Interpreting synoptic charts
advertisement

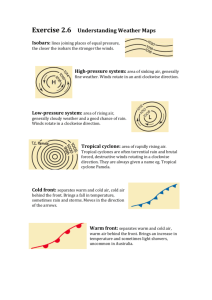
SEE, THINK, WONDER: SEE: I can see an outline of Australia. THINK: I think it is a weather map. WONDER: I wonder what the lines mean. I wonder what the triangles mean. How is atmospheric air pressure measured? With a mercurial barometer. What is an isobar? Are lines joining places of equal pressure. What is an anticyclone? High pressure system. What is a cyclone? Low pressure system. If Australia had a northerly wind, how would the temperature change? A northerly wind would mean an increase in temperature. If Australia had an easterly wind, how would the temperature change? Easterly winds would mean normal temperature, therefore no temperature change. Complete the following chart Symbol Name Low pressure system Description Area of rising air. Cold Front Separate warm and cold air, with the cold air behind the front. High pressure Area of sinking air. Isobars Lines joining places of equal pressure. Generally fine weather. Winds rotate around these systems in an anti-clockwise direction. Fall in temperature, may bring rain and storms. Front moves in the direction of the arrowheads. Generally fine weather. Winds rotate around these systems in a clockwise direction. The closer the isobars are, the stronger the winds. Warm Front Separate warm and cold air, with the warm air behind the front. Tropical cyclone Area of rapidly rising air. Increase in temperature may bring light showers. Uncommon in Australia. Torrential rain, very strong and destructive winds in a clockwise direction. 1. What is another name for a weather map? Synoptic charts 2. List three differences between a low and a high pressure system. 1. Clockwise wind (rising) 2. Anti-clockwise (sinking) 3. Different types of weather 3. What does a weather map indicate when: (a) isobars are close together? Strong wind (b) isobars are well apart? Isobars close together represent winds. The closer the isobars are the stronger the wind. 4. What do we call the lines that are drawn on weather maps to separate different air masses? Isobars 5. Observe the weather map below. (a) Estimate the wind direction in Adelaide. Is it windy or calm? High pressure system over Adelaide, winds are calm in an anti-clockwise direction. (b) Identify the pressure systems at A, B and C. A) High pressure B) Low pressure system C) Low pressure system (c) Identify the types of fronts at D and E. (D) warm front (E) Cold front Observe the above map: 1. What is developing on the west coast of Australia? A cold front. 2. What period is this map looking at? 13th of August 2013 at 10am Eastern standard time for Australia. 3. What other observations can you make from looking at the map? Currently over the middle of Australia there is a high pressure system, which will be followed by a low pressure cold front. Notes from Video on Interpreting Synoptic Charts Didn’t watch in class Create a poster or PowerPoint presentation about Australia’s Natural Resources and World Heritage sites. Search for information in your library. Put together a presentation and post to your blog. Key questions you might like to consider: - What are Australia’s natural resources? - Why are these resources important? - Statistics and facts that show the uniqueness of Australia - Where are our world heritage sites located? - Why are they listed at world heritage? What makes them unique? Significant - Collect images that show various world heritage sites/ natural resources in Australia. Done a poster on another document Homework: Read the information on page 38-39 of your textbook. Define the following: Species: Marsupials: A mammal of an order (Marsupialia) whose members are born incompletely developed and are typically carried and suckled in a pouch. Monotremes: Are unique in being the only mammals that lay eggs. Endemic: Is a plant. Australia has incredible variety in its flora and fauna. 80% of Australian flora and fauna is found no where else in the world. How many species do we have living in Australia? Australia has more than 378 mammal species, 828 bird species, 4000 fish species, 300 species of lizards, 140 snake species, 2 crocodile species and around 50 types of marine mammal. How does that compare to North America and Europe? Australia has more deadly snakes than any other country worldwide and many deadly animals as well. The estimated number of native and introduced species living in Australia about 1 million twice the number of species in the North America and Europe combined. What is unique about much of Australia’s flora and fauna? More than 80% of our plants, mammals, reptiles and frogs are unique to Australia. What type of trees dominate the forest? Eucalypts trees are still the main type and also wattle trees. Name the marsupial on the right: Bilby Most of Australia’s native animals are Placentals which means the young remain in the womb much longer and they don’t have pouches.