Name
advertisement

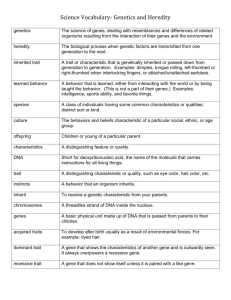
Name________________________________________________ Heredity Unit Review MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the answer that best completes the statement or answers the question. (40 points) 1) Mendel conducted his most memorable experiments on (C.1.g) A) guinea pigs. B) fruit flies. C) roses. D) peas. E) clones. 2) Varieties of plants in which self-fertilization produces offspring that are identical to the parents are referred to as (C.1.l) A) the F2 generation. B) independent crosses. C) hybrids. D) true-breeding. E) monohybrid crosses. 3) All the offspring of a cross between a black-eyed mendelien and an orange-eyed mendelien have black eyes. This means that the allele for black eyes is ________ the allele for orange eyes. (C.1.i) A) more aggressive than B) dominant to C) recessive to D) codominant to E) better than 4) The alleles of a gene are found at _________chromosomes. (C.1.i) A) the same locus on heterologous B) the same locus on homologous C) different loci on heterologous D) different loci on homologous E) the same locus on homologous mitochondrial 5) The phenotypic ratio resulting from a dihybrid cross showing independent assortment is expected to be (C.1.k) A) 3:1 B) 9:1:1:3 C) 1:2:1 D) 3:9:9:1 E) 9:3:3:1 6) A testcross is (C.1.i) A) a mating between two individuals of unknown genotype. B) a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual heterozygous for the trait of interest. C) a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual homozygous dominant for the trait of interest. D) a mating between two individuals heterozygous for the trait of interest. E) a mating between an individual of unknown genotype and an individual homozygous recessive for the trait of interest. 7) Dr. Smith's parents have normal hearing. However, Dr. Smith has an inherited form of deafness. Deafness is a recessive trait that is associated with the abnormal allele d. The normal allele at this locus, associated with normal hearing, is D. Dr. Smith's parents could have which of the following genotypes? (C.1.l) A) DD and DD B) Dd and DD C) DD and dd D) dd and dd E) Dd and Dd 8) Most genetic disorders of humans are caused by (C.1.m) A) multiple alleles. B) a mutation that occurs in the egg, sperm, or zygote. C) drinking during pregnancy. D) dominant alleles. E) recessive alleles. 9) All the offspring of a cross between a red-flowered plant and a white-flowered plant have pink flowers. This means that the allele for red flowers is ________ to the allele for white flowers. (C.1.i) A) pleiotropic B) incompletely dominant C) codominant D) dominant E) recessive 10) A person with AB blood illustrates the principle of (C.q.i) A) codominance. B) pleiotropy. C) blending inheritance. D) polygenic inheritance. E) incomplete dominance. 11) Which of the following terms refers to a situation where a single phenotypic character is determined by the additive effects of two or more genes? (C.1.m) A) codominance B) blending inheritance C) polygenic inheritanceD) pleiotropy E) incomplete dominance 12) Genes located close together on the same chromosomes are referred to as ________ genes and generally ________. (C.1.h) A) linked . . . do not sort independently during meiosis B) associated . . . sort independently during meiosis C) codependent . . . do not sort independently during meiosis D) linked . . . sort independently during meiosis E) homologous . . . are inherited together 13) Any gene located on a sex chromosome (C.1.j) A) is called a recessive gene. B) will exhibit codominance. C) will exhibit pleiotropy. D) is called a sex-linked gene. E) is called a dominant allele. 14) What is the normal complement of sex chromosomes in a human male? (C.1.j) A) one X chromosome and one Y chromosome B) one Y chromosome C) two Y chromosomes D) two X chromosomes E) two X chromosomes and one Y chromosome 15) A color-blind woman marries a man who is not color-blind. All of their sons, but none of their daughters, are color-blind. Which of the following statements correctly explains these results? (C.1.j) A) The gene for color vision is completely dominant to the gene for sex determination. B) The gene for color vision is linked to the Y chromosome. C) The gene for color vision is linked to the X chromosome. D) The gene for color vision is codominant with the gene for sex determination. E) The gene for color vision is incompletely dominant to the gene for sex determination. 