPi 435 # (2); 43 † 105** (DHAP) 108** (G3P) 1.0 † 1400** (DHAP) mass action irreversible k= 5000 † Table S3 continuation pH 6.0 Keq 656 * 1.2 # HK 50* 25** (Gluc) 121** (ATP) 1000† (G6P) 235** (ADP) 1.45 # 1.3 # Kact PPi 150 # KiAMP 36** HPI PPi-PFK ALDO (+ Co2+) TPI GPDH 122.6* 108.4* 73.5 *** 65 *** 121.6* 197.5* 103.3 *** 167.9 *** 84* 149.5* 28** (FBP) 67.2 *** 119.6 *** 75 (2) # 2298* 3209* 320** (G3P) 610** (G6P) 14 # 460** (F6P) 1.0 † 695** (F6P) 380 **(PPi) 109** (FBP) 2300** (Pi) 1.0 † Ki PPi 211 # 264** (DHAP) 210** (G3P) 1.0 † 445** (DHAP) mass action irreversible k=1000 † Vf and Vr in mU; Km in M. *Data on enzyme proportion and Vr were calculated from Saavedra et al 2007 [10]. ** Kinetic data taken from Saavedra et al 2005 [16]. *** Vm values adjusted (see main text). # Data determined in the present paper. † Data arbitrarily taken. Table S4. Effect of PPi on the HK activity from different sources Biological source Protein added in the assay (g) Activity mU (mg protein)-1 PPi activation, % Control E. histolytica recombinant 0.085 440, 000 178 E. histolytica native 30-219 73-360 157 29 (6) yeast commercial 0.05-0.066 106,000-351,000 169 (2) rat AS-30D hepatoma 54-77 80-320 96.5 20 (3) human HeLa cells 229-725 17-19 102 (2) The HK activity was assayed in the absence and in the presence of 1 mM PP i at pH 7.0 and 37C. For the enzymes from E. histolytica native, hepatoma and HeLa cells, cytosolic cell extracts were used, whereas for E. histolytica recombinant and yeast, the purified enzymes were diluted 1:200 and 1:1000, respectively. The assay was initiated by adding the enzyme. 400 250 -1 Flux, nmol min ; Metabolite, M [2PG] 200 300 [2PG] 150 200 100 100 50 [PEP] 50 40 15 30 Flux Flux 20 10 10 [PEP] 5 0 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200 150 175 200 0.9 0.9 PGAM PGAM 0.8 Flux Control Coefficient 0.8 0.7 0.3 0.2 ENO ENO 0.2 0.1 0.1 0 200 400 600 800 1000 1200 1400 PGAM Km3PG (M) 25 50 75 100 125 ENO Km2PG, M Figure S1. Effect of varying the Km values on flux control coefficient and, rate and metabolite concentrations at pH 6.0 The dotted lines indicate the experimentally determined Km values 3 Relative flux pH 6.0 pH 7.0 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 R factor 4 Figure S2A. Flux rate- Enzyme proportion relationship for the first glycolytic segment The r factor represents the simultaneous fold-variation in the five enzyme activities; with r = 1, the HK activity was 50 mU at both pH values, whereas the HPI, PP i-PFK,ALDO and TPI activities added were, respectively, 122.6, 121.6, 84 and 2298 mU at pH 6.0; and 122.2, 120, 148 and 1809 mU at pH 7.0. -1 flux (nmoles min ) 10 8 6 4 2 0 0 100 200 300 400 500 EhALDO (mU) Figure S2B. Flux control by ALDO in the absence of added Co2+ in the reconstituted upper segment.