1) In a single molecule of water, the two hydrogen atoms are bonded
advertisement

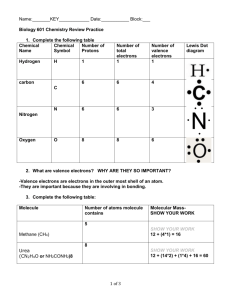
Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________ TEST 1 (CHAPTERS 1 AND 2) 1. In a single molecule of water, the two hydrogen atoms are bonded to a single oxygen atom by a. Hydrogen bonds b. Nonpolar covalent bonds c. Polar covalent bonds d. Ionic bonds e. Van der Waals interactions 2. The slight negative charge at one end of one water molecule is attracted to the slight positive charge of another water molecule. What is this attraction called? a. A covalent bond b. A hydrogen bond c. An ionic bond d. A hydrophilic bond e. A hydrophobic bond 3. In one modern classification system, organisms are grouped into five a. Kingdoms b. Phyla c. Genera (genus) d. Species e. Domains 4. What determines the cohesiveness of water molecules? a. Hydrophobic interactions b. Nonpolar covalent bonds c. Ionic bonds d. Hydrogen bonds e. Both A and C 5. Ice is lighter and floats in water because it is a crystalline structure in which each water molecule is bonded to a maximum of four other water molecules by which kind of bond? a. Ionic b. Hydrogen c. Covalent d. A and C only e. A, B, and C Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________ 6. In a living cell, which compound serves primarily as a substance in which most molecules and ions are dissolved? a. Glycerol b. Glucose c. Water d. Cellulose e. Sodium Chloride 7. Which of the following ionizes completely in solution and is consider to be a strong base? a. NaCl b. HCl c. NH3 d. H2CO3 e. NaOH 8. Which of the following solutions has the greatest concentration of hydroxide ions [OH-]? a. Lemon juices at pH 2 b. Vinegar at pH 3 c. Tomato juice at pH 4 d. Urine at pH 6 e. Seawater at pH 8 9. One liter of a solution of pH 2 has how many more hydrogen ions (H+) than 1 L of a solution of pH 6? a. 4 times more b. 400 times more c. 4,000 times more d. 10,000 times more e. 100,000 times more 10. Which four elements make up approximately 96% of living matter? a. Carbon, sodium, chlorine, nitrogen b. Oxygen hydrogen, calcium, sodium c. Carbon, sulfur, phosphorous, hydrogen d. Carbon, hydrogen, nitrogen, oxygen e. Carbon, oxygen, sulfur, calcium 11. The mass number of an element can be easily approximated by adding together the number of ___________ in an atom of that element. a. Protons and neutrons b. Energy levels c. Protons and electrons d. Neutrons and electrons e. Isotopes Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________ 12. How do isotopes of the same element differ from each other? a. Number of protons b. Number of electrons c. Number of neutrons d. Valence electron distribution e. Amount of radioactivity 13. Diagrams, tables, and graphs are used by scientists mainly to a. Design a research plan for an experiment b. Test a hypothesis c. Organize data d. Predict the independent variable e. Revise experiments for the future 3 14. H is a radioactive isotope of hydrogen. One difference between hydrogen-1 ( 1 H ) and 1 a. b. c. d. e. hydrogen-3 ( 3 H ) is that hydrogen-3 has 1 One more neutron and one more proton than hydrogen-1 One more proton and one more electron than hydrogen-1 One more electron and one more neutron than hydrogen-1 Two more neutrons than hydrogen-1 Two more protons than hydrogen-1 Figure 2.1 15. Refer to figure 2.1. Which drawing depicts the electron configuration of an atom of Neon, a non-reactive element? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 16. Refer to figure 2.1. Which drawing is of an atom with the atomic number of 6? