Feel the Burn
advertisement

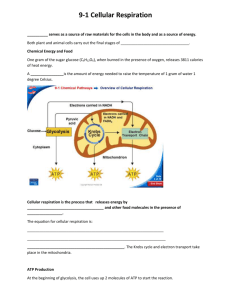
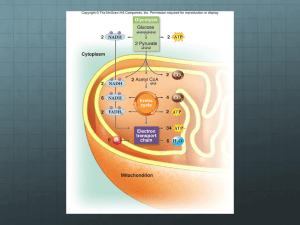
Feel the Burn Do you like to run, bike, or swim? These all are good ways to exercise. When you exercise, your body uses oxygen to get energy from glucose, a six-carbon sugar. 1. How does your body feel at the start of exercise, such as a long, slow run? How do you feel 1 minute into the run; 10 minutes into the run? 2. What do you think is happening in your cells to cause the changes in how you feel? 3. Think about running as fast as you can for 100 meters. Could you keep up this pace for a much longer distance? Explain your answer. Chapter 9-1 Chemical Pathways Chemical Energy & Food •Food – source of: •calorie –“Calorie” •Cells breakdown food slowly & gradually –Cells can’t use food energy directly –If all at once, too explosive and most energy lost as heat –Slowly releases energy of food to make ATP Cellular Respiration 6O2 + C6H12O6 6CO2 + 6H2O + Energy •Three main steps: Cellular Respiration: 3 Stages 1. Glycolysis ( 2. Krebs Cycle ( 3. Electron Transport Chain ( ) ) Mitochondrion ) Mitochondrion Electrons carried in NADH Electrons carried in NADH Electrons carried Pyruvic acid Pyruvic acid Electrons carried NADH inin NADH and and FADH 2 FADH2 Glucose Glucose Glycolysi s Glycolysis Electron Transport Chain Krebs Cycle Electron Transport Chain Krebs Cycle Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Cytoplasm Net vs. Gross •Gross –Ex: Made $20.00 babysitting •Net –Ex: Made $15.00 babysitting •$5.00 for gas to get to babysitting job •$20.00 babysitting made •$20.00 - $5.00 = $15.00 net Glycolysis –6 carbon molecule (glucose) to two 3-carbon molecules (pyruvic acid) •Does not require oxygen •2 ATP molecules must be added to get the reaction started •4 ATP molecules are produced (4 – 2 = net gain of 2 ATP) •2 NADH molecules are also created –NADH •Electron carrier = NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) •NAD+ + H+ + 2 high energy electrons NADH •Takes electrons to other parts of respiration •Glycolysis nets Glycolysis: Advantages vs. Disadvantages Advantages • – Can produce 1000s of ATP in a few milliseconds • – Can occur w/o oxygen Disadvantages • • – Can’t make more ATP Anaerobic Respiration = Fermentation • •NADH from glycolysis used, turned back into NAD+ –Goes back to glycolysis –Keeps glycolysis going –Generate as many ATP as possible an = “ aerobic = “ ” ” Alcoholic Fermentation • –Carried out by yeasts and a few other micoorganisms • pyruvic acid + NADH → alcohol + CO2 + NAD+ • Lactic Acid Fermentation • • pyruvic acid + NADH → lactic acid + NAD+ • –Lactic acid buildup in muscles causes painful, burning sensation = why muscles feel sore • –Used to make cheese, yogurt, buttermilk, sour cream, pickles, sauerkraut, and kimchi. Review Questions •1. What is cellular respiration? What is the equation for it? •2. What are the 3 stages of cellular respiration in order? •3. What is glycolysis and where does it take place in a cell? What are the products of glycolysis? •4. What are the advantages and disadvantages of glycolysis? •5. What is anaerobic respiration and what is its purpose? •6. Compare and contrast alcoholic fermentation with lactic acid fermentation.