Answer Key
advertisement

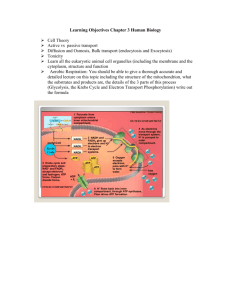
WHAT SHOULD I KNOW ABOUT RESPIRATION Be able to label parts in a mitochondrion and tell where the different reactions happen. What is a calorie? Amount of energy needed to raise temperature 1 gram of water 1 degree C What is a Calorie? 1000 calories/unit found on food labels How are these related? 1 Calorie = 1000 calories What is the chemical formula for cellular respiration? C6H12O6+6O26H2O+6CO2+energy(ATP) How does this equation compare to the equation for photosynthesis? It is the reverse of the photosynthesis equation. Be able to what is needed for each of the following as well as what each produces: Glycolysis- Glucose+2ATP4ATP+2NADH+2 pyruvic acid alcoholic fermentation-pyruvic acid+NADHalcohol+CO2+NAD+ lactic acid fermentation- pyruvic acid+NADHlactic acid+NAD+ Krebs cycle- 2 pyruvic acid 6CO2+ FADH2+2 ATP+ NADH Electron transport chain- NADH + FADH2 ATP (Net 32) Be able to identify the pathways that each of the following is found in: (glucose, pyruvic acid, Coenzyme A, acetyl-CoA, citric acid, FAD, NAD+, NADH, CO2, FADH2, citric acid, ATP, ATP synthase) Glycolysis- glucose, pyruvic acid, NAD+, NADH, ATP Alcohol fermentation – pyruvic acid, NADH, NAD+,C02 Lactic acid fermentation - pyruvic acid, NADH, NAD+ Krebs Cycle - pyruvic acid, Coenzyme A, acetyl-CoA, citric acid, FAD, NAD+, NADH, CO2, FADH2, citric acid, ATP ETC - ATP, ATP synthase, FAD, NAD+, NADH, FADH2 If given a diagram of a pathway, you should be able to fill in reactants and products and tell where does it go next? See above info, already written out. Be able to tell which stages require oxygen and which DON’T. Oxygen – Kreb’s and ETC No oxygen – glycolysis, alcoholic and lactic acid fermetation Which molecule forms when glucose is broken in half? Pyruvic acid What is the other name for Krebs cycle? Citric acid cycle What happens to CO2, produced during the Krebs cycle? Goes into the atmosphere What is the final electron acceptor at the end of Electron Transport? oxygen What happens to the NADH’s produced during glycolysis and Krebs cycle? If oxygen is present, goes to ETC. No oxygen onto fermentation. What high energy electron carriers are used in respiration? NAD+ and FAD How are these different from the carrier you learned about for photosynthesis? No phosphate How many ATP’s and CO2, molecules are produced in each stage? ATP CO2 Glycolysis 2 net --Lactic acid Ferm. ----Alcoholic Ferm. --2 Kreb’s Cycle 2 6 ETC 32 --What happens to the carbons in glucose as they pass through cellular respiration? Become CO2 released into atmosphere What does anaerobic mean? Without oxygen What does aerobic mean? With oxygen What needs to be added to make glycolysis happen? ATP, glucose What happens to pyruvic acid if there is no oxygen? Fermentation What are the two kinds of fermentation? Alcoholic and lactic acid Be able to give the equations for the two kinds of fermentation? pyruvic acid+NADHalcohol+CO2+NAD+ Be able to give examples where each of these is used. Alcohol – beer, wine, bread Lactic acid – muscles, kimchi, saurerkraut What molecule is burned to provide quick energy during exercise? ATP Why do cells use fermentation? (Hint: It’s NOT to make alcohol or lactic acid) To produce produce NAD+ for glycolysis to continue and that produces ATP Explain what happens during Electron Transport Chain? NADPH and FADH2 are used to produce ATP Which ion ends up in the intermembrane space during Electron Transport? H+ How does ATP synthase work to make ATP? It spins like a turbine when H+ ions travel through it and that energy is trapped in a bound that adds a phosphate to ADP making it ATP What is creatine and what does it do? natural substance found in muscles that regenerates ATP for extended energy for muscle activity which is used as a dietary supplement to increase muscle strength and performance