File
advertisement

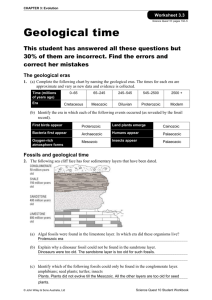
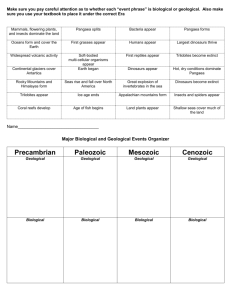
Geological Time Scales: Evidence For Evolution NAME: SOLUTION From your studies in ‘Are We Alone’ you should have learned that many scientists believe life could exist on other planets in the universe and that scientists have proposed a theory of how the universe began, known as the 'Big Bang Theory'. But how did life start on Earth and how do scientists explain the changes in life forms that have occupied our planet over time? Life on Earth The scientific community is divided on the question of how exactly life began on Earth. Two main theories are: 1. The basic chemical building blocks to make a living cell were present on Earth. An energy source (eg a lightning strike) may have provided the stimulus to convert these chemicals into amino acids, the chemicals needed to make proteins for living systems. 2. Life originated from elsewhere in space, and the chemicals needed to produce primitive living cells travelled to Earth on comets or meteors. Neither theory has enough evidence at present for the scientific community to give a definitive, accepted answer to this question. How life has changed on Earth Even though science has not fully explained the origin of the first living cell on earth, more scientific evidence is present to explain how primitive life changed (or evolved) into complex living systems we see on earth today. As this change from primitive to complex organisms is often a very slow process, geological timescales and the age of the Earth (around 4.6 billion years old) provides support for Darwin’s theory of change via the process of natural selection. Geological Time Scale Geologists (scientists studying changes on Earth) and palaeontologists (who study fossils) have developed a geological time scale, dividing the time they believe the earth has existed into periods. Each period has special fossils associated with it. For example, main types of fossils found from the Permian period are different to those found in the Triassic period. The end of most periods is marked by a large number of extinctions. The most famous of these is the extinction of many plants and animals, including dinosaurs, at the end of the Cretaceous Period. All of the periods have been dated by a process carried out on fossils called radioactive dating. Watch the BRAINPOP "Geologic Time" For You To Do 1. The table below shows the time-line of the Earth if it has been condensed into one hour. On the clock face below, label these events on it. Forests of ferns and conifers cover First mammals appear on Earth the land First flowers seen on Earth First reptiles walk on land First insects fly over Earth Extinction of dinosaurs First plants grow on land First humans First fish appear as fossils Animals with hard shells common Multicellular soft-bodied animals abundant Single celled microscopic life exists Single celled life abundant, oxygen in atmosphere 2. The diagram below is a geological time scale. Answer the questions which follow it. Geological Time Scale: The Earth’s Eons, Eras and Periods TRIASSIC millions of years ago (a) Rank these time intervals from longest to shortest: era, period and eon. Eon (longest as many eras), era (many periods) and then period (shortest) (b) How many years did the Devonian period last for? 48 million years (as it began 408 mya and finished 360 mya). (c) What was the shortest period? Quaternary (d) (e) Which period could be referred to as the: (i) age of fish? Devonian (ii) age of reptiles? (iii) age of gymnosperms? Triassic Rank in order of appearance in the geological record: (i) angiosperms, ferns, algae, gymnosperms 1. algae 2. ferns 3. gymnosperms (ii) (f) Jurassic 4. angiosperms fish, reptiles, birds, mammals, amphibians 1. fish 2. amphibians 3. reptiles 4. mammals and birds (close but mammals first) On a separate sheet of paper, draw a time line below, 1 m long, with the scale 10 cm = 500 million years. Mark on the line the start of each period (a geological time scale is found on the following page). What main feature do you observe from the timeline?