Social 11/21: Population and Wealth
advertisement

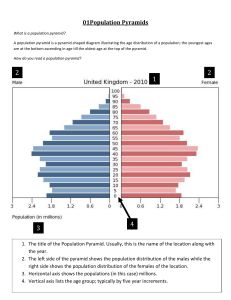
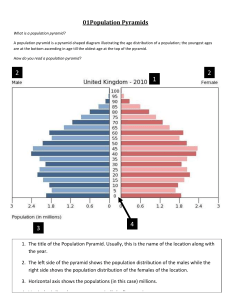
Social 11/21/31: Wealth, Economies, and Population Economy Definitions • Wealth: All the goods and services (including knowledge) that are produced and distributed within society. • Resources: Those things which are used to produce goods and services (wealth) individuals within a society need or want. • Scarcity: The relationship that occurs when needs and wants exceed the limited resources available to meet those wants. • Cost: The value of all the other things we have to give up in order to get that desired thing. • Standard of Living: The measure of the quantity and quality of goods and services available to people as well as leisure, surroundings, recreation, meaning, and purpose in life. – The perception of standard of living depends upon people’s expectations. – There is a constant debate about what criteria is used to define an acceptable standard of living. • Factors of Production: Land, labour, capital, and entrepreneurship are used in various combinations to produce goods and services. – Land is the raw materials in their natural state which are used in the production of goods and services. – Labour is the work done by people in the production of goods and services. – Capital are all the goods (tools, machinery, factories, etc) used to produce other goods. – Entrepreneurship is the organization necessary to bring all the resources together so that the production of goods and services can occur. Population Definitions • Natural Increase: The difference between the numbers of births and deaths in that population. • Birth Rate: The annual number of live births per 1000 population per year. • Death Rate: The annual number of people dying per 1000 population per year. It is determined by: – The level of nutrition available to a population, – The levels of sanitation, and – The ability to treat and control disease. • Fertility Rate: The number of births per 1000 women in their childbearing years (the ages of 15 and 44). • Population Change: Can occur in short periods of time and makes it difficult for governments to meet the changing needs of the population. • Carrying Capacity: A country’s ability to provide resources for human needs on a long term basis without being harmed. • Urbanization: The increase in population in cities. Urban populations have tripled in the past 35 years. Population Pyramids • A population pyramid is a graph that shows the spread of various age groups in a population, which forms the shape of a pyramid when the population is growing. • It consists of two bar graphs, with the population plotted on the X-axis and age on the Y-axis. One bar graph shows the number of males and the other shows the number females in a particular population. Males are shown on the left and females on the right. • Population pyramids are often the most effective way to graphically depict the age and sex of a population. • A great deal of information about the population broken down by age and sex can be read from a population pyramid, and this can determine how developed a country is. • A population pyramid also tells how many people of each age range live in the area. There tends to be more females than males in the older age groups, due to females' longer life expectancy. Types of Population Pyramids • Look at the population pyramid from Afghanistan in 2005. What can we tell about Afghanistan’s population? • Look at the population pyramid from China in 2005. When did they have a population boom? Your Assignment • Look at the Census data from 2006 and make a population pyramid for Canada. • Use your chart to answer the questions about Canada’s population.