predator biomes
advertisement

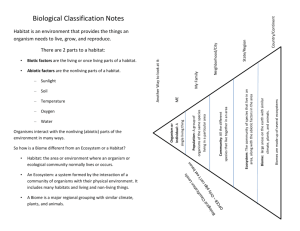
Study Guide-Ecology Unit 1. Ecology is the study of __________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________. 2. Non living parts of the environment are called ____________ and living parts are called ____________. 3. Ecological factors are organized into categories from largest to smallest, from the biosphere down to individual organisms. List these in order: Biosphere, ______________, _______________, ________________, and individual organism. 4. The part of earth where life exists is called the ______________. 5. ________________ are made of all the abiotic and biotic factors in an area. 6. ________________ are divisions of ecosystems with specific features and different species interacting with each other and competing with one another. 7. A _______________ is a group of one particular species living in a community. 8. The place where an organism lives is called its _____________. Organisms have specific adaptations that help them survive in their habitats. 9. A _______________ is the role that an organism has in its habitat. This refers to how it gets its food, where it sleeps, and how it mates. 10. Can two different species occupy the same niche? _______ Why? ___________ _____________________________________________________________ What is it called when one species out competes another and drives it to extinction? ___________________________ 11. ________________ is a close relationship between two different species. There are three different symbiotic relationships, _________________, _______________, and ________________. 12. In parasitism on organism _____________ and the other is _____________. The one that benefits is the parasite and the one harmed is the ____________. An example is __________________________________________________. 13. A relationship in which both organisms benefit is called _________________. An example is __________________________________________________. 14. In ________________ one organism benefits and the other is neither helped nor harmed. An example is ________________________________________. 15. What is an example of a predator-prey relationship? _____________________ Which one is the predator? _______________ Prey? ________________ 16. All organisms require energy. Some make their own and some must consume other organisms to get energy. Producers, or _____________, make their own food. Consumers, or ______________, must eat to get energy. 17. Heterotrophs are classified by the type of food they eat. _______________ eat only plants, _______________ eat other animals, and _______________ eat both plants and animals. 18. _____________ recycles nutrients in the air and soil by breaking down dead organisms. 19. _____________ are animals that eat the bodies of dead organisms. Ex. Vultures 20. A __________________ shows how energy moves in one direction through a community. These are no more than 4 or 5 organisms long. The arrows always point in the direction that the energy is moving. 21. A _________________ is more complex and shows all the possible feeding relationships in a community. Food chains and webs always start with a _____________. Be able to read and answer questions about food chains and food webs. 22. ______________ levels show how the energy transfer in food chain decreases with each organism added. Most of the energy in a food chain is in the first trophic level, the _______________. The least amount is in the top level. 23. Ecological pyramids give details about a community. There are three pyramids that we use _____________________________, _____________________, and _______________________________. What information can you get from each one? _____________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________ 24. What is biomass? _______________________________________________ 25. Know the four biogeochemical cycles (next pages). How are they different from food chains? ___________________________________________________ 26. What is a limiting factor? ________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________. 27. What does range of tolerance mean? ________________________________ _____________________. What are some organisms with a wide range of tolerance? ___________________________________________________ 28. The predictable natural changes and ___________ replacements that take place in an ecosystem are called _________________. 29. When an ecosystem has been completely destroyed and starting from nothing (like after a volcanic eruption) it is undergoing ____________ succession. When a natural disaster or human action occurs leaving nothing but soil in an ecosystem, it will undergo ______________ succession. 30. The first species to inhabit an area during succession is called a _____________ _________. An example for primary succession would be _____________. And for secondary succession _____________ is an example. 31. Succession is a long process that must take place in order to reach a stable ecosystem that undergoes little or no visible changes called a _______________ ____________. 32. A _______________ is a large group of ecosystems that share the same type of climax community. Biomes are either __________________ or __________________. 33. Biomes that are located in water are called _________________. They are classified as ______________, _______________, or ________________ and they make up _______% of the earth’s surface. 