Success Criteria for Topic 1: Cell Structure
advertisement

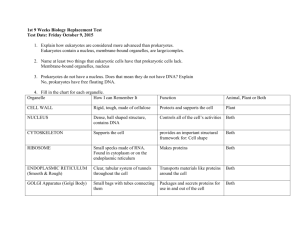
Success Criteria for Topic 1: Cell Structure I will know I am successful in Topic 1 if I can state the following: o Cells contain organelles which have functions. o o o o Bacterial cells are different from animal and plant cells as they have no organelles which have membranes and their cell wall is chemically different. o Fungi have a cell wall which is not made of cellulose. Success Criteria for Topic 1: Cell Structure o Bacteria have plasmids and circular DNA. o o o Organelle mitochondria o chloroplast o Cell membrane o vacuole o nucleus o o o ribosome plasmid Cell wall function o ATP is produced here when oxygen is present o absorbs light energy for photosynthesis o Controls movement of substances in and out of cell o stores water and solutes to regulate water content o controls cell activities and passes info to next generation o where proteins are formed o small circle of DNA found in bacteria o Provides shape and support to cells Success Criteria for Topic 2: Transport across the cell membrane I will know I am successful in Topic 2 if I can state the following: o o Cell membranes are made of lipids with protein molecules scattered between. o This structure is called the fluid mosaic model as the proteins are scattered among the phospholipids and the proteins can move. o Some substances can move in and out of the cell membrane while others cannot. o Diffusion is the movement of substances down the concentration gradient. o Diffusion needs no energy. Success Criteria for Topic 2: Transport across the cell membrane o Substances in high concentration outside the cell and needed by the cell enter by diffusion. o Cells need oxygen, glucose and amino acids and produce carbon dioxide. o Osmosis is the movement of water from high to low concentration across a semi permeable membrane. o Water enters a cell by osmosis down the water concentration gradient. o If water enters a plant cell by osmosis it becomes turgid. o If water leaves a plant cell by osmosis it becomes plasmolysed. o If water enters an animal cell by osmosis it may burst. o If water leaves an animal cell by osmosis it will shrink o When potato is placed in water, the water enters and the potato gets bigger. o If a potato is placed in a strong salt solution there is more water in the potato cells so water leaves the potato and it shrinks. o Active transport is when a substance moves across a cell membrane against a concentration gradient, carried by a protein molecule. It needs energy. Success Criteria for Topic 2: Transport across the cell membrane o Sodium and potassium move in and out of a nerve cell by active transport. o Both active transport, osmosis and diffusion involve substances moving across the cell membrane. o Active transport unlike diffusion is movement up the concentration gradient and it needs energy. o Active transport involves protein molecules which carry the substances across and act as a ‘pump’. Success Criteria for Topic 3: Producing new cells I will know I am successful in Topic 7 if I can state the following: o Body cells have 2 sets of chromosomes and are diploid. o Cells which have only 1 set of chromosomes are haploid. o Gametes such as sperm and egg are haploid. o Cheek cells, white blood cells and bone cells are diploid. o A zygote and embryo are diploid. o A haploid sperm and a haploid egg fuse to form a diploid zygote which goes on to divide by mitosis. o Cell division by mitosis keeps the chromosome number (complement) the same. o Cell division by mitosis allows organisms to grow, replace and repair. o The nucleus contains chromosomes and controls the cell activities. o Cells require 2 sets of chromosomes so they can have a full set of information for complete cell function. Success Criteria for Topic 3: Producing new cells o Stages of mitosiso The chromosomes (DNA strands) make copies of themselves. o o The 2 copies are called chromatids and they line up on the equator of the cell. o Spindle fibres pull the chromatids apart to opposite poles. o The cytoplasm divides and the nuclear membrane reforms. o 2 separate identical cells are formed. o Cell culture allows the growing of cells in a dish in a lab. o To produce cells by cell culture, aseptic techniques, the correct medium, pH, temperature and oxygen levels are needed. o Aseptic techniques- lab coat to be worn, hands washed before and after, work surfaces disinfected before and after, all equipment and media sterilised, inoculating loops flamed before and after, Petri dish lids only opened when needed and then sealed and all used plates disposed of when finished in a plastic bag to be autoclaved. o Cells can be grown in agar or broth as mediums. o A fermenters is a container used to grow cells. Oxygen, temperature and pH are controlled, substrates enters and products are removed. Success Criteria for Topic 4: DNA and the production of proteins I will know I am successful in Topic 7 if I can state the following: o DNA is a found in the nucleus. o It carries the code to produce proteins. o It has 2 strands held together by 4 complementary base pairs - A, T, C, G. o A combines with T and C combines with G. o DNA is a double helix held together by the complimentary base pairs. o The base order decides the order amino acids are joined together and this decides which protein is produced. o The order of the bases is called the genetic code and it is held in the chromosomes. o The protein is put together in the cytoplasm on a ribosome. o DNA is too big a molecule to leave the nucleus so a smaller molecule called mRNA copies the DNA code and takes it out into the cytoplasm to a ribosome. o mRNA is a single strand with the DNA code on it. o The amino acids line up along the RNA acording to the order of the bases on the RNA. o Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds. I will know I am successful in Topic 7 if I can state the following: o Protein molecules have different shapes and amino acid orders, this decides the protein function. o All proteins are made of amino acids. o Amino acids are held together by peptide bonds. o