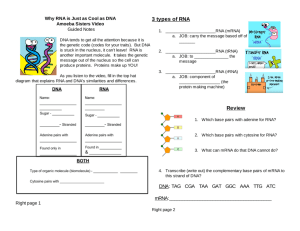
Name: Period: ______ Date: Page #: __15__ Protein Synthesis
advertisement
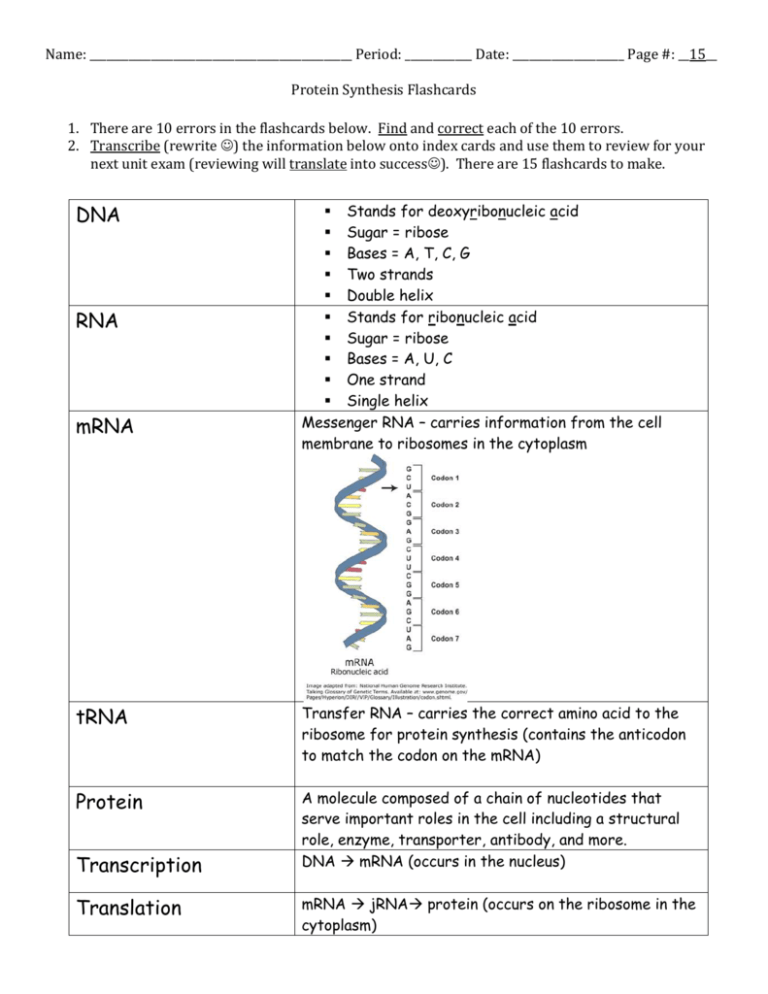
Name: _______________________________________________ Period: ____________ Date: ____________________ Page #: __15__ Protein Synthesis Flashcards 1. There are 10 errors in the flashcards below. Find and correct each of the 10 errors. 2. Transcribe (rewrite ) the information below onto index cards and use them to review for your next unit exam (reviewing will translate into success). There are 15 flashcards to make. DNA RNA mRNA Stands for deoxyribonucleic acid Sugar = ribose Bases = A, T, C, G Two strands Double helix Stands for ribonucleic acid Sugar = ribose Bases = A, U, C One strand Single helix Messenger RNA – carries information from the cell membrane to ribosomes in the cytoplasm tRNA Transfer RNA – carries the correct amino acid to the ribosome for protein synthesis (contains the anticodon to match the codon on the mRNA) Protein A molecule composed of a chain of nucleotides that serve important roles in the cell including a structural role, enzyme, transporter, antibody, and more. DNA mRNA (occurs in the nucleus) Transcription Translation mRNA jRNA protein (occurs on the ribosome in the cytoplasm) Base Pairing Rules (DNA) Base Pairing Rules (when transcribing RNA) Replication A pairs with C C pairs with G Central Dogma of Biology Nucleotide RNA RNA Protein Amino Acid The building block of protein that is coded for by an mRNA anticodon. There are 20 amino acids involved in protein synthesis. Term used to describe DNA replication. Means that each new molecule of DNA is half old and half old DNA. A special group of chemicals involved in the passing of inherited information. Controls all the activity in the cell. Semi-conservative Nucleic Acid A pairs with U T pairs with A C pairs with G G pairs with C 1 DNA strand 2 RNA strands (creates an exact copy of DNA for when a cell divides) Sugar, Phosphate, Base