Verbs, tense, aspect and mood

ENG1100 Introduction to English Grammar
Johan Elsness 2003 II http://folk.uio.no/elsness/
Verbs, tense, aspect and mood
Specification of verbs
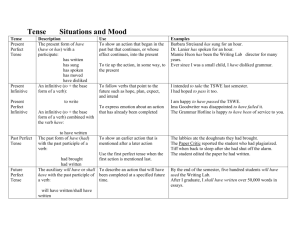
Tense :
Aspect : present past (preterite)
Tense is a deictic category. progressive perfect(ive)
Aspect is a non-deictic category.
Voice : active/passive
Mood : indicative imperative subjunctive
-s,
-ed
Ø
BE + -ing
HAVE + past participle
Categories of the verb expressed by two elements:
I
II perfect(ive) progressive
HAVE + past participle
BE + -ing
III passive BE + past participle
I + III
II + III
1 The house has been painted.
2 The house is being painted.
I + II 3 Joan has been painting the house.
I+II+III + modal 4 If Peter had gone in through that door, he would have been being eaten by the lions now.
Marginal modals
5
He daren’t tell her.
6
He doesn’t dare to tell her.
7 We didn’t need to pay.
8 We needn’t have paid.
9 We used to meet once a week.
Cf. 10 We usually meet once a week.
Auxiliary equivalents
The English modals being morphologically defective, having only finite forms, various auxiliary equivalents are often used in other functions, and sometimes as finite forms as well.
11 Alexander will be able to help you.
12
We’ve had to postpone the exam.
13 We weren’t allowed to smoke in the canteen.
Catenatives
14 He tends to agree with the last speaker.
15 She keeps telling me about her problems.
16 They seemed to be very hostile.
Cf. 17
I’ve managed to solve my problems.
The present tense usually refers to present time, which may vary from punctual to
(virtually) unlimited :
18 I put the rabbit back in the hat.
(Demonstration by conjuror)
19 Two plus two is four. (Eternal truth)
20 This cake is delicious. (Cf. Norwegian Denne kaken var deilig.
)
21 That's a nice dress. (Cf. Norwegian Det var en pen kjole.
)
The present tense can also refer to the future :
22 Her train leaves at eight o'clock tonight.
23 If/When Peter comes, we'll tell him.
The historical present is most common in colloquial English:
24 I was in the pub last night, when suddenly this funny man walks in.
The past tense denotes distance , usually in time but sometimes in reality :
25 John left yesterday.
26 If John left, we would have all the cake for ourselves.
Mood refers to the distinction between the indicative , the imperative and the subjunctive .
The indicative is the unmarked mood, the imperative is used to express orders and commands, while the subjunctive, although not very common in present-day English, survives in certain non-factive constructions.
A. The subjunctive in the present tense, identical with the base form of the verb:
Wishes:
27 God bless America!
28 Long live the King!
In that -clauses expressing requests, suggestions, etc., acting as subjects or objects, or as appositions in noun phrases:
29 She recommends that the trip be postponed.
30 We have to consider the recommendation that the trip be postponed.
31 It is essential that the trip be postponed.
B. The subjunctive in the past tense, distinct from the indicative only with the verb BE, occurring in hypothetical subordinate clauses:
32 She behaves as if she were the owner of the company.
33 If I were you, ... . (Subjunctive mandatory.)
The present perfect in English is used much as in Norwegian, with two major exceptions
(cf. the results of an elicitation test with American and British students used as informants - scores: 1='totally unacceptable', 5='perfectly OK'):
A. The past tense is consistently preferred if the past situation is unique , i.e. if it is known to have occurred once and only once in the past:
AmE BrE
34 Do you know who has written this book?
35 Do you know who wrote this book?
2.5
4.9
3.1
4.8
b
36
37
This cake is delicious. Have you made it yourself?
This cake is delicious. Did you make it yourself?
1.6 2.6 c
4.9 4.9
B. Especially in AmE the past tense is increasingly used where the present perfect might be expected. There are clear AmE/BrE differences with certain adverbs :
38 Have you finished the book already?
AmE
4.6
BrE
4.9 c
39 Did you finish the book already?
40
41
Have you told them the news yet?
Did you tell them the news yet?
4.1 1.5 c
4.8 4.9 b
4.3 1.9 c