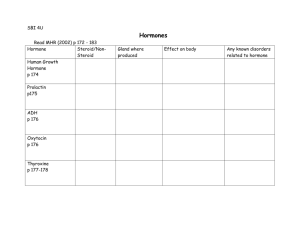
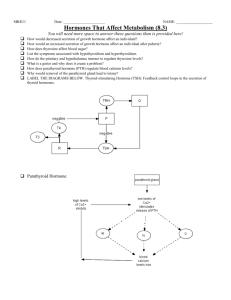
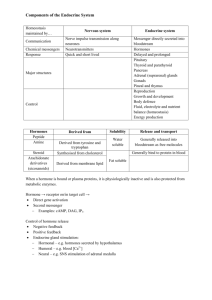
Endocrine System Study Questions: AP Biology
advertisement
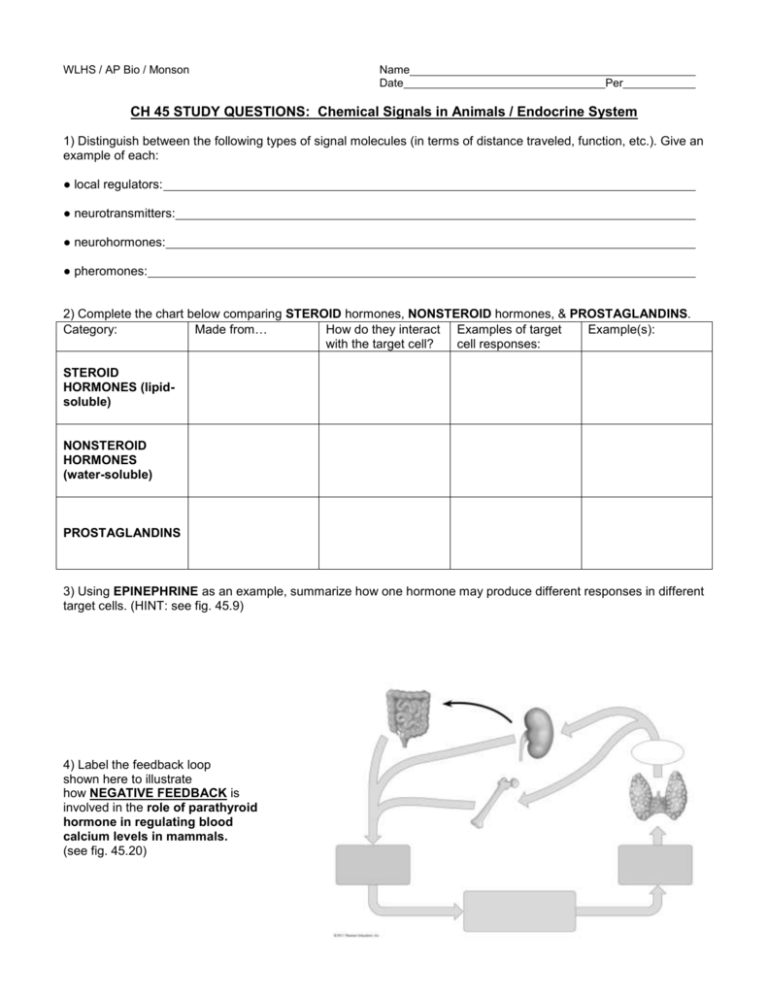
WLHS / AP Bio / Monson Name Date Per CH 45 STUDY QUESTIONS: Chemical Signals in Animals / Endocrine System 1) Distinguish between the following types of signal molecules (in terms of distance traveled, function, etc.). Give an example of each: ● local regulators: ● neurotransmitters: ● neurohormones: ● pheromones: 2) Complete the chart below comparing STEROID hormones, NONSTEROID hormones, & PROSTAGLANDINS. Category: Made from… How do they interact Examples of target Example(s): with the target cell? cell responses: STEROID HORMONES (lipidsoluble) NONSTEROID HORMONES (water-soluble) PROSTAGLANDINS 3) Using EPINEPHRINE as an example, summarize how one hormone may produce different responses in different target cells. (HINT: see fig. 45.9) 4) Label the feedback loop shown here to illustrate how NEGATIVE FEEDBACK is involved in the role of parathyroid hormone in regulating blood calcium levels in mammals. (see fig. 45.20) 5) How does positive feedback differ from negative feedback? Describe 2 examples when the human body may utilize positive feedback. 6) Complete the chart below comparing type I and type II diabetes. (see page 983) Type: How diagnosed? Age of onset: Cause: Type I Type II 7) List the short-term and long-term effects of STRESS. (see fig. 45.21, pg. 991)) Short-term effects: Long-term effects: 8) Label the following anatomical diagram showing the major endocrine glands (use the left side of diagram), as well as organs that contain endocrine cells (use the right side of diagram). SEE Fig. 45.4 for guidance. Treatment: 9) Complete the following chart, summarizing the various hormones of the endocrine system, their target cell or organ, and their general function(s). (use Table 45.1 as well as info. in chapter / notes) Hormone HYPOTHALAMUS: Releasing hormones ANTERIOR PITUITARY: Growth hormone Prolactin (PRL) Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) Adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) Luteinizing hormone (LH) POSTERIOR PITUITARY: Antidiuretic hormone (ADH) Oxytocin THYROID GLAND: Thyroxine (T4) & Triiodothyronine (T3) Calcitonin PARATHYROID GLAND: Parathyroid hormone (PTH) ADRENAL GLANDS – ADRENAL MEDULLA: Epinephrine & norepinephrine ADRENAL GLANDS – ADRENAL CORTEX: Aldosterone (“mineralocorticoids”) Cortisol (“glucocorticoids”) PANCREAS: Glucagon Insulin PINEAL GLAND: Melatonin (one more diagram…!)…on back. Target cell / organ Action(s) / Function(s) 10) Label the following diagram showing the maintenance of glucose homeostasis by insulin and glucagon. (HINT: see fig. 45.13)