Structure of Atom and Periodic Table
advertisement

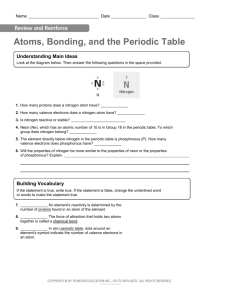
Structure of Atom and Periodic Table TEKS (5) Matter and energy. The student knows that matter is composed of atoms and has chemical and physical properties. The student is expected to: (A) describe the structure of atoms, including the masses, electrical charges, and locations, of protons and neutrons in the nucleus and electrons in the electron cloud; (B) identify that protons determine an element's identity and valence electrons determine its chemical properties, including reactivity; (C) interpret the arrangement of the Periodic Table, including groups and periods, to explain how properties are used to classify elements; I CAN STATEMENTS identify the parts of the atom and their location within the atom Identify that the protons determine the identity of an element Identify the mass and charge of subatomic particles Identify valence electrons Identify the role valence electrons play in an atoms reactivity Use and interpret the periodic table to identify characteristics including valence electrons, energy levels, charges, metals non-metals and metalloids Identify groups and periods on the periodic table Recognize that elements within a group have similar properties Use an elements properties to explain its location of the periodic table CONCEPTS/PROCESS SKILLS Atoms Parts and charge(proton, neutron, electron) Protons determine location on Periodic Table and identity of element. Valence levels and relationship of valence to reactivity. Periodic table Groups and periods Physical properties are similar in groups. Vocabulary: Atomic Number, Atomic Mass, Proton, Neutron, Electron, Electron Cloud, Nucleus, Mass, Ion Energy Levels, Valence Electron, Chemical Properties, Reactivity, Group(Column) , Period, (Row) Metal, Nonmetal, Metalloid, Physical Property, Horizontal, Vertical, Energy Level