Antenatal care
advertisement

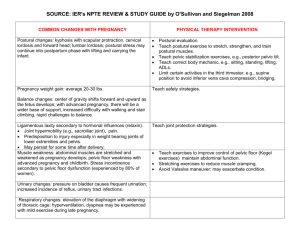
Antenatal care Antenatal care means "care before birth“ (During pregnancy) Antenatal care aims to Monitor and promote the wellbeing of a mother and her developing baby, and to provide information, advice and reassurance as well as monitoring, screening and treatment where necessary... Who provide antenatal care? Obstetricians. Pediatrions. Obstetric physical therapy. Dietitians. Antenatal education: • It takes the form of programmed course in the third trimester. • Each team member reinforce the role of the others and this requires good communication with regular contact to operate an effective referral system Aims of adequate antenatal care : • To detect and treat any physical or psychological defect. • Prepare the parents for the birth of the baby. • Give confidence to the women in her own abilities through an understanding of how her body functions and various changes occurring during pregnancy and birth. 1 Psychological preparation for pregnant women: • primigravidae and large number of multigravidae experience an increase in anxiety during pregnancy and have fears about childbirth due to : a. Baby will die in uterus. b. Baby will not be born normally. c. Baby will not be healthy. d. Childbirth will be traumatic and pain relief will not be provided. e. Drugs taken during pregnancy may cause birth defects . f. Birth-child will alter the relationship between the woman and her husband. • The greater the anxiety, the greater the chance that labour will be more difficult. • So the pregnant women should talk about their anxieties. Doctors and other team members must describe to them, the changes which are occurring in their bodies and explain the purpose of investigation they make. Physical preparation for pregnant woman: Physical plane should be given to help a young women through phases of childbearing cycle. This plane should include certain anatomical structure of : 1. The bony pelvis, its size and shape. 2. Its position in the body in relation to posture. 3. The attachment of pelvic inlet and outlet. 4. The attachment of the muscle of the pelvic floor. 5. The development of muscles, ligaments, joints. 6. The role of pelvic floor muscles and abdominal muscles during labour. A selected number of illustration will greatly assist the information given by spoken word 2 Physical therapy program for normal pregnant woman: Experienced Physical therapist conduct courses and give intensive training in physical, mental preparation and care of pregnant woman in small classes to: Allow meeting between pregnant woman with another at the same state of pregnancy. Emphasize that pregnancy is physiological process. Date of starting physical therapy program, depends on the medical advisor and should be before the woman increases her weight. Role of physical therapy during pregnancy: a. Assess physical health and identify any musculoskeletal or neuromuscular problems. b. Advise on back care and lifting, back strain is minimized when the spin is held in its normal curves, so postural correction exercises are practiced from different positions (standing, sitting, lying position, crock lying positions( c. Lifting advices (from height and from ground) The principles to follow when lifting are: 1. The foot should be apart to increase the base of support. 2. Any object to be lifted should be close to the body. 3. Objects lifted from ground should be light enough. 4. Objects lifted from height should be close to the body and its height should be easy reached. Teach methods for controlling tension and pain during labour e.g. Relaxation technique,Breathing exercises. (to preserve energy.) Treat any problem with appropriate physiotherapy skills e.g. Pubic pain, Lumber pain, Cramps. 3 • Teach positions that may be used for labour (crock lying position) Physical therapy skills: 1. Leg exercises to prevent varicose veins. 2. Abdominal contractions from different positions. 3. Pelvic tilting and postural correction. 4. Pelvic floor contractions are taught in stride sitting with elbow resting on the knees. 5. Relaxation techniques. 6. Breathing exercises. 7. Walking and lining forward exercises. 8. TENS to relive pain. 9. Pelvic support ( firm elastic corset which modified and fitted under the main pubic when pubic pain is related to rectus abdominal muscles diastasis. Model of physical therapy program for normal pregnant women: From the end of 6th month till the end of 8th month of pregnancy. Deep breathing exercises. Relaxation training. Pelvic rocking exercises (upward, backward) Leg exercises Pelvic floor contraction. Abdominal exercises. Arm exercises for preparation of lactation and to allow free flow of milk. During the last month of pregnancy: Instruction about onset of labour. 4 Stages of labour. Breathing exercises. Explanation for TENS and its effect in relieving pain. Medical antenatal care for normal pregnant women The objectives of antenatal care are: 1) Regular observation for early detection and if possible prevention of complications of pregnancy. E.g. toxemia or hemorrhage. 2) Detection and management of any complicating general diseases .e.g. anemia and diabetes. 3) Detection of complications which affect labour such as mal-presentation. 4) Instruct the patient about hygiene and diet. 5) Laboratory studies as blood group, Rh typing, serological examination to detect the conditions which may affect the fetus. Frequency of examination: • Every month until the7th month and every 2 weeks until the last month and every week in the last month. • The 1st visit: includes history taken, general abdominal and vaginal examination, urine analysis for albumin and sugar, blood examination for hemoglobin and blood group. • Return visits: ask about warning symptoms, weight the mother, look for edema and measure blood pressure, do abdominal examination and urine analysis for albumin and sugar. Reassurance and advices: 1. Exercises and traveling: 5 2. Avoid vigorous exercises e.g. swimming, tennis and cycling. 3. Avoid traveling on hard roads and for long distances specially during last month. 4. Sleep and rest. 5. Breast care: washing, massage the nipple with a mixture of glycerin and alcohol to reduce the incidence of cracking. 6. Bowel habits : avoid constipation (cause piles and genital prolapse). 7. Closes should be loose, comfortable, avoid tight breast support. The shoes should be easily fitting with low heels. 6