M1bpstfl
advertisement

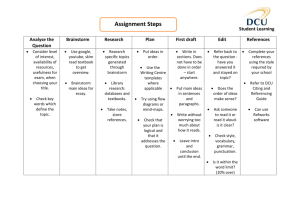
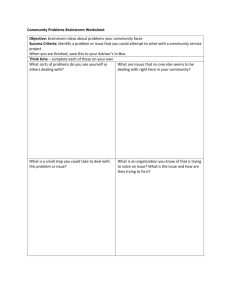
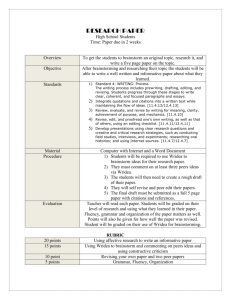
Module M1 Basic Problem Solving Tools - Training Facilitator Flow Learning Objective: application of relevant BPST in day to day activities to foster ‘can do’ attitude. Topic Materials Time Description 1. Introduction Slides No. 2 & 3 5 Introduce everyone to each other. Introduce training. Why are we here? 2. Exercise 1 – what are problem solving tools Flipcharts & pens 10 Divide the group into 2 and get them to write down on a flipchart, what problem solving tools they have come across before. 3. Review Flipcharts Slide No. 4 6 2 groups feedback all the problem solving tools that they have heard of. Summarise by suggesting they had used brainstorming to answer this question (or problem) and that today’s training will just focus on : Brainstorming, Cause & Effect Diagrams and Pareto Analysis. 4. Brainstorming Slides No.5 to 8 10 Brainstorming-what is it? How do it? Structured and unstructured. Talk through and obtain feedback from group on their past experiences. 15 Break into 2 groups. Get one group to do an unstructured brainstorm on “Why did Arsenal not win the Premier League?” and another group to do a structured brainstorm around “Why do the police get poor fuel consumption from their cars?” 10 Each group presents back ideas from the brainstorm 5 What to be aware of when brainstorming. 5. Exercise 2 Brainstorm 6. Obstacles M E Pitman Flipchart, pens Slide 9 Page 1 of 2 2/12/2016 Module M1 Basic Problem Solving Tools - Training Facilitator Flow Learning Objective: application of relevant BPST in day to day activities to foster ‘can do’ attitude. Topic Materials Time Description What is it? What does it do? Why use it? -obtain feedback from group on their past experiences 7. Cause & Effect Slides No. 10 & 11 10 8. Exercise 3 - Categories Flipchart Slid No. 12 & 13 10 9. Exercise 4 – constructing a Fishbone Diagram Flip chart, pens, slide No. 14 to 16 10 10. Pareto Slide No. 17 to 19 5 Pareto – what is it? Get each group to come up with the categories they could summarise the brainstorm into. Write out all the outputs from the brainstorm and put into 4 lists. Present the 4 categories back to the group. 2 groups- Each group constructs the fishbone showing the riblets and interdependencies and presents back to the group pointing out key dependencies. 11. Pareto cont. Slide No. 20 & 21 15 What does it do? 80:20 rule look at biggest issues, look for root cause – e.g. 80% of downtime caused by 20% of problems which best to impact upon. Data collection from check sheets /sic. Discuss real life examples. 12. Review Slide No. 22 5 Problem solving cycle; introduce and explain the links. M E Pitman Page 2 of 2 2/12/2016