Chemical Bonding
advertisement

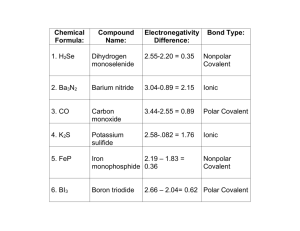
Page |1 Chemical Bonding Q.1. Elements X, Y, Z have atomic numbers 6, 9 and 12 respectively. Which one : i. ii. iii. forms anion – negative ion; forms cation – positive ion; has 4 electrons in the outermost orbit. Ans : i. ii. iii. Y Z X. Q. 2. Name a covalent compound which becomes electrovalent when dissolved in water. Ans : - HCl or NH3. Q. 3. Elements A, B and C have atomic number 9, 20 and 10 respectively. i. ii. State which one is (1) a non-metal; (2) a metal; (3) chemically inert. Write down the formula of the compound formed by two of the above elements. Ans : - (i) (1) A (2) B (3) C (ii) BA2. Q. 4. Draw electron dot diagram to depict the formation of : (i) Magnesium oxide from 24Mg12and 16O8. (ii) a molecule of chlorine from two atoms of 35Cl17. Ans.: .. (i) Mg : + : O : → MgO .. .. .. .. (ii) :Cl . + . Cl : → : Cl : Cl : .. .. .. .. Q. 5. (a) Write down the electronic configuration of the following: (i) 27X13 (ii) 35Y17. (b) Write down the number of electrons in X & neutrons in Y & the formula of the compound formed by X & Y. Ans.: (a) Page |2 (i) Electronic configuration of X = 2, 8, 3. (ii) Electronic configuration of Y = 2, 8, 7. (b) Number of electrons in X = 13; Number of neutrons in Y = 35 – 17 = 18; Formula of the compound is XY3. Q.6. Covalent compounds are usually liquids or gases. Explain. Ans : - In covalent compounds, molecules have weak force of attraction between them and hence exist in liquids or gases state. Q.7. Draw electron diagrams for the formation of : (i) sodium chloride (ii) hydrogen sulphide [ 2311Na; 3517Cl; 11H; 3216S]. Ans :.. .. (i) Na . + . Cl : → Na : Cl : .. .. .. (ii) H * . S . * H .. Q. 8. Show the formation of carbon tetrachloride molecule using an electron “dot and cross” diagram. Ans : .. : Cl : .. ..*.. : Cl . *C* . Cl : . . *. . . : Cl : .. Q. 9. State two differences normally found between the properties of ionic and covalent compounds. Ans : Electrovalent (ionic) compound Covalent compound 1. Exists as hard solid state. e.g. NaCl 1. Exists as soft solid, liquid or gases state. e.g. CCl4 2. It is non-volatile. NaCl 2. It is volatile. CCl4 3. High melting & boiling point. NaCl 3. Low melting & boiling point. CCl4 4. Good conductors of heat. 4. Bad or non-conductors of Page |3 NaCl heat. CCl4 5. Non-conductors of electricity in solid state but good conductors in molten or aq. solution state. NaCl 5. Non-conductors of electricity. CCl4 6. Can be electrolysed in molten or aq. solution state. NaCl 6. Cannot be electrolysed in normal state. Polar covalent compounds undergo electrolysis in solution state. CCl4 .Soluble in water but insoluble in organic solvents. NaCl 7. Soluble in organic solvent (non-polar) but insoluble in water (polar). CCl4 8. Undergo high speed ionic reactions. NaCl 8. Undergo slow speed molecular reactions. CCl4 9. Undergo electrolytic dissociation on passage of electric current. NaCl 9. Undergo ionization in solution state on passage of electric current. CCl4 Q. 10. State two differences between the properties of carbon tetrachloride and sodium chloride. Ans : - Consult answer of question 8. Q. 11. Element X is a metal with a valency 2. Element Y is a non-metal with a valency 3. (i) Write equations to show how X and Y form ions. (ii) If Y is a diatomic gas, write the equation for the direct combination of X and Y to form a compound. (iii) If the compound formed between X and Y is melted and an electric current passed through the molten compound, the element X will be obtained at the………… and Y at the ……….. of the electrolytic cell. (Provide the missing words). Ans : (i) X → X2++ + 2eY + 3e-- → Y3(ii) 3X + Y2→ X3Y2 (iii) Cathode, Anode. Q.12. Compound X consists of molecules. Choose the letter corresponding to the correct answer from the choices A, B, C and D given below : (i) The type of bonding in X will be : (a) Ionic (b) Electrovalent (c) Covalent (d) Molecular. (ii) X is likely to have a : (a) low melting point and high boiling point (b) High melting point and low boiling point (c) low melting point and low boiling point (d) high melting point and high boiling point. (iii) In the liquid state, X will Page |4 (a) become ionic (b) be an electrolyte (c) conduct electricity (d) not conduct electricity. Ans : - (i) (C) (ii) (C) (iii) (D) Q.13. Electrons are getting added to an element Y. (i) Is Y getting oxidized or reduced? (ii) What charge will Y have after the addition of electros? (iii) Which electrode will Y migrate to during the process of electrolysis? Ans : - (i) reduced (ii) negative (iii) anode. Q.14. i. ii. iii. iv. Acids dissolve in water and produce positively charged ion. Draw the structur of these positive ions. Explain why carbon tetrachloride does not dissolve in water? Elements Q and S react together to form an ionic compound. Under normal conditions which physical state will the compound QS exist in? Can Q and S both be metals? Ans : - (i) ..+ !H–O–H! ! ↓ ! ! H ! (ii) Carbon tetrachloride is a non-polar covalent compound and does not dissolve in polar solvents water. (iii) Solid (iv) No, because for the formation of ionic compound, one element should be metal and the other metal. like non- Q. 15. (i) What is lone pair of electrons? (ii) Draw an electron dot diagram of a hydronium ion and label the lone pair of electrons. (iii) Name a neutral covalent molecule which contains one lone pair electrons. Ans : - (i) Lone pair of electrons is a pair of electrons present on an atom in a molecule which does not take part in bond formation : . . → Lone pair of electrons H:N:H .. H (ii) Lone pair of electrons → . . + H:O:H .. H (iii) Ammonia, . . → Lone pair of electrons H:N:H .. H Q.16. (i) Name the charged particles which attract one another to form electrovalent compounds. (ii) In the formation of electrovalent compounds, electrons are transferred from one element to Page |5 another. How are electrons involved in the formation of a covalent compound? (iii) The electronic configuration of nitrogen is 2, 5. How many electrons in the outer shell of a nitrogen atom are not involved in the formation of nitrogen molecule? (iv) In the formation of magnesium chloride (by direct combination between magnesium and chlorine), name the substance that is reduced. Ans : - (i) Cation and anion (ii) There is a mutual sharing of electrons (iii) Two (iv) Magnesium is oxidized and chlorine is reduced. Q. 17. Which of the following is not a common characteristic of an electrovalent compound. A : High melting point B : Conducts electricity when molten C : Consists of oppositely charged ions. D : Ionizes when dissolved in water. Ans : - C. Q.18. Why is carbon tetrachloride which is a liquid – a non-electrolyte. Ans : - As CCl4 has not free ions and hence are non-conductors. Hence it a non-electrolyte. Q.19. What are the terms defined in each case : (i) A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons, each bonding atom contributing one electron to the pair. (ii) A bond formed by a shared pair of electrons with both electrons coming from the same atom. Ans : - (i) Covalent bond, (ii) Covalent bond.