16) Sex-linked conditions are more common in men than in women because (C.1.j) A) the sex chromosomes are more active in men than in women. B) men acquire two copies of the defective gene during fertilization. C) the genes associated with the sex-linked conditions are linked to the Y chromosome, which determines maleness. D) men need to inherit only one copy of the recessive allele for the condition to be fully expressed. E) women simply do not develop the disease regardless of their genetic composition. 17) Which of the following people conducted the experiments that demonstrated that DNA is the genetic material of bacteriophages? (C.1.b) A) Watson and Crick B) Griffith C) Pauling D) Hershey and Chase E) Franklin 18) The monomers of DNA and RNA are (C.1.a) A) amino acids. B) fatty acids. C) nucleotides. D) monosaccharides. E) nucleic acids. 19) The shape of a DNA molecule is most like (C.1.a) A) a diamond ring. B) a gold necklace. C) a set of railroad tracks. D) the letter X. E) a twisted rope ladder. 20) If one strand of DNA is CGGTAC, the corresponding strand would be (C.1.a) A) GCCAUC B) TAACGT C) CGGTAC. D) GCCTAG E) GCCATG 21) DNA replication (C.1.a) A) uses each strand of a DNA molecule as a template for the creation of a new strand. B) occurs through the addition of nucleotides to the end of the DNA molecule. C) begins when two DNA molecules join together to exchange segments. D) results in the formation of four new DNA strands. E) produces two daughter DNA molecules that are complementary to each other. 22) Which of the following options best depicts the flow of information when a gene directs the synthesis of a cellular component? (C.1.a) A) DNA > RNA > protein B) DNA > tRNA > mRNA > protein C) DNA > amino acid > RNA > protein D) protein > RNA > DNA E) RNA > DNA > RNA > protein 23) Which of the following options most accurately lists the sequence of events in translation? (C.1.a) A) peptide bond formation > codon recognition > translocation > termination B) codon recognition > peptide bond formation > translocation > termination C) codon recognition > translocation > peptide bond formation > termination D) codon recognition > peptide bond formation > termination > translocation E) peptide bond formation > translocation > codon recognition > termination 24) What combines with sugar and a phosphate group to form a nucleotide? (EOC C.1.a) A) amino acid B) deoxyribose C) glycerol D) nitrogenous base 25) DNA and RNA have many structural similarities. Which structure in DNA and RNA is similar? (EOC C.1.a) A) purine bases B) pyrimidine bases C) type of sugar D) attached proteins 26) A trisomy of chromosome number 21 causes what condition? (EOC C.1.m) A) albinism B) dwarfism C) down syndrome D) color blindness 27) Cystic fibrosis is a genetic disease in which excess mucus accumulates in the lungs and digestive system of affected individuals. Males and females must inherit 2 alleles with this mutation to have the disease. What is the mode of inheritance of cystic fibrosis? (EOC C.1.m) A) autosomal dominant B) autosomal recessive C) sex-linked dominant D) sex-linked recessive 28) Which example best illustrates Mendel's law of independent assortment? (EOC C.1.g) A) Two short-haired cats produce a litter of 4 kittens including 1 long-haired and 3 short-haired B) A color-blind man and a woman with normal vision produce a son with normal vision and a color-blind daughter. C) A tall purple-flowered pea plant and a short whiteflowered pea plant are crossed, producing offspring including tall white-flowered pea plants. D) A red-flowered snapdragon and a white-flowered snapdragon are crossed, producing offspring with pink flowers. 29) Patch, a short-haired cat, has black and orange spots. Two distinct autosomal gene loci produce this pattern. One gene locus produces spots as a recessive trait (ss). Another gnee locus determines the color of the spots. Homozygous BB cats have black spots, while homozygous GG cats have orange spots. Heterozygous cats have black and orange spots. According to the law of independent assortment, Patch would most likely produce gametes in what proportion? (EOC C.1.g) A) All ss B) All BGss C) Half BS and half GS D) Half Bs and half Gs 30) In humans, pigmented skin is dominant to nonpigmented skin (albinism). What is the genotype of an individual with albinism? (EOC C.1.i) A) carrier