There are over 20 different amino acids. o Different amino acid orders give different proteins with different functions. o Enzymes have an active site which fits their substrate and are denatured by high temperatures. It changes the shape of the active site. o Proteins also make hormones which are chemical messengers, antibodies which fight infection, protein carriers which transport substances across cell membranes and some form hair and nails. o Enzymes are biological catalysts which speed up chemical reactions but are unchanged by them and are found in all living things. o Because enzymes are proteins they work best at optimum temperature and ph. o They only speed up reactions when at optimum conditions. At low temperatures enzymes work slowly, at high temperatures they change shape (denatured) and stop working. Success Criteria for Topic 5: Proteins and enzymes o Enzymes are all specific, have optimum conditions and all speed up reactions o Some enzymes break large molecules down (digest) into smaller ones, some build up (synthesis) small molecules into large ones. o Enzymes include amylase which breaks starch into maltose, lipase which breaks fats down into fatty acids and glycerol, catalase which breaks hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water and pepsin which breaks proteins down into peptides. o Enzymes fit their substrate exactly like a lock and key. o Because the shape of a substrate must be exactly complementary to the enzyme at the active site it is specific. o Above 45 degrees the active site changes shape and the substrate will not fit. o This is denaturing. Denaturing o o Enzymes are most active at their optimum temperature and less active either side of this temperature. Success Criteria for Topic 5: Proteins and enzymes o Enzymes work best at optimum conditions eg temp, pH. o Enzymes lower the energy needed for a reaction to take place. o Pepsin has a working pH range of 1.6-4.5, amylase 5.1-8.9, and catalase 6- 11.9. o Catalase works best at pH9, amylase 7, pepsin 2.5. Success Criteria for Topic 6: Genetic Engineering I will know I am successful in Topic 7 if I can state the following: o DNA can be transferred naturally by bacterial plasmids or viruses. o DNA can also be transferred by genetic engineering. o To begin genetic engineering the gene needed is identified, removed and cut out of the chromosome using enzymes. o The plasmid from the bacteria is removed and cut open with the enzyme and the required gene inserted using another enzyme. o The plasmid is put into another bacterium which multiplies with the new gene present in the next generation of bacteria. o Examples of genetic engineering are blight resistant potatoes, bacteria producing human insulin and growth hormone. Success Criteria for Topic 7: Photosynthesis I will know I am successful in Topic 7 if I can state the following: o Word equation iscarbon dioxide + water -> glucose+sugar +oxygen, using light energy and chlorophyll. o Raw materials for photosynthesis are carbon dioxide and water. o By product of photosynthesis is oxygen. o Light and chlorophyll are also requirements. o Photosynthesis is a series of enzyme controlled reactions in 2 stages. o Light energy is changed into chemical energy. o The first stage is the Light reaction. o Water is split into hydrogen and oxygen. Excess oxygen diffuses from the cells and the hydrogen and ATP are used in the next stage. o The next stage is Carbon Fixation. o Hydrogen joins with carbon dioxide. o Hydrogen and carbon dioxide form glucose. o ATP produced in photolysis provides the energy. o Glucose can be used for respiration by the plant or converted into starch for storage or cellulose for new cell walls. Success Criteria for Topic 7: Photosynthesis Continued o A limiting factors if present in limited amounts slows a reaction down. o Carbon dioxide, temperature and light can limit the rate of photosynthesis and are known as limiting factors. o o At A1 light is the limiting factor but at A2 carbon dioxide is the limiting factor. Success Criteria for Topic 8: Respiration I will know I am successful in Topic 8 if I can state the following: o The chemical energy in glucose is released in a series of enzyme controlled reactions called respiration. o Respiration generates ATP from ADP and phosphate. o Glucose + oxygen -> water +carbon dioxide + ATP is the word equation for aerobic respiration. o Products of aerobic respiration are water, carbon dioxide and ATP. o The breakdown of a glucose molecule without oxygen in animal cells to lactic acid produces 2 ATP molecules (lactic acid fermentation). o Products of anaerobic respiration in animal cells are lactic acid and a small amount of ATP. o The breakdown of a glucose molecule without oxygen in plant and yeast cells produces alcohol, carbon dioxide and 2ATP molecules (alcohol fermentation). o Products of anaerobic respiration in yeast cells are alcohol, carbon dioxide and a small amount of ATP. o Glucose contains chemical energy. o Respiration releases the energy in living cells. o During respiration molecules of ADP and phosphate join together to make ATP. Success Criteria for Topic 8: Respiration o ATP is a high energy compound. o ADP + phosphate -> ATP. o ATP breaks down to produce ADP and a phosphate and releases the energy stored. o This energy can be used for muscle contraction, mitosis, cell repair, protein formation and heat. o Heat energy provides enzymes with the correct temperature to work well. o The breakdown of a glucose molecule with oxygen to produce carbon dioxide and water produces 38 ATP molecules. o Glucose-> pyruvate-> carbon dioxide+water+38 ATP. o Glucose -> pyruvate takes place in the cytoplasm. The next stage takes place in the mitochondria. o The breakdown of a glucose molecule without oxygen in plant and yeast cells produces alcohol, carbon dioxide and 2ATP molecules (alcohol fermentation). o Fermentation occurs in the cytoplasm. o Anaerobic respiration (fermentation) takes place in the cytoplasm of yeast cells. o Anaerobic respiration in muscle cells produces only 2 ATP. o During anaerobic respiration in muscle cells pyruvate acid breaks down into lactic acid.