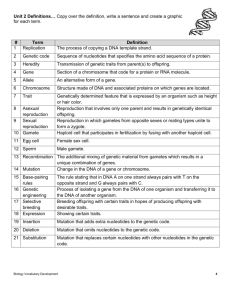
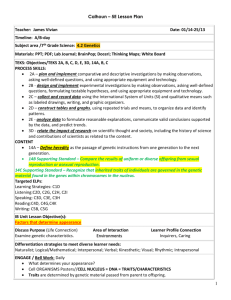
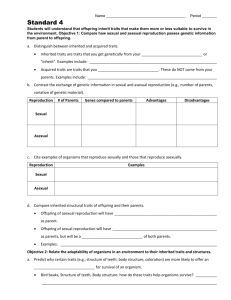
Sexual & Asexual Reproduction, Heredity Study Guide
advertisement
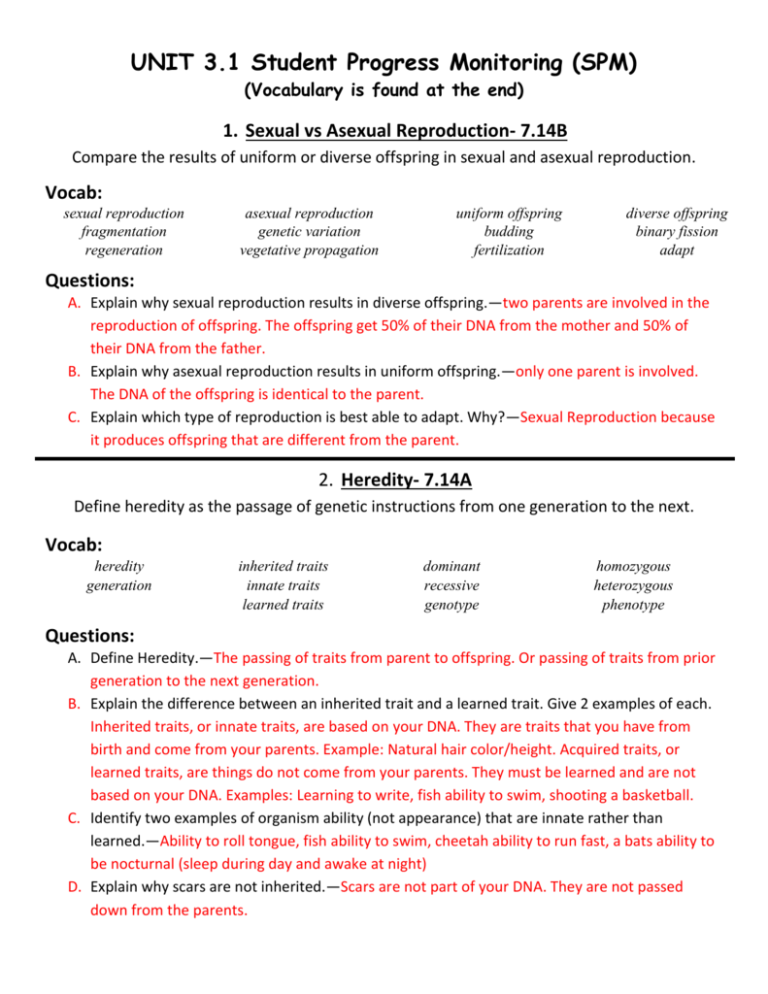
UNIT 3.1 Student Progress Monitoring (SPM) (Vocabulary is found at the end) 1. Sexual vs Asexual Reproduction- 7.14B Compare the results of uniform or diverse offspring in sexual and asexual reproduction. Vocab: sexual reproduction fragmentation regeneration asexual reproduction genetic variation vegetative propagation uniform offspring budding fertilization diverse offspring binary fission adapt Questions: A. Explain why sexual reproduction results in diverse offspring.—two parents are involved in the reproduction of offspring. The offspring get 50% of their DNA from the mother and 50% of their DNA from the father. B. Explain why asexual reproduction results in uniform offspring.—only one parent is involved. The DNA of the offspring is identical to the parent. C. Explain which type of reproduction is best able to adapt. Why?—Sexual Reproduction because it produces offspring that are different from the parent. 2. Heredity- 7.14A Define heredity as the passage of genetic instructions from one generation to the next. Vocab: heredity generation inherited traits innate traits learned traits dominant recessive genotype homozygous heterozygous phenotype Questions: A. Define Heredity.—The passing of traits from parent to offspring. Or passing of traits from prior generation to the next generation. B. Explain the difference between an inherited trait and a learned trait. Give 2 examples of each. Inherited traits, or innate traits, are based on your DNA. They are traits that you have from birth and come from your parents. Example: Natural hair color/height. Acquired traits, or learned traits, are things do not come from your parents. They must be learned and are not based on your DNA. Examples: Learning to write, fish ability to swim, shooting a basketball. C. Identify two examples of organism ability (not appearance) that are innate rather than learned.—Ability to roll tongue, fish ability to swim, cheetah ability to run fast, a bats ability to be nocturnal (sleep during day and awake at night) D. Explain why scars are not inherited.—Scars are not part of your DNA. They are not passed down from the parents. 3. Location of Genetic Material- 7.14C Recognize that inherited traits of individuals are governed in the genetic material found in genes within chromosomes in the nucleus Vocab: genetic material DNA genes chromosomes nucleus cell Questions: A. Identity the levels of organization for the location of the genetic material starting with DNA and ending with a cell.—The order from smallest to largest of genetic material is… DNA—genes—chromosomes—nucleus--cell B. What material in a cell controls genetic traits?