EARTH SCIENCE Unit 5 Study Guide KEY
advertisement

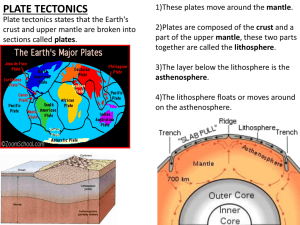
EARTH SCIENCE Unit 5 Study Guide Use this Study Guide to direct your study. Also study your Unit 5 Stapled Packet which should include your notes, practice sheets, and diagrams. Plate Tectonics 1. What causes tectonic plates to move? Convection currents in the mantle layer of the Earth 2. What features are associated with tectonic plate movement? Mountain ranges, earthquakes, increased volcanic activity 3. What does reversal of the Earth’s magnetic poles indicate to plate tectonic scientists? The Earth’s magnetic poles have exchanged position from time to time in the past, which is evidence that supports Plate Tectonics 4. What would be the age of rocks that are 20 km west of the mid-ocean ridge? Use the key given. Normal – The magnetic minerals in these rocks indicate magnetic North as it is today. Reverse – The magnetic minerals in these rocks indicate magnetic North where magnetic South is today 5. Why do volcanoes and ridges form at points where seafloor spreading occurs? As plates pull apart (separates), magma moves to the surface to fill the space. When this happens ridges form. 6. When plates are moving past each other in opposite directions, what kind of boundary is it? Transform 7. Compare & contrast oceanic and continental crust: Oceanic crust is thinner and denser, made of basaltic rock Continental crust is thicker and less dense, made of granitic rock. 8. Compare & contrast convergent and divergent boundaries: Convergent boundaries -- collision (con-con) and subduction (oc-oc, oc-con) zones with volcanoes & thrust block fault mountains. Divergent boundaries -- spreading fault (seafloor spreading) or continental rift valley with mid-ocean ridges & fissure volcanoes (in space left by moving plates) 9. Why did the scientific community not support Alfred Wegener’s Continental Drift theory for a long time? Because he didn’t know about the underlying mechanism of Plate Tectonics, which supports it. 10. At a continental-ocean boundary, what usually forms? A subduction zone 11. What do colliding continental-continental tectonic plates create? Mountains composed of deformed sedimentary layers which are still increasing in elevation (Himalayas) 12. Why does seafloor spreading occur? Because molten rock in the mantle rises to the surface due to convection currents 13. What is the best supporting evidence for Pangaea and Continental Drift? Identical rock types, identical fossils, similar mountain ranges – all found on different continents currently located far away from each other. 14. Make a quick drawing of the three kinds of boundaries using boxes and arrows, labeling plate & asthenosphere, and typical features. Volcanoes 15. How were the Cascade Mountains in the American Northwest formed? Volcanism, Mt Saint Helens 1980 is most recent 16. How is tephra sized, from smallest to largest? Ash, cinders, bombs, blocks 17. Where is the Ring of Fire located? Why is it there? Pacific Plate; convergent boundaries with volcanoes and earthquakes 18. Compare and contrast types of volcanoes: Shield – broad, gentle slopes with quiet eruptions, basaltic lava Composite – broad base, tall & steep slopes with alternating quiet/explosive eruptions, andesitic lava Cinder Cone—tall, steep slopes with explosive eruptions, granitic lava 19. What lava is most fluid? Basaltic, because it is low silica (silica flows very slowly) 20. When looking at the Hawaiian Islands, which one is the oldest one? Why? The furthest one away from the current active one which sits on the hot spot. The plate is moving past the hot spot, making new islands as it goes. Earthquakes 21. Draw a picture of each of the kinds of faults and stresses: 22. When comparing seismic stations, which would receive P and S waves the fastest? The closest one 23. What is the point where an earthquake originates called? Focus 24. Looking at these seismograms, which one best represents the true scenario? 25. What are the different arrival times for each of these cities? Previous Material 26. How can a river in Pennsylvania affect the water quality in Virginia? Because the delta (mouth of the river) is located in Virginia at the Chesapeake Bay 27. What are the correct coordinates for these 6 points? 28. What are the coordinates for Richmond, Virginia? 39 degrees N, 76 degrees W 29. What is Karst Topography characterized by? Limestone caves 30. Which cities are in the Chesapeake watershed?