NTWS Geological Processes
advertisement

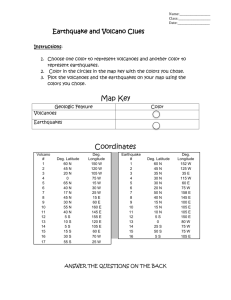
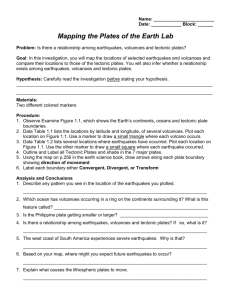
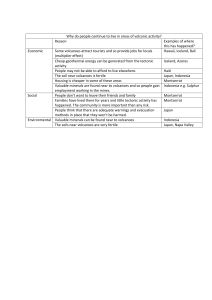
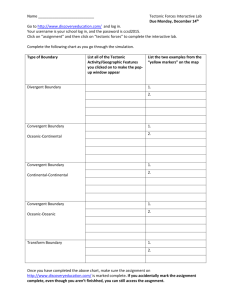
AP Environmental Science: Geological Process 1. What influence does Earth’s hot interior have on the Planet? 2. Because Earth’s crust can bend and break, what structures form? 3. Why are volcanoes important in their influence on the biosphere? 4. What is the Moho, and how do we know where it is? 5. What causes the tectonic plates to move? 6. What are the evolutionary consequences of tectonic movement? 7. What area is ultimately responsible for the convection currents within the mantle? 8. What is the significance of the different spin velocities (speed and directions) within the Earth’s core? 9. What is created that helps protect Earth from solar debris? 10. What is a geologic hot spot (not to be confused with an ecological hot spot)? 11. Where is the “Ring of Fire”, and why is it geologically significant? 12. A tectonic boundary that moves together, or is destructive, is known as what? 13. What forms when convergent boundaries exist between • Oceans and Continents? • Two continents? • Two oceanic plates? 14. A tectonic boundary that moves apart, or is constructive is known as…? 15. What forms along divergent plate boundaries? When they occur in the ocean? When they occur on continents? 16. While earthquakes can occur along any type of tectonic boundary, they are most common along… 17. What forms many times when earthquakes occur near to, or beneath the ocean? 18. What is the greatest risk in an earthquake? 19. How do we detect tsunamis? 20. Why are converging subduction zones most often associated with volcanoes? 21. What two features of most volcanic eruptions put people most at risk? 22. How are hot spot volcanoes different from simple convergent/subduction-caused volcanoes? 23. Give two examples of hot-spot volcanoes.