Name: Date: Period: ______ Chapter 15.2: Landforms Created by
advertisement

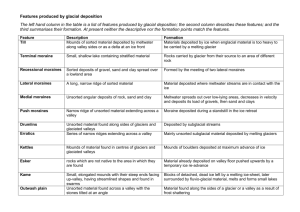
Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ Chapter 15.2: Landforms Created by Glaciers 1. Glacial Erosion a. The process that formed the ________________ begins with a glacier still _________ in the valley. i. As a glacier ________________ its way through a narrow ____________, it breaks off rock from the valley __________, causing the walls to become __________________. ii. _______________ of rock are also pulled from the __________ of the upper valley. iii. A _______________ is a bowled shape ___________________ created by these ________________ actions. 1. Cirque means “___________” in French, as it refers to the circus like ___________ depression of a circus theater. iv. _____________ means spine in French, and refers to the ____________ and jagged ____________ that form between the cirques. v. A _____________ is a cluster of several _____________ that form a ___________________ like peak. b. When a ________________ moves down a valley it picks up many ________________ ranging in size from _____________ to boulders. i. These ____________ that are now being ____________ by the glacier act as another ________________ agent. ii. As the _________________ and rocks pass over the _________ they _______________ and round larger rock _____________. 1. These rounded _____________________ have a smooth, gently ________________ side facing the direction from which the ______________ came, with the far side being ______________ and jagged as rock was pulled away when the _________ passed over. 2. These rocks are called _____________ _____________, which means “_____________ _____________” in French, because they _____________ the backs of sheep. c. The shape of valleys are originally a “___” shape. However, once a glacier _______________ through them, it cuts them out to a “____” shape. This is an easy way for ________________ to tell if the valley was __________________ by a glacier. Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ d. A __________________ glacier is a glacier that flows into a ________________ glacier. i. Tributary _________________ do not cut as deep “U” _______ since they are much _________________ than the main glacier, and when the ______ melts they are left _______ in the valley. ii. These _______________ formed from the ______________ ice of a tributary glacier are called __________________ _______. e. The ________________ process of _________________ ice sheets is very different from __________________ glaciers. i. Continental ice _____________ generally level ____________ and produce ____________, rounded ____________________. 1. _____________________ valleys are _______________ out and deepened, and rock surfaces are _____________ and grooved by rocks carried at the ____________ of the ice sheet. These scratches and grooves run ___________ to the direction of __________________ movement. Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ 2. Glacial Deposition a. Glacial __________________ occurs when valley _______________ reach lower __________________ or when climate change melts continental _________ _________________. b. Glacial _________ is the general term given to all _______________ deposited by a glacier or by the __________________ from a glacier. i. When the glacier _________ all of the _______________ in the glacier is deposited onto the __________. ii. _______________ are large boulders that have been _________ by the glacier and do not ___________ the composition of the ______________________ that they are now on. iii. ________ is made of unsorted _____________ of rock material that is deposited from __________________ scraped off by the _________ of the glacier or is left behind when glacial ice ________________. iv. _________________ drift is material that has been sorted and deposited in ____________ by streams flowing from the ____________________. c. ______ deposits are _________________ made from glacial till called _____________________. i. Moraines are _____________ of unsorted __________ material on the ground or on the _____________. We will be discussing __________ types of till ____________________ or moraines. 1. A ___________________ moraine is one that is deposited along the ________ of a valley glacier, usually as a long _______________. 2. A _____________________ moraine occurs when two or more valley glaciers ______________, and their adjacent _________________ moraines combine. 3. ____________________ moraine is the _____________ material left ___________________ the glacier when the ice melts. a. Much of the _______________ in Ohio is covered with ground _______________________. 4. ___________________ are long, low, tear-___________ mounds of till, often found in ___________________. 5. A ________________________ moraine is the till that is deposited at the ________________ or front of a melting Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ _______________. They are belts of small ___________ of till with many ______________________ that contain lakes or ponds. 6. In front of a terminal _________________, and after meltwater has ____________________ its small rock _________________ is a large ________________ plain. a. An outwash plain is a _____________ of stratified drift, which usually lies in ________ of a terminal moraine and is crossed by many meltwater ________________. 7. A _____________ forms when a portion of glacial ice is _____________ in drift, and when the ice ____________ it leaves a _____________ in the drift, and often forms ____________________. a. Kettles are mostly found in _____________ plains. 8. An _______________ is formed when ______________ ice sheets ____________ and long, winding ridges of ________________ and coarse sand may be left behind. a. Eskers ________________ of stratified drift deposited by streams of meltwater _____________ in ice _________________ within the glaciers, and may extend for tens of kilometers. Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ 3. Glacial Lakes a. ____________ commonly form lake ___________ by eroding out surface _______, leaving depressions in the ____________________, and deepening existing ___________________. b. Glaciers also commonly form ___________ basins by depositing _______. Many __________ basins were created by the uneven surfaces of ground __________________ deposited by glaciers. c. Another way _______________ form lakes is when ______________ and _________________ moraines block existing ________________ and create a lake _______________. d. The _____________ ______________ are the result of a combination of __________________ and ____________________ by continental ice ____________. i. Glacial ____________ widened and deepened broad ________ valleys covered by ice sheet. ii. ________________ to the south blocked off the ends of these _________________. iii. As the _____ sheets melted, the ___________________ flowed into the __________________ and was trapped by the moraines to form the _______________ Lakes. 1. During the early stages of the ice ___________ the great lakes were much ____________ and drained to the _____________. As the _______ __________ retreated, the lakes became _____________ and the drainage patter changed. ________________ of the land, and further ice retreat, _______________ the Great Lakes to their present ________ and established current ____________ northeast through the St. Lawrence River. e. In areas where ___________________ is high and _______________ is low lakes with high ___________ content can be formed. i. In the area where the ice age _________ __________________ once was is the current, and much smaller _________ _______ in Utah. ii. This lake became very ___________ due to the fact that it had no _________________, and the only way water could leave was through _________________. When the water evaporated, the ________ was left behind forming the current Salt Lake. Name: ____________________________________ Date: __________________ Period: ______ iii. These high salt ______________ lakes can also be a location of valuable ______________ depending on the dissolved minerals it ____________________. 1. Minerals can either be ________________ in by streams or are the result from the ____________________ and ____________________ processes occurring in the lake. iv. The salt _________________ left in the dry _________ of ancient salt lakes often contain valuable minerals such as _______________, which is used as a _____________ material and in the manufacturing of __________ and ____________. 1. Currently the dry lake beds of the __________________ ___________________ in California contain borax.