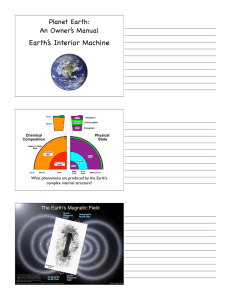
Earth’s Interior Machine Magnetic Field and Plate Tectonics Earth’s magnetic field
advertisement

Earth’s Interior Machine Magnetic Field and Plate Tectonics What phenomena are produced by the Earth’s complex internal structure? Earth’s magnetic field •Generated by movement of currents in liquid outer core around solid inner core. •Shields the Earth from the solar wind •Prevents the atmosphere from being slowly stripped away by the solar wind. •Causes the aurora borealis and aurora australis. magnetic force lines around a bar magnet • • • • Aurora Borealis (Australis) Northern (Southern) Lights Caused by solar wind particles trapped in the lines of Earth’s magnetic field. Charges particles flow downward toward the poles, collide with gases in the atmosphere. Ionized gas glows red, green, and blue. Pattern of aurora activity around the north pole. Questions for Discussion What is the Solar Wind? Why is it a potential problem? What causes the aurora borealis / australis What will happen to the Earth’s magnetic field when the core freezes? What will happen to the Earth’s atmosphere after the core freezes? Planetary Atmospheres • 96% CO2 3% N2 • • Sulfuric Acid • trace H2O • 90 atm at surface 78% N2 • 21% O2 • H2O • • < 1% CO2, CH4 • 1 atm at surface • • • • 95% CO2 4% N2 .13 % O2 .01 atm at surface Question for Discussion - all groups Mars is a smaller planet than Earth. Mars has no magnetic field. Based on these observations, construct a hypothesis to explain the extremely thin atmosphere on Mars. What observations could be collected to test your hypothesis? What phenomena result from the peculiar structure of the Earth? Plate Tectonics • Movement and recycling of the Earth’s oceanic lithosphere. • Production of continental crust. • “Continental Drift” • Plate collisions and mountain building • Volcanism and Earthquakes Mafic (Ma / Fe) Plate Sialic (Si / Al) Rock in the Earth’s mantle flows via convection, driven upward by the flow of interior heat and pulled downward by gravity. shield volcanoes Divergent Plate Boundary stratovolcanoes Convergent Plate Boundary Shield Volcano Basaltic Lava High volume magma eruptions Relative size Stratovolcano Andesitic Lava Explosive ash eruptions Shield Volcano Sierra Negra (Isabela / Galápagos Islands) Eruption on the north rim of the Sierra Negra caldera, October 2005. Video by Karen Harpp, Colgate University photo is courtesy of Aksel Voigt Lava flow on the island of Hawaii Shield Volcano and Aa lava flow Fernandina, Galápagos Physical Geology - Rock Cycle and Isostasy Stratovolcanoes Mt. Saint Helens prior to 1980. Stratovolcanoes Mt. Saint Helens after 1980 eruption. Cotopaxi Stratovolcano Ecuador Volcanic ash and pumice deposit Otavalo, Ecuador Physical Geology - Rock Cycle and Isostasy Questions for Discussion Why are there volcanoes at divergent plate boundaries? Why are there volcanoes at convergent plate boundaries? What might cause shield volcanoes and stratovolcanoes to erupt so differently? Besides rock, what else descends into the mantle when a tectonic plate is subducted? Why is the asthenosphere melting above the subducting ocean plate? Melting of dry mantle rock Partial melting of rock due to mixing with water Silica Density 3.01 2.77 Seafloor What is the origin of oceanic crust? What is the origin of continental crust? 2.69 Continents Why is the elevation of Earth’s surface bimodal, while Mars and Venus are unimodal?