34. What type of water is found in each of these aquatic biomes? a. Marine- _________________ b. Estuary- _________________ c. Freshwater- ______________ 35. The marine biome is divided into three zones. The _____________ zone is the part near the surface where light is present. The aphotic zone is __________________________________________________________________ _______. And the intertidal zone is ____________________________. 36. What causes the ocean tides? ______________________________________. 37. Where in freshwater biomes is the population density lowest? ______________. 38. The bottom of ponds and lakes are made of _____________. 39. Biomes that are located on land are called _______________. There are six main terrestrial biomes: ______________, _____________, _____________, ______________, ______________, and ______________. 40. The coldest biome is the _____________, which is also characterized by short growing seasons and a layer of frozen soil called ______________. This soil prevents any large trees from growing. The plant life is made up of _________ ___________________________________________________________. 41. Just south of the tundra is the ____________. This biome is populated mostly by __________________ trees. 42. The ________________________ is home to trees that lose their leaves annually called ________________ trees. This is part of the reason for the rich layer of ________________.This is also the biome that we live in! 43. The ___________________ gets its name from the large amount of grasses it supports. It also occupies ________ area than any other terrestrial biome. Other names for it include _______________________________________. 44. The _____________ is the driest biome. It receives about ______ cm of precipitation annually. __________ are the most abundant types of plants found here. 45. The biome with the most biodiversity is the _________________________. However, the soil is _________ in nutrients. Why? ____________________ ___________________________________________________________. This biome is warmer than others because it is closer to the ______________. 46. As a population gets larger, it grows faster. What type of growth is it experiencing? _________________ What would it look like on a graph? ___ 47. When a population has reached the maximum amount that the ecosystem can support it has reached the ____________________. This turns the J-shaped graph into an ___shaped graph. Be able to read a graph and determine when it is in exponential growth and when it has reached carrying capacity. 48. What type of limiting factors affect a population greater as its density increases? __________________ What are examples? __________________ 49. What type of limiting factors affect populations the same no matter the density? ___________________ What are examples? _________________________ 50. What two organism interactions in the community affect the population size? ___________________________ What example did we use for predation? __________________ Explain their relationship. ______________________ ____________________________________________________________________ 51. What is demography? ____________________________________________ 52. What can demographers look at to predict population growth in specific countries? _____________________ What is emigration and immigration? ____________________________________________________________ Be able to interpret an age structure chart. 53. What is biodiversity? ___________________________________________ There is about ___ million species identified in the world. The estimated total is about ___ million! 54. Terrestrial biodiversity tends to _____________ as you get closer to the equator. The tropical regions contain ____ of all land species on earth. 55. One of the reasons biodiversity is important is because people enjoy it. This is described as _____________, meaning “love of life.” Also, if one species is lost it could ____________________________. People also depend on living things for many reasons. List some reasons we need to protect biodiversity. _________ _____________________________________________________________ ____________________________________________________________ 56. A species becomes ____________ when the numbers begin declining rapidly. A species is ____________ when the numbers are so low that extinction is possible. ____________ occurs when there are no more organisms of a species left. 57. The biggest threat to biodiversity is _______________. 58. Habitat ______________ is the separation of wilderness areas from other areas. This happens when roads are constructed or large building projects. 59. Habitat ____________ is when a habitat is damaged by pollution. The 3 types of pollution are ______________________. 60. A species that has been brought into an area where it is not natively found is an _______________. These can be problems for native species because they have no natural predators and they may out compete for resources. What are some examples? __________________________________________________ __________________________________________________________ 61. _____________ Biology is a new field of biology started to protect biodiversity. Also the Endangered Species Act was started in _____ by President _________. 62. When an animal is held by people it is in ____________. Programs that hold animals captive for a period of time and then release them back into the wild are called _________________________.