File - Chris Van Bibber
advertisement

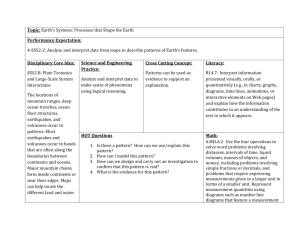
Earthquakes 1. Southern Greece Magnitude: 4.6 Date: March 20th 2012 Time: 1:51am Depth: 60.80 km Tectonic Plate Boundary: Oceanic - Continental 2. Oaxaca, Mexico Magnitude: 7.4 Date: March 20th 2012 Time: 12:02 pm Depth: 20.0 km Tectonic Plate Boundary: Oceanic-Continental 3. Alaska, Peninsula Magnitude: 4.6 Date: March 18th 2012 Time: 2:37am Depth: 54.70 Tectonic Plate Boundary: Oceanic - Oceanic 4. Minahasa, Sulawesi, Indonesia Magnitude: 5.0 Date: March 19th 2012 Time 1:04am Depth: 34.90 Tectonic Plate Boundary: Oceanic - Continental 5. Antofagasta, Chile Magnitude: 4.9 Date: March 19th 2012 Time: March 19th 2012 Depth: 72.80 Tectonic Plate Boundary: Oceanic - Continental Volcanoes 1. Kilauea Volcano Type: Shield Volcano Tectonic Plate Boundary: Divergent Status: Glow was visible, minor lava flow, not actively flowing above surface. 2. Cleveland Volcano Type: Composite Tectonic Plate Boundary: Convergent Status: Heightened unrest with increased potential of eruption. Minor ash emissions. 3. Michoacan Guanajuato Volcano Type: Cinder Cone Tectonic Plate Boundary: Divergent 4. Galapagos Hot Spot Type: Hot Spot Tectonig Plate Boundary: Divergent Assignment Reflection Describe the correlation is between earthquakes and volcanoes in terms of the Theory of Plate Tectonics. From the USGS article “Plate Tectonics and People,” it states that most earthquakes and volcanic eruptions do not strike randomly but occur in specific areas, such as along plate boundaries. Throughout this assignment, it has been obvious that certain natural disasters occur in very specific areas. Most earthquakes and volcanoes are associated with areas where plate tectonic boundaries have seismic activity occurring. Earthquakes occur along the plate boundaries as the plates move parallel to other plates. As these plates descend into the earth they grind and produce earthquakes which cause the hot liquid in the earth, magma to emerge upward through volcanoes and vents. Volcanoes generally occur at areas of subduction, where one plate is sinking below another. Analyze the spatial relationship that exists with these forces of nature. Their spatial relationship is because one event leads to another. Magma moving up the cone of a volcano causes earthquakes if it has a high enough viscosity or resistance to the flow. Just like there is a circle of life to the food chain, in a sense, there is a similar cycle with how the earth recycles itself and the continents continue to move and make new. Analyze the spatial distribution that exists with these forces of nature. Both earthquakes and volcanoes happen along tectonic plate boundaries where the conditions are just right and the earth shakes and causes earthquakes to shake the earth and volcanoes to form. Where ever the plates meet, is where the volcanoes tend to form due to the subduction of the plates causing magma to be produced, which in turn brings volcanoes into the equation. Describe what you learned about earthquakes and volcanoes that you did not know before this course There is so much more to what brings an earthquake or a volcano to the point of activity. As plate tectonics continuously shift and move they cause effects all along the way. Not only do these effects include earthquakes which can cause mass destruction on the upper mantle of the earth’s crust but they are what form the mountains and the earth as we know it. Volcanoes, in all their majesty, have always fascinated me. However, I’ve never considered all that goes into their creation. While plate tectonics play a leading role in their activity, I have been very interested as I have learned the different types of volcanoes. From Cinder cones to Shield volcanoes, there are so many different types and that has been exciting to learn about.