polar molecules0

electronegativity: a measure of the electron attracting ability of the atoms in a molecule
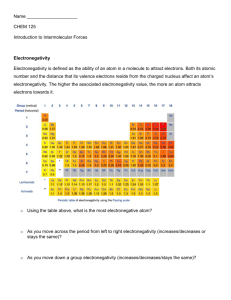
Below are ten common elements with their electronegativity values. Your textbook has a more complete list.
Electronegativity of the elements increases ase you move UP the periodic table and to the RIGHT.
Fluorine has the highest electronegativity of all atoms.
F 4.0 C 2.5
O 3.5 S 2.5
Cl 3.0 H 2.1
N 3.0 Na 0.9
Br 2.8 K 0.8
Polarity of Bonds
Two types of bonds are ionic and covalent. Covalent bonds are further subdivided into non-polar covalent and polar covalent.
Electronegativity values are useful in determining if a bond is to be classified as nonpolar covalent, polar covalent or ionic. What you do is look at the two atoms in a given bond. Calculate the difference between their electronegativity values. Only the absolute difference is important.
Bond Electron
Sharing equal non-polar covalent polar covalent ionic unequal none – complete transfer of electrons
Polarity of Molecules
Examples of Bonds
Cl-Cl, H-H, F-F, C-S
N-H, H-O, C-Cl, H-O, H-F
NaCl, MgCl
2
Electronegativity
Difference (
∆
∆
Bond is between metal and non-metal.
∆ EN)
EN is less than 0.5
EN is greater than 0.5
Both the polarity of the bonds and the shape of the molecule determine if a molecule is polar or non-polar.
The polarity of the bond is shown by an arrow, pointing from the positive ( δ+ ) to the negative ( δ) end of the bond. The arrow represents the bond dipole . Bond dipoles are vector quantities and can be added together to determine the polarity for the whole molecule.
In general,
A non-polar molecule has no net dipole.
This can be achieved by the molecule having:
- only non-polar bonds
- polar bonds arranged symmetrically so that the dipoles cancel out
A polar molecule has a net dipole.
This is achieved by the molecule having:
- polar bonds arranged unsymmetrically so that the dipoles do not cancel out.
Examples:
Non-polar Molecules
H
2
H - H
Only non-polar bonds present is non-polar since both hydrogen atoms making up the molecule have equal electronegativity so there is no net dipole.
NCl
CO
3
2
O = C = O
NCl
3
is non-polar since the nitrogen atom and the chlorine atoms making up the molecule have the same electronegativity so there is no net dipole.
Polar bonds arranged symmetrically
Each C - O bond is polar since oxygen is more electronegative than carbon, however, these bonds are arranged symmetrically (all angles are 180 o ) so that the two dipoles cancel out resulting in no net dipole for the molecule.
AlCl
CH
4
3
Each Al-Cl bond is polar since chlorine is much more electronegative than aluminium, however, each Al-Cl bond in AlCl
3
is arranged symmetrically (all angles are 120 o ) so that the dipoles cancel out resulting in no net dipole for the molecule.
Each C-H bond is polar since carbon is more electronegative than hydrogen, however, each C-H bond in CH
4
is arranged symmetrically (all angles are 109.5
o ) so that the dipoles cancel out resulting in no net dipole for the molecule.
Polar Molecules
HCN
H
2
O
Polar bonds arranged unsymmetrically
---------------------->
Both the C-H and the C-N bonds are polar.
Nitrogen is more electronegative than carbon which is more electronegative than hydrogen. So that the hydrogen takes on a partial positive charge and the nitrogen takes on a partial negative charge. This results in an unequal sharing of the bonding electrons resulting in a net dipole for molecule since the two dipoles do not cancel out.
Each O-H bond is polar since oxygen is more electronegative than hydrogen so each hydrogen takes on a partial positive charge and the oxygen atom takes on a partial negative charge. The two
O-H bonds are arranged unsymmetrically (angle between bonding pair < angle between bonding pair and lone pair < angle between lone pair and lone pair) resulting in a net dipole since the two dipoles do not cancel out.
NH
CH
3
3
Cl
Each N-H bond is polar since nitrogen is more electronegative than hydrogen so each hydrogen takes on a partial positive charge and nitrogen takes on a partial negative charge. The three N-H bonds are arranged unsymmetrically (angle between bonding pairs < angle between bonding pairs and lone pair) resulting in a net dipole since the three dipoles do not cancel out.
Each C-H bond is polar since carbon is more electronegative that hydrogen, and the C-Cl bond is polar since chlorine is more elctronegative than either carbon or hydrogen. Each hydrogen atom will take on a partial positve charge and the chlorine atom will take on a partial negative charge resulting in a net dipole since the dipoles will not cancel out owing to the difference in electronegativities of carbon, hydrogen and chlorine.
Predicting the Polarity of a Molecule
Step 1: Draw the Lewis structure for the molecule.
Step 2: Use the number of electron pairs and VSEPR rules to determine the shape around the central atom.
Step 3: Use electronegativities to determine the polarity of each bond.
Step 4: Add the bond dipole vectors to determine if the final result is zero (nonpolar molecule) or non-zero (polar molecule).
Practice: Use the shape and bond polarity to determine the polarity of the molecule.
(a) SiBr
4
(b) BeF
2
(c) PCl
3
(d) SCl
2