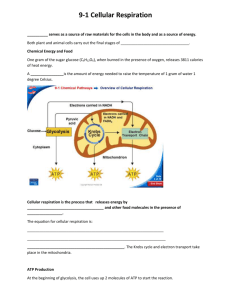
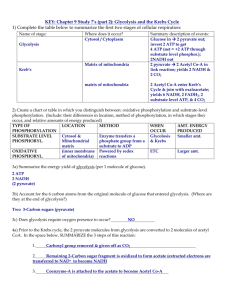
Power Point (ETC, Chemiosmosis, Animations)
advertisement

Anaerobic Respiration - “anaerobic” = without oxygen a way to obtain energy from nutrients without oxygen this is done by repeating glycolysis and continuously making 2 net ATP (much less than aerobic respiration which makes 36 net ATP) During glycolysis… GLUCOSE 2 NAD+ 2 NADH 2 ADPto 2 ATP - the cell does not directly require O2 for glycolysis, - however, NAD+, needs to be regenerated for glycolysis to continue. - NADH is turned back into NAD+ when NADH gives its electrons to the glycerol-phosphate shuttle to make FADH2 in the matrix PYRUVATE - - O2 is the final electron acceptor of the electron transport chain. It accepts electrons to make H2O If there is no O2 then, the ETC will become clogged with electrons because there won’t be a molecule to accept the electrons As a result, the ETC will not be free to oxidize the coenzymes NADH and FADH2 o Thus protons will not be pumped into the innermembrane space and thus a proton motive force will not be created to produce ATP o and FAD will not be regenerated to pick up the electrons from the NADH made in glycolysis o as a result, the NADH in the cytoplasm will not be turned back into NAD+, and so glycolysis won’t continue. Organisms have evolved a way of recycling NAD+ and continuing glycolysis without O2 Electrons of NADH will be transferred to organic molecules instead of the ETC. The process is called FERMENTATION o 1. ethanol formation o 2. lactic acid formation 1) Ethanol Fermentation - NADH transfers hydrogen atoms to acetaldehyde Acetaldehyde is converted into ethanol and in the process NADH is oxidized to NAD+ so glycolysis can continue In this way, 2 ATP is continuously made to meet energy needs Ethanol fermentation is carried out by yeast Used to make breads, pastries, wine, beer, liquor, soy sauce…. - Ex: Bread o Live yeast cell mixed with starches (in flour) o Yeast ferments glucose in starch to make CO2 and ethanol o The CO2 make the bread rise o The ethanol evaporates when bread is baked - Ex: beer, wine making o Yeast ferments sugars in fruit juices o Fermentation ends when ethanol concentration is ~12% because this concentration will kill the yeast cells. 2.) Lactic Acid Fermentation x - during strenuous exercise, breakdown glucose faster than O2 can be supplied lactate fermentation takes over NADH gives its electrons to pyruvate to make lactate (lactic acid) Accumulation of lactic acid in muscles cause stiffness, soreness, and fatigue. When exercise stops, lactate is converted back to pyruvate for aerobic respiration.