B) heterozygous C) homozygous dominant D) homozygous recessive 31) Jeanine inherited 2 alleles for round eye shape and has round eye shape. Her brother inherited 1 allele for round eye shape and 1 allele for almond eye shape and has almond eye shape. What type of trait is round eye shape? (EOC C.1.i) A) co-dominant B) dominant C) recessive D) sex-linked 32) Horses born to 2 palomino (golden-coated) horses have a 25% chance of having a white coat, a 25% chance of having a chesnut (brown) coat, and a 50% chance of having a palomino coat. Which description of inheritance best explains the coat-color trait in these horses? (EOC C.1.i) A) palomino coat color is a recessive trait B) palomino coat color is a dominant trait C) coat color is an incompletely dominant trait D) coat color is a sex-linked trait 33) In human, red-green color blindness is a recessive, sex-linked trait. The chromosomes and alleles associated with color blindness are represented in this chart. X = X chromosome Y = Y chromosome B = allele for normal color vision b = allele for color blindness Which child could NOT be born to these parents: a female (XBXb) and a male (XBY)? (EOC C.1.j) A) color-blind daughter B) color-blind son C) daughter with normal color vision D) son with normal color vision 34) The genotype for F1 individuals from a dihybrid cross is AaBb X AaBB. What is the expected ratio of AaBb individuals in the F2 generation? (EOC C.1.k) A) 8/16 B) 4/16 C) 2/16 D) 1/16 35) Keisha passes a local dairy farm that has many brown cows, bout only a few white cows. A dominant allele produces brown hair in cows and a recessive allele produces white hair. Which characteristic of any brown cow can Keisha identify? (EOC C.1.l) A) the genotype of both of the cow's parents B) the genotype of the cow's hair color C) the phenotype of both of the cow's parents D) the phenotyep of the cow's hair color 36) Adrenoleukodystrophy (ALD) is a sex-linked recessiv etrait that affects the nervous system. In one family, the father, mother, daughter, and elder son do not have ALD, while the younger son has ALD. Who must be a carrier of the ALD allele? (EOC C.1.l) A) father B) mother C) daughter D) elder son 39) Alkaptonuria is a genetic disorder of protein metabolism. The disorder is determined by 2 alleles at 1 locus. 37) This pedigree shows 3 generations of a family and the family's incidences of color blindness, a sex-lnked, recessive trait. What is the genotype for individual 1 in the diagram? (EOC C.1.l) A) AA or Aa B) AA C) Aa D) aa 40) This chart shows the RNA sequences that code for various amino acids. Which pair of females must have the same genotype? (EOC C.1.l) A) 3 and 5 B) 7 and 11 C) 8 and 13 D) 10 and 14 38) Two black guinea pigs bred and produced 3 black offspring and 2 albino offspring. Assuming no mutations, which guinea pigs must be heterozygous? (EOC C.1.l) A) all 3 black offspring B) exactly 2 of the black offspring C) both albino offspring D) both parents The mRNA sequence ACU codes for the amino acid Thr. A mutations occurs, and the resulting mRNA sequence is AUU. What amino acid will replace Thr? A) Val B) Met C) Ile D) Ala Name_________________________________________________________ Heredity Unit Review Constructed Response. Write your answer in the space provided or on a separate sheet of paper. 41) A biologist identifies the DNA sequence, or gene, that codes for a protein that stops the production of eggs in mosquitoes. She labels this gene Sequence 1. During her investigation of the replication, transcription , and translation of the gene, she observes mosquitoes in which the protein coded by this gene does not function. She labels the DNA sequence for this version Sequence 2. The first table shows one DNA strand for each gene sequence. Use the mRNA Codon Chart to complete the following tasks. (EOC C.1.a, C.1.c, C.1.d) Using your understanding of mutations and the genetic code, analyze these nucleotide sequences. As part of your answer, be sure to : . Determine the mRNA sequence that complements Sequence 1. . Use the mRNA Codon Chart to translate the mRNA sequence in the previous bullet into an amino acid chain. . Identify the type of mutation in Sequence 2, describe how this mutation specifically affects the amino acid sequence of the protein, and describe how this change results in a protein that does not function correctly.








![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)