Solutions Test REVIEW PACKET
advertisement

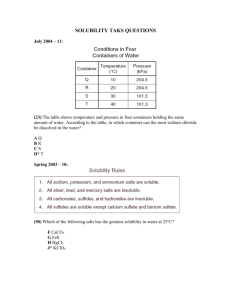
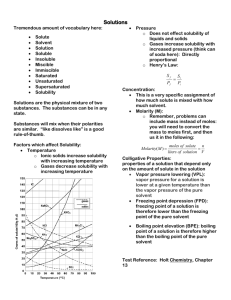
Solutions Test REVIEW PACKET I. Vocabulary: Must make flashcards Boiling pt elevation Colligative property Colloid Concentration Freezing point depression Immiscible Insoluble Miscible Molarity Saturated solution Solubility Soluble Solute Solvation/hydration TEST: March 12th 2014 Solvent Supersaturated solution Suspension Tyndall effect Unsaturated solution electrolytes Graphs: Solubility Curve Formulas: Molarity Dilution II. Solutions A. Fill in the following paragraph with terms from the word bank provided. “Like dissolves like” Homogeneous Soluble Solvation Solvent Solute A substance that can be dissolved into a solution is __________________. Solutions are ________________ mixtures. To make salt water, salt must dissolve in water. The salt is the ___________ because it is being dissolved. The water is the ______________ which does the dissolving. For this dissolving to take place, the water molecules must surround the sodium and chlorine ions in a process called _________________. This process occurred because ______________. B. Describe the quickest way to make salt water. Express how the water molecules will surround the salt particles. C. Solubility Curve-Answer the following questions using the graph provided. 1. 1. What is the solubility of potassium chloride at 10C? 2. What is the solubility of NH3 at 50C? 3. Is ammonia a solid or gas? What happens to the solubility of gases as temperature increases? 4. At 90C, 10 g of potassium chlorate is dissolved in 100 g of water. Is this solution saturated, unsaturated, or supersaturated? 5. A saturated solution of potassium chlorate is dissolved in 100 g of water. If the saturated solution is cooled from 90C to 60C, how many grams of precipitate will be formed? 6. What is the mass of sodium sulfate that will dissolve in 250 g of water at 30C? III. Colligative Properties A. Colligative properties are properties that are affected by the ________________ of particles but not the _____________ of the dissolved solute particles. B. Solutions that conduct an electric current are called ____________________. C. Vapor pressure decreases as the number of solute particles ____________________. D. The boiling point of a solution is ___________________ than the boiling point of the solution’s solvent. E. The freezing point of a solution is ____________________ than the freezing point of the solution’s solvent. IV. Mixtures Mixture Particle Size Scatters Light Settles Separated by Filtering Solution Colloid Suspension V. Concentration/Dilution Practice Problems 1. What is the molarity of a solution with 96 g of magnesium sulfide in 600mL of solution? 2. How many grams are needed to make a 12 M hydrochloric acid solution using only 100 mL of water? Explain how to make this solution. 3. How many liters are needed to dilute 200 mL of a 2.5 M solution to a concentration of 1.6 M? 4. What is the molality of a solution with 62.5 g of potassium nitride in 100 g of water? 5. What is the starting concentration of a 500 mL solution that is diluted to 750 mL with a concentration of 0.55 M? 6. How many liters are there in a 4.65 M solution containing 0.06 moles of sodium chloride? 7. If 48 g of carbon dioxide is dissolved in 600 g of soda, what is the molality of the solution? 8. What is the mass of lithium bromide dissolved in 450 g of water with a molality of 3.75 mol/kg? 9. How many grams of water are needed to dissolve 125 g of barium nitrate to make a 2.95 molal solution? 10. If I have 300 mL of a sulfuric acid with a concentration of 3.45 M and added 250 mL of water to it, what is the new concentration? 11. If 500 mL is added to a 3 M nitric acid solution to make 945 mL of a 0.75 M solution, what is the original volume of the acid? 12. How many kilograms of water are required to dissolve 482 g of calcium oxide to make a 4.32 molal solution? 13. What is the mass of lithium bromide required to make a 7.92 molal solution using 2500 g of water? 14. How many liters are needed to make a 2.65 molar cesium chloride solution using only 55 g of cesium chloride? 15. What is the final concentration of a 300 mL solution that has an initial concentration of 5.21 M and volume of 100 mL?