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________ 17. Refer to figure 2.1. Which drawing depicts an atom with a valence number of 3? a. A b. B c. C d. D e. E 18. What are the chemical properties of atoms whose valence shells are filled with electrons? a. They form ionic bonds in aqueous solutions b. They form covalent bonds in aqueous solutions c. They are stable and chemically unreactive or inert d. They exhibit similar chemical behaviors e. Both C and D are correct Figure 2.2 19. Refer to Figure 2.2. Based on the electron configuration, which of these elements would exhibit chemical behavior most like that of oxygen? a. Carbon b. Hydrogen c. Nitrogen d. Sulfur e. Phosphorous 20. What do atoms form when they share electron pairs a. Elements b. Ions c. Aggregates d. Isotopes e. Molecules 21. What do the four elements most abundant in life-carbon, oxygen, hydrogen, and nitrogen- have in common? a. They all have the same number of valence electrons b. Each element exists in only one isotopic form c. They are equal in electronegativity d. They are elements produced only by living cells e. They all have unpaired electrons in their valence shells Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________ 22. A covalent bond is likely to be polar when a. One of the atoms sharing electrons is more electronegative than the other atom b. The two atoms sharing electrons are equally electronegative c. The two atoms sharing electrons are of the same element d. It is between two atoms that are both very strong electron acceptors e. The two atoms sharing electrons are different elements 23. Which of the following represents a polar covalent bond a. H-H b. C-C c. H-O d. O-O e. I-I 24. The ionic bond of sodium chloride is formed when a. Chlorine gains an electron from sodium b. Sodium and chlorine share an electron pair c. Sodium and chlorine both lose electrons from their outer valence shells d. Sodium gains an electron from chlorine e. Chlorine gains a proton from sodium 25. What is the difference between covalent bonds and ionic bonds? a. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of protons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms b. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of neutrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms c. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of electrons between atoms and ionic bonds involve the electrical attraction between atoms d. Covalent bonds involve the sharing of protons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of neutrons between atoms e. Covalent bonds involve the transfer of electrons between atoms; ionic bonds involve the sharing of neutrons between atoms 26. What results from a transfer of electron(s) between atoms? a. A nonpolar covalent bond b. A polar covalent bond c. An ionic bond d. A hydrogen bond e. A hydrophobic interaction Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________ 27. Tomato plants in a garden are not growing well. The gardener hypothesizes that the soil is too acidic. To test this hypothesis accurately, the gardener could a. Plant seeds of a different kind of plant b. Move the tomato plants to an area with less sunlight c. Change the pH of the soil d. Reduce the amount of water available to the plant e. Eat the tomatoes 28. Water is able to form hydrogen bonds because a. Oxygen has a valence of 2 b. The water molecule is shaped like a tetrahedron c. The bonds that hold together the atoms in a water molecule are polar covalent bonds d. The oxygen atom in a water molecule has a weak positive charge e. Each of the hydrogen atoms in a water molecule is weakly negative in charge 29. A neutral solution has a pH of a. 1 b. 7 c. 9 d. 14 e. None of the above 30. Which term best describes a solution with a pH of 5? a. Acidic b. Neutral c. Basic d. Colorless e. Indicator 31. Which is the most specific term used to classify humans? a. Sapiens b. Homo c. Animal d. Chordate e. Mammal 32. Which of these elements is found in the smallest amount in living matter? a. Iodine b. Carbon c. Nitrogen d. Oxygen e. Hydrogen Name: ____________________________________________ Date: ____________ Short Answer 33. Chlorine and fluorine have similar reactivities because they both lack one electron in their valence shell. Explain then, why hydrogen DOES NOT have a similar reactivity as chlorine and fluorine if hydrogen also lacks one electron from its valence shell. (*HINT – include a drawing in your answer) 34. Describe how you could determine whether or not an unknown solution is an acid or a base by using the equipment listed below 1. UNKNOWN SOLUTION 2. REACTION PLATE 3. EYE DROPPER 4. PHENOLPHTALEIN 5. BROMOTHYMOL BLUE 6. DISTILLED WATER