Main Ideas - TeacherWeb
advertisement
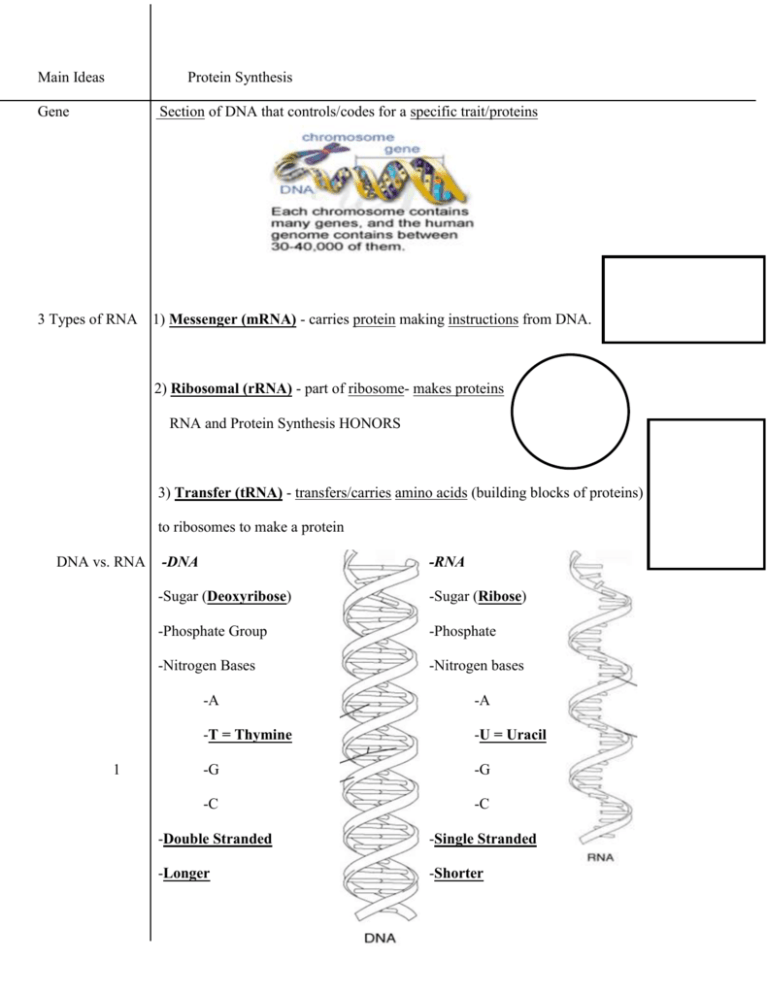
Main Ideas Protein Synthesis Gene Section of DNA that controls/codes for a specific trait/proteins 3 Types of RNA 1) Messenger (mRNA) - carries protein making instructions from DNA. 2) Ribosomal (rRNA) - part of ribosome- makes proteins RNA and Protein Synthesis HONORS 3) Transfer (tRNA) - transfers/carries amino acids (building blocks of proteins) to ribosomes to make a protein DNA vs. RNA 1 -DNA -RNA -Sugar (Deoxyribose) -Sugar (Ribose) -Phosphate Group -Phosphate -Nitrogen Bases -Nitrogen bases -A -A -T = Thymine -U = Uracil -G -G -C -C -Double Stranded -Single Stranded -Longer -Shorter Main Ideas Protein Synthesis Protein Synthesis Overview 2 main processes: 1) Transcription- DNA copied into RNA (in nucleus) 2) Translation- RNA made into proteins (in cytoplasm) Transcription DNA to RNA 1) DNA unzipped by RNA polymerase at a gene promoter begins copying 2) 1 strand of DNA template is transcribed (copied) into RNA using complimentary bases. 3) RNA polymerase reaches “termination signal”/ end of gene, stops copying Inside cell Codon 3 consecutive nucleotides (bases) on mRNA that code for/specify 1 particular amino acid Main Ideas Protein Synthesis (continued) Flow of Genetic Info DNA RNA Protein (Central Dogma) Transcription Translation Translation Decode mRNA to Proteins Steps: 1) ________ strand broken into codons 2) ___________ reads codons and ___________ them into amino acids 3) __________ calls for ________ to bring correct ____________ 4) ______ _________ match up with _______ _________ 5) Amino acids are ________________________________ until a ______ codon is reached 6) _________________- ribosome complex falls apart. ____________________________________ On the picture AT RIGHT, label ALL of the following for FULL credit: 1.) mRNA, 2.) rRNA, 3.) tRNA, 4.) the first 5 codons 5.) anti-codon, 6.) amino acid, 7.) nucleus 8.) Promoter codon 9.) Termination/stop codon 10.)Growing protein Using the genetic code chart to the right complete the following: 1. Transcribe (from DNA to RNA) the following DNA sequence. Then, Translate it to an amino acid chain. DNA-ATCGCCATA mRNAAmino Acids2. Transcribe AND translate the following DNA sequence: DNA- ATCGCCATAGCG mRNAAmino Acids3. Transcribe and translate the following DNA sequence: DNA-ATCGCCATAGCGCGA mRNAAmino Acids- Main Ideas Protein Path Path of Proteins 1) ________________ DNA copied to mRNA 2) _________________ Synthesize proteins and send to Golgi. 3) ____________________Modifies, packages, sorts, ships proteins in/out of cell. 4) ________________ carries proteins from Golgi (in vesicles) to be released from cell.








