3U SN DNA and Mitosis student note handout0
advertisement

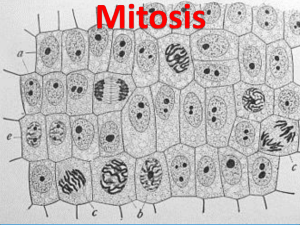
SBI 3U The Structure and Replication of the Genetic Material In sexually reproducing species, offspring obtain a unique combination of genetic information from their parents. How is this different from organisms that reproduce asexually? ______________________________________________________________________________ ______________________________________________________________ The Genetic Material DNA or __________________________________________________ Where is it found? _________________________________________ DNA is organized into ________________________ Genes are units of inherited information that carry a code for __________________________ ____________________________________________________ Many genes code for _____________________ The information contained in genes is responsible for_______________________. Packaging of DNA For much of a cell's life, its DNA exists as a mass of very long, thin fibres called ___________ ,a combination of _______________________________. As a cell is preparing to divide, its chromatin fibres condense, becoming visible compact structures called chromosomes. A ___________________________ consists of one long, condensed DNA molecule containing hundreds or thousands of __________________. The number of chromosomes inside a body cell varies among different species. We call this the __________________________ (or 2n). (Humans 2n = 46, fruit flies 2n =8 etc.) DNA consists of a long chain of subunits called _______________________. A nucleotide has three parts: 1) A ring-shaped sugar called deoxyribose 2) A phosphate group 3) A nitrogenous base (or base): a single or double ring of carbon & nitrogen atoms. There are four types of nucleotides in DNA, which differ only in their nitrogenous bases (thymine (T), adenine (A), cytosine (C) & guanine (G). Scientists discovered that there are bonds between specific base pairs that provide enough force to hold the two strands in the helix together. It is the placement of these bonds that twists DNA into a spiral shape. A pairs with T; C pairs with G. DNA Sequences We use the 26 letters of the alphabet to spell an almost countless number of words. Like letters of the alphabet, nucleotides can combine in various sequences. Since nucleotide chains also vary in length, from a few hundred to millions of nucleotides, the number of possible nucleotide sequences is essentially unlimited. The arrangement of nucleotides in DNA stores information. The genes in this information code for specific cell proteins and functions. The Cell Cycle: Two main stages: 1) Interphase - the growing stage, cell carries out its metabolic processes, performs regular cellular activities - DNA is duplicated, centrioles replicate - the cell spends most of its time (90%) Chromatid - a “chromosome” attached to another “chromosome” by a centromere. 2) Mitotic phase - mitosis (cell division); the nucleus and the duplicated chromosomes divide and are evenly distributed between two "daughter" nuclei - cytokinesis - division of the cytoplasm (usually begins before mitosis is complete) Three Reasons why we need mitosis: 1) ______________________________________________________________ 2) ______________________________________________________________ 3) ______________________________________________________________ The Four Phases of Mitosis: 1) Prophase - the start of mitosis - double chromosomes attached at the centromere become visible under a microscope and can each be called a _______________________ - chromosomes ______________________ (get shorter and thicker) - spindle fibers start to ________________ - spindle fibers: protein structures that __________________ chromosomes during cell division. 2) Metaphase - The double chromosomes are lined up on the _________________ and separate so that one chromatid from each pair goes towards a ___________________________________. - when the chromatids separate they are called __________________________. 3) Anaphase - the chromosomes, assisted by the spindle fibres move towards the _____________. Each pole will get an identical set of chromosomes. 4) Telophase - last stage of mitosis, begins when chromosomes reach the poles. - chromosomes elongate, uncoil and assume the threadlike appearance of ________________. - the spindle _______________________. - nuclear __________________________ form - nucleolus (nucleoli) _______________________ Cytokinesis in Animal Cells: - aka - division of the cytoplasm - the cell membrane pinches together (forms cleavage furrow) starting in late anaphase and ending in telophase Cytokinesis in Plant Cells: - a cell plate forms in the middle of the dividing cell and extends out to connect with the existing cell wall. - cell wall is secreted out from each newly formed cell …the cycle begins again. Work: p.90 #1-4, 6-8 + 10, 11