Pharmaceutics
advertisement

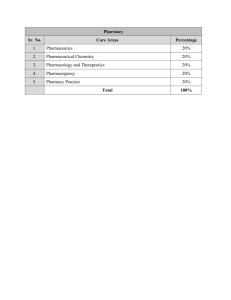
Quality Assurance Unit Faculty of Pharmacy Course Specifications 1- Basic Information: Course code: 216 Course title: Year: 2nd Pharmaceutics I Semester: 1 Theoretical: 3 hrs Practical: 2 hrs 2- Course Goals: 1. Develop the knowledge gained by studying and understanding the Physical pharmacy in first year, in liquid dosage forms formulation 2. Study the basic information for production of liquid dosage forms for drug administration. 3. Study the different pharmaceutical liquid dosage form available in the market 4. Study the difference between solutions, suspensions, and emulsions as a form of liquid preparations. 5. Study the types of incompatibilities: intentional and non-intentional, Physical or chemical incompatibilities that may be encountered during the preparation of the different pharmaceutical dosage forms. 3- Intended Learning Outcomes of Course (ILOs): a. Knowledge and After completing the course the student should be able to: understanding a.1. Understand the principles of liquid dosage forms. a.2. Understanding the various methods employed for evaluation of liquid pharmaceutical preparations. a.3. Identify the properties of different liquid dosage forms including novel drug delivery systems. 1 Quality Assurance Unit Faculty of Pharmacy a.4. Identify the different types of physical, chemical and therapeutic incompatibilities. b. Intellectual After completing the course the student should be able to: Skills b.1. Identify the role of pharmaceutical excipients in formulation of liquid dosage forms b.2. Recognize and control possible physical and chemical incompatibilities that may occur during dispensing. b.3. Calculate and adjust dosage and dose regimen of medications b.4. Utilize the pharmaceutical knowledge in the formation of safe and effective medicines. c. Professional After completing the course the student should be able to: and Practical c.1. Design compound, dispense, label and store liquid dosage forms Skills (Solution, suspension and emulsion) effectively and safely. c.2. Solve problems encountered during formulation of liquid dosage forms. c.3. Use the pharmaceutical abbreviations properly d. General and After completing the course the student should be able to: Transferable Skills d.1. Retrieve and evaluate information from different sources to improve professional competencies d.2. work effectively in a team d.3. Practice independent learning needed for continuous professional development. 4- Course Content: 1. Pharmaceutical solutions as dosage forms (aqueous and non-aqueous) 2. Pharmaceutical excipients use in Formulation of different pharmaceutical solutions (coloring agents, flavouring agents, sweetening agents, preservatives. …… 3. Dispersed systems 4. Colloids and macromolecular systems 2 Faculty of Pharmacy Quality Assurance Unit 5. Coarse dispersions 6. Pharmaceutical suspensions (formulation, excipients, stability) 7. Pharmaceutical emulsions (formulation, excipients, stability) 8. Incompatibilities (Types and how to overcome different types of incompatibilities. 5- Teaching and Learning Methods: 1. Lectures √ 2. Laboratory work √ 3. Assignments - 6- Student Assessment: Methods of Assessment Weighting Assessment Schedule % Practical exam 30 7th and 14th week Written Exam 50 15th week Oral Exam 20 15th week 7- List of Textbooks and References: 1. Course Notes: 2. Essential Books (Text Books): 3. Recommended Books: Pharmaceutics; the Science of Dosage Form Design; Ed. Aulton. Churchill Livingstone, 2001 Pharmaceutical Preformulation and Formulation. Gibson, M, CRC Press Modern Pharmaceutics4th Edition 4. Periodicals, Web Sites: http://www.vonl.com/chips/phardos3.htm http://www.pharm-int.com/ 3 Faculty of Pharmacy Quality Assurance Unit 8- Required Facilities for Teaching & Learning: 1. Personal Computer (available for each staff member), 2. Power Point Displayer (Data-Show); easy available for the usual lectures and Labs. 3. Lecture Hall 4. Equipped laboratories 9- Matrix of knowledge and skills: Topics Number of weeks Knowledge and understanding Intellectual Skills Professional and Practical Skills General and Transferable Skills Theor. Pract. 1. Pharmaceutical solutions as dosage forms (aqueous and non-aqueous) 4 6 a1, a2, a3, a4 b1, b2, b3, b4 c1, c2, c3 d1, d2, d3 2. Pharmaceutical excipients use in Formulation of different pharmaceutical solutions (coloring agents, flavouring agents, sweetening agents, preservatives. …… 6 2 a1, a2, a3, a4 b1, b2, b3, b4 c1, c2, c3 d1, d2, d3 3. Dispersed systems 2 3 a1, a2, a3, a4 b1, b2, b3, b4 c1, c2, c3 d1, d2, d3 4. Colloids and macromolecular systems 6 2 a1, a2, a3, a4 b1, b2, b3, b4 c1, c2, c3 d1, d2, d3 5. Coarse dispersions 4 2 a1, a2, a3, a4 b1, b2, b3, b4 c1, c2, c3 d1, d2, d3 6. Pharmaceutical suspensions (formulation, excipients, stability) 4 4 a1, a2, a3, a4 b1, b2, b3, b4 c1, c2, c3 d1, d2, d3 4 Faculty of Pharmacy Quality Assurance Unit 7. Pharmaceutical emulsions (formulation, excipients, stability) 6 4 a1, a2, a3, a4 b1, b2, b3, b4 c1, c2, c3 d1, d2, d3 8. Incompatibilities (Types and how to overcome different types of incompatibilities. 4 1 a1, a2, a3, a4 b1, b2, b3, b4 c1, c2, c3 d1, d2, d3 Course Coordinator: Signature: Name: Dr. Eman Saddar Head of Department: Signature: Name: Dr Dalia Samuel Shaker Date: Academic year: 5