—genes are sections of DNA that give instructions for your traits C. In what organelle is genetic material found?—Nucleus holds the genetic material found inside of the cell. Vocabulary Terms Section 1 Sexual Reproduction—2 parents required, creates a unique offspring Asexual Reproduction- 1 parent required, creates a uniform offspring (identical, clone, copy) Uniform Offspring—happens from asexual reproduction Diverse Offspring—happens from sexual reproduction, these offspring have a greater chance of survival compared to offspring produced by asexual reproduction. Fragmentation—a type of asexual reproduction. The parent organism splits into 2 and both halves grow into their own identical organisms Genetic Variation—results from sexual reproduction. The offspring have traits that are similar to the parents, but are different. Budding—a type of asexual reproduction. The offspring grows on the side of the parent organism and splits off when it has become big enough. Binary Fission—a type of asexual reproduction. Cell division where one cell copies its DNA and splits into 2 cells. Regeneration—a type of asexual reproduction. Organism has ability to reproduce a damaged organ or limb. Example starfish, or lizard losing its tail. Fertilization—when the egg and sperm meet to form the zygote during sexual reproduction. Adapt—organisms that reproduce sexually have a better ability to survive due to genetic variations from parent of offspring. Section 2 Heredity—the passing on of traits from parents (prior generation) to offspring (next generation) Inherited traits—traits that come from the parents. These traits are decided by an organisms DNA. Example: Fishes ability to swim, Cheetah’s ability to run fast. Dominant—the trait that “wins out” and most likely shows up. Homozygous—Two of the same alleles. Two dominant or two recessive. Example-RR or rr Generation—parents are the prior generation, offspring is the next generation Innate traits—same as Inherited traits. Recessive—usually “loses out”, masked by the dominant trait Heterozygous—two different alleles. One dominant and one recessive. Example Rr or Bb Learned traits—same as Acquired traits. Genotype—The genetic code Example: Bb or RR Phenotype—The trait that is physically shown Example: Brown Hair or Blue Eyes. Section 3 Genetic material—DNA, genes, chromosome, nucleus, and cell; They hold the instructions for how organisms look and function. DNA-Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid, one step of the double helix ladder, These are the instructions for how you will function and looks. Genes-A section of DNA, these are the traits for the organism. Found on the chromosome. Chromosomes-a group of genes, these are found inside the nucleus of a cell. Nucleus-control center of the cell. Holds the chromosomes and other genetic material. Cell-basic unit of life. Holds all genetic material.