this is only a study guide is is not meant to be your only source of
advertisement

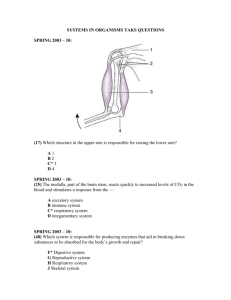
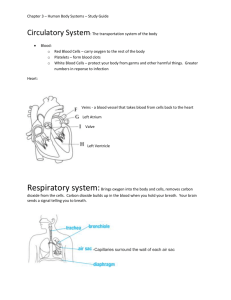
THIS IS ONLY A STUDY GUIDE IS NOT MEANT TO BE YOUR ONLY SOURCE OF INFORMATION FOR THE UP COMING TEST. Match the system to the correct description Respiratory Circulatory Excretory Digestive Endocrine Integumentary Reproductive Nervous 1. Reproductive System facilitates the continuation of a species 2. Endocrine System uses hormones to help regulate the body’s activities 3. Excretory System filters waste from blood to be expelled from the body 4. Respiratory System acquires oxygen for the body and releases carbon dioxide 5. Circulatory System dioxide works with the above system to move oxygen to all cells and remove Carbon 6. breaks down large molecules so they can be absorbed by the body Digestive System 7. Nervous System activities uses electrical impulses to control the body’s 8. Integumentary System protects from infection and helps regulate body temperature 9. What three systems aid in body movement skeletal, muscular and nervous systems. 10. What 2 systems work together to control and coordinate body functions: endocrine system and nervous system. 11. Explain what it means when we say the systems are interdependent? It means all the body systems depend on each other to maintain our body’s homeostasis. No system can do its job or function properly unless ALL are doing their part / functioning properly. 12. Where specifically does the exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen take place in the body?The exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen takes place at the cell level between individual cells and the capillaries of the circulatory system. The exchange of carbon dioxide and oxygen at the body or system level takes place between the alveoli located in the lungs of the respiratory system and the capillaries of the circulatory system that surround the alveoli. Fill in the chart: Body System Function Organs / main parts Respiratory To exchange oxygen and carbon dioxide between the body and atmosphere Trachea, bronchi, alveoli, lungs, diaphragm Nervous To coordinate and control the activities of all body systems using electrical impulses Brain, spinal cord, nerves,senses Endocrine To work with nervous system to control and coordinate certain activities using chemical signals called hormones To filter waste materials form the blood and prepare them to be expelled from the body Glands (pituitary, adrenal, pancreas) , hormones To carry oxygen from the lungs and nutrients form the small intestine to all body cells, to remove waste products from all body cells To allow movement of the whole body or materials within the body To give the body support, strength, and shape, protect internal organs To protect body from infection, help maintain body temperature, gather information from external environment To ensure the survival of a species, produce offspring Heart, blood vessels (arteries, veins, capillaries), blood To break large food molecules into small nutrients the body can use Mouth, salivary glands, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, liver, gall bladder, pancreas Excretory Circulatory Muscular Skeletal Integumentary Reproductive Digestive Kidney, ureter, unrinary bladder, urethra Muscles, tendons Bones, ligaments, bone marrow Skin, hair, nails Ovaries, eggs Testes, sperm 13. Explain how the digestive system, muscular system, and the circulatory system work together to supply all cells with the nutrients they need to function properly, INCLUDE the role the villi play in this process. The digestive system mechanically and chemically breaksdown food into small molecule that the body can use, muscle line the digestive system organs and move the food materials through the system with peristalsis, Once the molecules are small enough for the cells to use they are absorbed by the villi in the small intestine and passed into the circulatory system to be transported throughout the body. 14. Explain how the respiratory system, circulatory system, integumentary system, excretory system, and the digestive system work to remove waste from your body. The respiratory system receives carbon dioxide gas form the circulatory system which is released form your body when you exhale. The circulatory system picks up carbon dioxide and other waste from all cells in the body. The excretory system filters the blood in the kidneys removing waste and forming urine which is sent to the urinary bladder to be stored until your body expels it. The digestive system releases solid waste in the form of feces. Feces is the food materials tha our body could not digest. Finally the integumentary releases small amounts of excess salt and other waste with sweat. 15. Explain how the endocrine system and the reproductive system work together to ensure the survival of a species. The nervous system uses electrical impulses to coordinate and control the activities of the body. The endocrine system receives direction from the nervous system then uses chemical signals called hormones to coordinate growth and other specific activities of the body systems. 16. Explain the difference between a response and a stimulus. Explain the difference between an external stimulus and an internal stimulus. A stimulus is a change in the environment that causes a response. A response is the reaction / action taken due to a stimulus. An internal stimulus comes from inside your body (hunger, thirst etc.) while and external stimulus comes from outside your body. 17. Compare and contrast sexual and asexual reproduction – include number of parents, which increases diversity within a species, the material responsible for passing traits from parent to offspring, and whether offspring are identical or similar to the parents Asexual reproduction = 1 parent, no combining of genetic material therefore the offspring are identical to the parent. Sexual reproduction = 2 parents, combining of genetic material from 2 sources therefore the offspring are similar to parents but NOT identical to the parents. Sexual reproduction creates more variation / diversity within a species. Variation and diversity within a species usually increases a species change of survival. For each diagram below identify the organ, its main function, and the organ system it belongs to. 18. Lungs, take in air (oxygen) and release carbon dioxide, respiratory system 20. kidneys, filter waste form blood creates urine, Excretory system 19.heart, pump blood throughout body, circulatory system 22. stomach, begins to breakdown proteins, breaksdown food, digestive system 21. Urinary Bladder, store urine from kidneys, excretory system REMEMBER THIS IS ONLY A STUDYGUIDE - ITS PURPOSE IS TO DIRECT YOUR STUDYING AND HELP KEEP YOU FOCUSED. YOU SHOULD REVIEW YOUR JOURNALS AND THE APPLICABLE TEXTBOOK CHAPTERS.